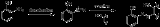
2-Aminophenol
Encyclopedia
2-Aminophenol is an organic compound
with the formula C6H4(OH)NH2. Along with its isomer
4-aminophenol, it is an amphoteric molecule and a reducing agent
. It is a useful reagent for the synthesis of dye
s and heterocyclic compound
s. Reflecting its slight hydrophilic character, white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallised
from hot water.
.
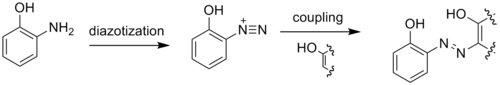

Due to the adjacency of the amino and hydroxyl groups, 2-aminophenol readily forms heterocycles. These heterocycles, such as benzoxazoles, can be biologically active and useful in the pharmaceutical industry:
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the formula C6H4(OH)NH2. Along with its isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
4-aminophenol, it is an amphoteric molecule and a reducing agent
Reducing agent
A reducing agent is the element or compound in a reduction-oxidation reaction that donates an electron to another species; however, since the reducer loses an electron we say it is "oxidized"...
. It is a useful reagent for the synthesis of dye
Dye
A dye is a colored substance that has an affinity to the substrate to which it is being applied. The dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution, and requires a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber....
s and heterocyclic compound
Heterocyclic compound
A heterocyclic compound is a cyclic compound which has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring. The counterparts of heterocyclic compounds are homocyclic compounds, the rings of which are made of a single element....
s. Reflecting its slight hydrophilic character, white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallised
Recrystallization (chemistry)
-Chemistry:In chemistry, recrystallization is a procedure for purifying compounds. The most typical situation is that a desired "compound A" is contaminated by a small amount of "impurity B". There are various methods of purification that may be attempted , which includes recrystallization...
from hot water.
Synthesis
2-Aminophenol (and its isomer, 4-aminophenol) is industrially synthesized by reducing the corresponding nitrophenol by hydrogen in the presence of various catalysts. The nitrophenols can also be reduced with ironIron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
.
Structure
The compound contains an internal hydrogen bond between the neighbouring amine and hydroxyl groups that partly co-ordinates with the same groups on a neighbouring molecule as well. As a result, 2-aminophenol has a rather high melting point compared to other molecules with a similar molecular mass such as methylphenol.Applications
2-Aminophenol has a variety of uses. As a reducing agent, it is marketed under the names of Atomal and Ortol to develop black and white photographs. 2-Aminophenol is an intermediate in the synthesis of dyes. It is particularly useful in yielding tridentate ligands for metal-complex dyes when diazotized and coupled to a phenol, naphthol, or other aromatic or resonant dye species. Metal complex dyes using copper or chromium are commonly used for producing dull colors. Tridentate ligand dyes are particularly useful, since they are more stable than their bi- or mono-dentate counterparts.

Due to the adjacency of the amino and hydroxyl groups, 2-aminophenol readily forms heterocycles. These heterocycles, such as benzoxazoles, can be biologically active and useful in the pharmaceutical industry:


