
Atomic percent
Encyclopedia
The atomic ratio is a measure of the ratio
of atoms of one kind (i) to another kind (j). A closely related concept is the atomic percent (or at.%), which gives the percentage of one kind of atom relative to the total number of atoms. The molecular
equivalents of these concepts are the molar fraction, or molar percent.

where Ni are the number of atoms of interest and Ntot are the total number of atoms, while the atomic ratio is
For example, the atomic percent of hydrogen
in water
(H2O) is , while the atomic ratio of hydrogen
to oxygen is .
, where this may refer to isotopic ratios or isotopic abundances. Mathematically, the atomic percent is (see comment above)
where Ni are the number of atoms of the isotope of interest and Ntot is the total number of atoms, while the atomic ratio is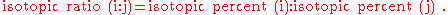
For example, the isotopic ratio of deuterium
(D) to hydrogen
in Heavy water
is roughly (corresponding to an isotopic abundance of 0.00014%).
however, the atomic ratio may refer to the doping ratio or the doping fraction.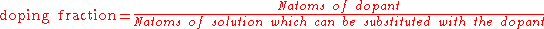
For example, a 100% doped Yb:Y3Al5O12 is pure Yb3Al5O12. The ambiguity of this term can lead to confusion.
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
of atoms of one kind (i) to another kind (j). A closely related concept is the atomic percent (or at.%), which gives the percentage of one kind of atom relative to the total number of atoms. The molecular
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
equivalents of these concepts are the molar fraction, or molar percent.
Atoms
Mathematically, the atomic percent is (There is a problem here - there is no 100, therefore this is a fraction and not a percent. TT)
where Ni are the number of atoms of interest and Ntot are the total number of atoms, while the atomic ratio is

For example, the atomic percent of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
in water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
(H2O) is , while the atomic ratio of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
to oxygen is .
Isotopes
Another application is in radiochemistryRadiochemistry
Radiochemistry is the chemistry of radioactive materials, where radioactive isotopes of elements are used to study the properties and chemical reactions of non-radioactive isotopes...
, where this may refer to isotopic ratios or isotopic abundances. Mathematically, the atomic percent is (see comment above)

where Ni are the number of atoms of the isotope of interest and Ntot is the total number of atoms, while the atomic ratio is
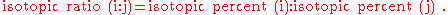
For example, the isotopic ratio of deuterium
Deuterium
Deuterium, also called heavy hydrogen, is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. It has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in of hydrogen . Deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% of all naturally occurring hydrogen in Earth's oceans, while the most common isotope ...
(D) to hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
in Heavy water
Heavy water
Heavy water is water highly enriched in the hydrogen isotope deuterium; e.g., heavy water used in CANDU reactors is 99.75% enriched by hydrogen atom-fraction...
is roughly (corresponding to an isotopic abundance of 0.00014%).
Doping in laser physics
In laser physicsLaser Physics
Laser Physics is an international scientific journal published by Nauka/Interperiodica. It is distributed through the Springer.-Topics covered:The journal specializes in laser physics, but also publishes papers about:...
however, the atomic ratio may refer to the doping ratio or the doping fraction.
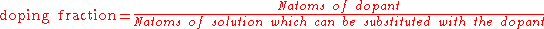
For example, a 100% doped Yb:Y3Al5O12 is pure Yb3Al5O12. The ambiguity of this term can lead to confusion.
See also
- Table of concentration measures

