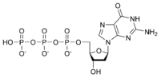
Deoxyguanosine triphosphate
Encyclopedia
Deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP) is a nucleoside triphosphate
, and a nucleotide
precursor used in cells for DNA synthesis
. The substance is used in the polymerase chain reaction
technique, in sequencing
, and in cloning
. It is also the competitor of inhibition onset by acyclovir in the treatment of HSV
virus
.
Nucleoside triphosphate
Nucleoside triphosphate is a nucleoside with three phosphates. Natural nucleoside triphosphates include adenosine triphosphate , guanosine triphosphate , cytidine triphosphate , 5-methyluridine triphosphate , and uridine triphosphate . These terms refer to those nucleoside triphosphates that...
, and a nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
precursor used in cells for DNA synthesis
DNA replication
DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. The process starts with one double-stranded DNA molecule and produces two identical copies of the molecule...
. The substance is used in the polymerase chain reaction
Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction is a scientific technique in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence....
technique, in sequencing
Sequencing
In genetics and biochemistry, sequencing means to determine the primary structure of an unbranched biopolymer...
, and in cloning
Cloning
Cloning in biology is the process of producing similar populations of genetically identical individuals that occurs in nature when organisms such as bacteria, insects or plants reproduce asexually. Cloning in biotechnology refers to processes used to create copies of DNA fragments , cells , or...
. It is also the competitor of inhibition onset by acyclovir in the treatment of HSV
Herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 , also known as Human herpes virus 1 and 2 , are two members of the herpes virus family, Herpesviridae, that infect humans. Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 are ubiquitous and contagious...
virus
Virus
A virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea...
.

