
Economy of Alaska
Encyclopedia
The 2007 gross state product
was $44.9 billion, 45th in the nation. Its per capita personal income for 2007 was $40,042, ranking 15th in the nation. The oil and gas industry dominates the Alaskan economy, with more than 80% of the state's revenues derived from petroleum extraction. Alaska's main export product (excluding oil and natural gas) is seafood, primarily salmon, cod, Pollock and crab.
Agriculture represents only a fraction of the Alaskan economy. Agricultural production is primarily for consumption within the state and includes nursery stock, dairy products, vegetables, and livestock. Manufacturing is limited, with most foodstuffs and general goods imported from elsewhere.
Employment is primarily in government and industries such as natural resource extraction, shipping, and transportation. Military bases are a significant component of the economy in both Fairbanks and Anchorage. Federal subsidies are also an important part of the economy, allowing the state to keep taxes low. Its industrial outputs are crude petroleum, natural gas, coal, gold, precious metals, zinc and other mining, seafood processing, timber and wood products. There is also a growing service and tourism sector. Tourists have contributed to the economy by supporting local lodging.
employers in 2010:
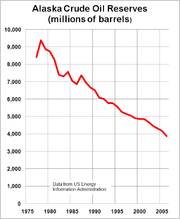 Alaska has vast energy resources. Major oil and gas reserves are found in the Alaska North Slope (ANS) and Cook Inlet basins. According to the Energy Information Administration
Alaska has vast energy resources. Major oil and gas reserves are found in the Alaska North Slope (ANS) and Cook Inlet basins. According to the Energy Information Administration
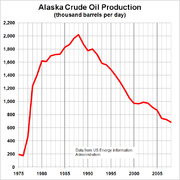
, Alaska ranks second in the nation in crude oil production. Prudhoe Bay on Alaska's North Slope is the highest yielding oil field in the United States and on North America, typically producing about 400000 oilbbl/d.
The Trans-Alaska Pipeline can pump up to 2.1 Moilbbl of crude oil per day, more than any other crude oil pipeline in the United States. Additionally, substantial coal deposits are found in Alaska's bituminous, sub-bituminous, and lignite coal basins. The United States Geological Survey estimates that there are 85.4 Tcuft of undiscovered, technically recoverable gas from natural gas hydrates on the Alaskan North Slope. Alaska also offers some of the highest hydroelectric power potential in the country from its numerous rivers. Large swaths of the Alaskan coastline offer wind and geothermal energy potential as well.
 Alaska's economy depends heavily on increasingly expensive diesel fuel for heating, transportation, electric power and light. Though wind and hydroelectric power are abundant and underdeveloped, proposals for state-wide energy systems (e.g. with special low-cost electric interties) were judged uneconomical (at the time of the report, 2001) due to low (<$0.50/Gal) fuel prices, long distances and low population. The cost of a US gallon of gas in urban Alaska today is usually $0.30–$0.60 higher than the national average; prices in rural areas are generally significantly higher but vary widely depending on transportation costs, seasonal usage peaks, nearby petroleum development infrastructure and many other factors.
Alaska's economy depends heavily on increasingly expensive diesel fuel for heating, transportation, electric power and light. Though wind and hydroelectric power are abundant and underdeveloped, proposals for state-wide energy systems (e.g. with special low-cost electric interties) were judged uneconomical (at the time of the report, 2001) due to low (<$0.50/Gal) fuel prices, long distances and low population. The cost of a US gallon of gas in urban Alaska today is usually $0.30–$0.60 higher than the national average; prices in rural areas are generally significantly higher but vary widely depending on transportation costs, seasonal usage peaks, nearby petroleum development infrastructure and many other factors.
Alaska accounts for one-fifth (20 percent) of domestically produced United States oil production. Prudhoe Bay (North America's largest oil field) alone accounts for 8% of the U.S. domestic oil production.
is a legislatively controlled appropriation established in 1976 to manage a surplus in state petroleum revenues from the recently constructed Trans-Alaska Pipeline System
. From its initial principal of $734,000, the fund has grown to $40 billion as a result of oil royalties and capital investment programs.
Starting in 1982, dividends from the fund's annual growth have been paid out each year to eligible Alaskans, ranging from $331.29 in 1984 to $3,269.00 in 2008 (which included a one-time $1200 "Resource Rebate"). Every year, the state legislature takes out 8 percent from the earnings, puts 3 percent back into the principal for inflation proofing, and the remaining 5 percent is distributed to all qualifying Alaskans. To qualify for the Alaska State Permanent Fund one must have lived in the state for a minimum of 12 months, and maintain constant residency.
(USPS) workers and active-duty military members, receive a Cost of Living Allowance usually set at 25% of base pay because, while the cost of living has gone down, it is still one of the highest in the country.
The introduction of big-box store
s in Anchorage, Fairbanks (Wal-Mart in March 2004), and Juneau also did much to lower prices. However, rural Alaska suffers from extremely high prices for food and consumer goods, compared to the rest of the country due to the relatively limited transportation infrastructure. Many rural residents come into these cities and purchase food and goods in bulk from warehouse clubs like Costco
and Sam's Club
. Some have embraced the free shipping offers of some online retailers to purchase items much more cheaply than they could in their own communities, if they are available at all.
, about 60 miles (96.6 km) southwest of Anchorage. The short 100-day growing season limits the crops that can be grown, but the long sunny summer days make for productive growing seasons. The primary crops are potatoes, carrots, lettuce, and cabbage. Farmers exhibit produce at the Alaska State Fair. "Alaska Grown" is used as an agricultural slogan.
Alaska has an abundance of seafood, with the primary fisheries in the Bering Sea and the North Pacific, and seafood is one of the few food items that is often cheaper within the state than outside it. Many Alaskans fish the rivers during salmon season to gather significant quantities of their household diet while fishing for subsistence, sport, or both.
Hunting for subsistence, primarily caribou, moose
, and Dall sheep
is still common in the state, particularly in remote Bush
communities. An example of a traditional native food is Akutaq
, the Eskimo ice cream, which can consist of reindeer fat, seal oil, dried fish meat and local berries.
Alaska's reindeer herding is concentrated on the Seward Peninsula
where wild caribou can be prevented from mingling and migrating with the domesticated reindeer.
Most food in Alaska is transported into the state from "Outside", and shipping costs make food in the cities relatively expensive. In rural areas, subsistence hunting and gathering is an essential activity because imported food is prohibitively expensive. The cost of importing food to villages begins at 7¢ per pound (15¢/kg) and rises rapidly to 50¢ per pound ($1.10/kg) or more. The cost of delivering a 1 gallons (3.8 l) of milk is about $3.50 in many villages where per capita income can be $20,000 or less. Fuel cost can exceed $8.00 per gallon.
Gross state product
Gross state product is a measurement of the economic output of a state or province...
was $44.9 billion, 45th in the nation. Its per capita personal income for 2007 was $40,042, ranking 15th in the nation. The oil and gas industry dominates the Alaskan economy, with more than 80% of the state's revenues derived from petroleum extraction. Alaska's main export product (excluding oil and natural gas) is seafood, primarily salmon, cod, Pollock and crab.
Agriculture represents only a fraction of the Alaskan economy. Agricultural production is primarily for consumption within the state and includes nursery stock, dairy products, vegetables, and livestock. Manufacturing is limited, with most foodstuffs and general goods imported from elsewhere.
Employment is primarily in government and industries such as natural resource extraction, shipping, and transportation. Military bases are a significant component of the economy in both Fairbanks and Anchorage. Federal subsidies are also an important part of the economy, allowing the state to keep taxes low. Its industrial outputs are crude petroleum, natural gas, coal, gold, precious metals, zinc and other mining, seafood processing, timber and wood products. There is also a growing service and tourism sector. Tourists have contributed to the economy by supporting local lodging.
Largest employers
According to the Alaska Department of Labor and Workforce Development, the following were the state's largest private sectorPrivate sector
In economics, the private sector is that part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is run by private individuals or groups, usually as a means of enterprise for profit, and is not controlled by the state...
employers in 2010:
| Rank | Name | Average Monthly Employment in 2010 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Providence Health & Services | 4,000+ |
| 2 | Walmart/Sam's Club Sam's Club Sam's Club is a chain of membership-only retail warehouse clubs owned and operated by Wal-Mart Stores, Inc., founded in 1983 and named after Wal-Mart founder Sam Walton. , the Sam's Club chain serves more than 47 million U.S. members... |
3,000-3,249 |
| 3 | Carrs Safeway Alaska Division | 2,750-2,999 |
| 4 | Fred Meyer Fred Meyer Fred Meyer, Inc., is a chain of hypermarkets founded in 1922 in Portland, Oregon, by Fred G. Meyer. The company was one of the pioneers of one-stop shopping, eventually combining a complete grocery supermarket with a drugstore, clothing store, shoe store, fine jewelers, home decor store, home... |
2,500-2,749 |
| 5 | ASRC Energy Services | 2,500-2,749 |
| 6 | Trident Seafoods Trident Seafoods Trident Seafoods is the largest seafood company in the United States. It manages a network of fishing ships, processing plants, and a vertically integrated distributorship of its products. Founded in 1973, and based in Seattle, Washington, the company acquired Tyson Seafoods in 1999. Trident... |
2,250-2,499 |
| 7 | BP Exploration Alaska | 2,000-2,249 |
| 8 | CH2M HILL CH2M Hill CH2M Hill is an American-based global provider of engineering, construction, and operations services for corporations, nonprofits, and federal, state, and local governments. The firm is headquartered in Meridian, an unincorporated area of Douglas County, Colorado in the Denver-Aurora Metropolitan... |
1,750-1,999 |
| 9 | NANA Management Services | 1,750-1,999 |
| 10 | Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium The Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium is a non-profit health organization based in Anchorage, Alaska which provides health services to about 130,000 Alaska Natives and American Indians in Alaska... |
1,500-1,749 |
| 11 | Alaska Airlines Alaska Airlines Alaska Airlines is an airline based in the Seattle suburb of SeaTac, Washington in the United States. The airline originated in 1932 as McGee Airways. After many mergers with and acquisitions of other airlines, including Star Air Service, it became known as Alaska Airlines in 1944... |
1,500-1,749 |
| 12 | GCI Communications | 1,250-1,499 |
| 13 | Banner Health Banner health Banner Health is a non-profit health system in the United States, based in Phoenix, Arizona. It operates 23 hospitals as well as specialized facilities... (including Fairbanks Memorial Hospital) |
1,250-1,499 |
| 14 | Southcentral Foundation Southcentral Foundation Southcentral Foundation is an Alaska Native health care organization established by Cook Inlet Region, Inc. in 1982 to improve the health and social conditions of Alaska Natives, enhance culture, and empower individuals and families to take charge of their lives. Alaska Native people own, manage,... |
1,250-1,499 |
| 15 | Yukon-Kuskokwim Health Corporation Yukon-Kuskokwim Health Corporation The Yukon-Kuskokwim Health Corporation , a fully accredited JCAHO organization, administers a comprehensive health care delivery system for over 50 rural communities in Southwest Alaska.... |
1,000-1,249 |
| 16 | FedEx FedEx FedEx Corporation , originally known as FDX Corporation, is a logistics services company, based in the United States with headquarters in Memphis, Tennessee... |
1,000-1,249 |
| 17 | ConocoPhillips Alaska ConocoPhillips Alaska ConocoPhillips Alaska, Inc. is a subsidiary of ConocoPhillips, with its headquarters in Anchorage, Alaska. The company has major lease holdings on the North Slope and is Alaska's largest producer of oil and gas, employing about 1,000 persons.... |
1,000-1,249 |
| 18 | Alaska USA Federal Credit Union Alaska USA Federal Credit Union Alaska USA Federal Credit Union is a credit union headquartered in Anchorage, Alaska, chartered and regulated under the authority of the National Credit Union Administration... |
1,000-1,249 |
| 19 | United Parcel Service United Parcel Service United Parcel Service, Inc. , typically referred to by the acronym UPS, is a package delivery company. Headquartered in Sandy Springs, Georgia, United States, UPS delivers more than 15 million packages a day to 6.1 million customers in more than 220 countries and territories around the... (UPS) |
1,000-1,249 |
| 20 | McDonald's Restaurants of Alaska McDonald's McDonald's Corporation is the world's largest chain of hamburger fast food restaurants, serving around 64 million customers daily in 119 countries. Headquartered in the United States, the company began in 1940 as a barbecue restaurant operated by the eponymous Richard and Maurice McDonald; in 1948... |
750-999 |
| 21 | Wells Fargo Wells Fargo Wells Fargo & Company is an American multinational diversified financial services company with operations around the world. Wells Fargo is the fourth largest bank in the U.S. by assets and the largest bank by market capitalization. Wells Fargo is the second largest bank in deposits, home... |
750-999 |
| 22 | Doyon Universal Services | 750-999 |
| 23 | Home Depot | 750-999 |
| 24 | Alaska Regional Hospital | 750-999 |
| 25 | The Alaska Club | 750-999 |
| 26 | Icicle Seafoods | 750-999 |
| 27 | Southeast Alaska Regional Health Consortium (SEARHC) | 750-999 |
| 28 | Hope Community Resources | 750-999 |
| 29 | UniSea | 750-999 |
| 30 | Alaska Commercial Company Alaska Commercial Company The Alaska Commercial Company is a company that operated retail stores in Alaska during the early period of Alaska's ownership by the United States. From 1901 to 1992, it was known as the Northern Commercial Company . In 1992, it resumed business as the Alaska Commercial Company under the... |
750-999 |
| 31 | Costco Costco Costco Wholesale Corporation is the largest membership warehouse club chain in the United States. it is the third largest retailer in the United States, where it originated, and the ninth largest in the world... |
750-999 |
| 32 | Spenard Builders Supply | 750-999 |
| 33 | Lowe's Lowe's Lowe's Companies, Inc. is a U.S.-based chain of retail home improvement and appliance stores. Founded in 1946 in North Wilkesboro, North Carolina, the chain now serves more than 14 million customers a week in its 1,710 stores in the United States and 20 in Canada. Expansion into Canada began in... |
750-999 |
| 34 | Alyeska Pipeline Service Company Alyeska Pipeline Service Company The Alyeska consortium refers to the major oil companies that own and operate the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System through the Alyeska Pipeline Service Company.-History:... |
750-999 |
| 35 | Alaska Communication Systems (ACS) | 500-749 |
| 36 | First National Bank Alaska First National Bank Alaska First National Bank Alaska is an American bank founded in 1922 by Winfield Ervin, Sr., as First National Bank of Anchorage. The first branch stood on the corner of Fourth and G in Anchorage, Alaska.-History:... |
500-749 |
| 37 | Central Peninsula Hospital | 500-749 |
| 38 | First Student | 500-749 |
| 39 | Westward Seafood | 500-749 |
| 40 | Mat-Su Regional Medical Center Mat-Su Regional Medical Center Mat-Su Regional Medical Center is a 74-bed general hospital in the U.S. state of Alaska owned by Community Health Systems . Located between Palmer and Wasilla, it is the principal hospital for the Matanuska-Susitna Valley... |
500-749 |
| 41 | Alaska Consumer Direct Personal Care | 500-749 |
| 42 | Tanana Chiefs Conference Tanana Chiefs Conference Tanana Chiefs Conference , the traditional tribal consortium of the 42 villages of Interior Alaska, is based on a belief in tribal self-determination and the need for regional Native unity... |
500-749 |
| 43 | PeterPan Seafoods | 500-749 |
| 44 | Udelhoven Oilfield System Services | 500-749 |
| 45 | Job Ready (ReadyCare) | 500-749 |
| 46 | Schlumberger Technologies | 500-749 |
| 47 | Maniilaq Association | 500-749 |
| 48 | Alaska Hotel Properties (Princess Hotels) | 500-749 |
| 49 | Alyeska Resort Alyeska Resort Alyeska Resort is a ski resort that is located in Girdwood, Alaska, approximately 27 miles from the city of Anchorage. Mount Alyeska is part of the Chugach mountain range... (includes O'Malley's on the Green) |
500-749 |
| 50 | Ocean Beauty Seafoods | 250-499 |
Energy

Energy Information Administration
The U.S. Energy Information Administration is the statistical and analytical agency within the U.S. Department of Energy. EIA collects, analyzes, and disseminates independent and impartial energy information to promote sound policymaking, efficient markets, and public understanding of energy and...
, Alaska ranks second in the nation in crude oil production. Prudhoe Bay on Alaska's North Slope is the highest yielding oil field in the United States and on North America, typically producing about 400000 oilbbl/d.
The Trans-Alaska Pipeline can pump up to 2.1 Moilbbl of crude oil per day, more than any other crude oil pipeline in the United States. Additionally, substantial coal deposits are found in Alaska's bituminous, sub-bituminous, and lignite coal basins. The United States Geological Survey estimates that there are 85.4 Tcuft of undiscovered, technically recoverable gas from natural gas hydrates on the Alaskan North Slope. Alaska also offers some of the highest hydroelectric power potential in the country from its numerous rivers. Large swaths of the Alaskan coastline offer wind and geothermal energy potential as well.

Alaska accounts for one-fifth (20 percent) of domestically produced United States oil production. Prudhoe Bay (North America's largest oil field) alone accounts for 8% of the U.S. domestic oil production.
Permanent Fund
The Alaska Permanent FundAlaska Permanent Fund
The Alaska Permanent Fund is a constitutionally established permanent fund, managed by a semi-independent corporation, established by Alaska in 1976, primarily by the efforts of then Governor Jay Hammond...
is a legislatively controlled appropriation established in 1976 to manage a surplus in state petroleum revenues from the recently constructed Trans-Alaska Pipeline System
Trans-Alaska Pipeline System
The Trans Alaska Pipeline System , includes the Trans Alaska Pipeline, 11 pump stations, several hundred miles of feeder pipelines, and the Valdez Marine Terminal. TAPS is one of the world's largest pipeline systems...
. From its initial principal of $734,000, the fund has grown to $40 billion as a result of oil royalties and capital investment programs.
Starting in 1982, dividends from the fund's annual growth have been paid out each year to eligible Alaskans, ranging from $331.29 in 1984 to $3,269.00 in 2008 (which included a one-time $1200 "Resource Rebate"). Every year, the state legislature takes out 8 percent from the earnings, puts 3 percent back into the principal for inflation proofing, and the remaining 5 percent is distributed to all qualifying Alaskans. To qualify for the Alaska State Permanent Fund one must have lived in the state for a minimum of 12 months, and maintain constant residency.
Cost of living
The cost of goods in Alaska has long been higher than in the contiguous 48 states. This has changed for the most part in Anchorage and to a lesser extent in Fairbanks, where the cost of living has dropped somewhat in the past five years. Federal government employees, particularly United States Postal ServiceUnited States Postal Service
The United States Postal Service is an independent agency of the United States government responsible for providing postal service in the United States...
(USPS) workers and active-duty military members, receive a Cost of Living Allowance usually set at 25% of base pay because, while the cost of living has gone down, it is still one of the highest in the country.
The introduction of big-box store
Big-box store
A big-box store is a physically large retail establishment, usually part of a chain. The term sometimes also refers, by extension, to the company that operates the store...
s in Anchorage, Fairbanks (Wal-Mart in March 2004), and Juneau also did much to lower prices. However, rural Alaska suffers from extremely high prices for food and consumer goods, compared to the rest of the country due to the relatively limited transportation infrastructure. Many rural residents come into these cities and purchase food and goods in bulk from warehouse clubs like Costco
Costco
Costco Wholesale Corporation is the largest membership warehouse club chain in the United States. it is the third largest retailer in the United States, where it originated, and the ninth largest in the world...
and Sam's Club
Sam's Club
Sam's Club is a chain of membership-only retail warehouse clubs owned and operated by Wal-Mart Stores, Inc., founded in 1983 and named after Wal-Mart founder Sam Walton. , the Sam's Club chain serves more than 47 million U.S. members...
. Some have embraced the free shipping offers of some online retailers to purchase items much more cheaply than they could in their own communities, if they are available at all.
Agriculture
Due to the northern climate and steep terrain, relatively little farming occurs in Alaska. Most farms are in either the Matanuska Valley, about 40 miles (64.4 km) northeast of Anchorage, or on the Kenai PeninsulaKenai Peninsula
The Kenai Peninsula is a large peninsula jutting from the southern coast of Alaska in the United States. The name Kenai is probably derived from Kenayskaya, the Russian name for Cook Inlet, which borders the peninsula to the west.-Geography:...
, about 60 miles (96.6 km) southwest of Anchorage. The short 100-day growing season limits the crops that can be grown, but the long sunny summer days make for productive growing seasons. The primary crops are potatoes, carrots, lettuce, and cabbage. Farmers exhibit produce at the Alaska State Fair. "Alaska Grown" is used as an agricultural slogan.
Alaska has an abundance of seafood, with the primary fisheries in the Bering Sea and the North Pacific, and seafood is one of the few food items that is often cheaper within the state than outside it. Many Alaskans fish the rivers during salmon season to gather significant quantities of their household diet while fishing for subsistence, sport, or both.
Hunting for subsistence, primarily caribou, moose
Moose
The moose or Eurasian elk is the largest extant species in the deer family. Moose are distinguished by the palmate antlers of the males; other members of the family have antlers with a dendritic configuration...
, and Dall sheep
Dall Sheep
The Dall sheep , Ovis dalli, is a species of sheep native to northwestern North America, ranging from white to slate brown in color and having curved yellowish brown horns...
is still common in the state, particularly in remote Bush
Bush Alaska
The Bush is a term Alaskans use to describe portions of their state that are not connected to the North America road network. A majority of Alaska's native populations live in the Bush, where they make their living in similar fashion to their ancestors....
communities. An example of a traditional native food is Akutaq
Akutaq
Akutaq or agutak , also known as Eskimo ice cream, is a common food in western Alaska, consisting of whipped fat mixed with berries, with optional additions such as fish and sugar...
, the Eskimo ice cream, which can consist of reindeer fat, seal oil, dried fish meat and local berries.
Alaska's reindeer herding is concentrated on the Seward Peninsula
Seward Peninsula
The Seward Peninsula is a large peninsula on the western coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It projects about into the Bering Sea between Norton Sound, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi Sea, and Kotzebue Sound, just below the Arctic Circle...
where wild caribou can be prevented from mingling and migrating with the domesticated reindeer.
Most food in Alaska is transported into the state from "Outside", and shipping costs make food in the cities relatively expensive. In rural areas, subsistence hunting and gathering is an essential activity because imported food is prohibitively expensive. The cost of importing food to villages begins at 7¢ per pound (15¢/kg) and rises rapidly to 50¢ per pound ($1.10/kg) or more. The cost of delivering a 1 gallons (3.8 l) of milk is about $3.50 in many villages where per capita income can be $20,000 or less. Fuel cost can exceed $8.00 per gallon.

