
Equilibrium moisture content
Encyclopedia
The moisture
content of wood below the fibre saturation point
is a function of both relative humidity
and temperature
of surrounding air. The equilibrium moisture content (EMC) is the moisture content at which the wood is neither gaining or losing moisture; this however, is a dynamic equilibrium and changes with relative humidity and temperature.
The moisture content (M) of wood is defined as:
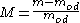
where m is the mass of the wood (with moisture) and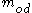 is the oven-dry mass of wood (i.e. no moisture). If the wood is placed in an environment at a particular temperature and relative humidity, its moisture content will generally begin to change in time, until it is finally in equilibrium with its surroundings, and the moisture content no longer changes in time. This moisture content is the EMC of the wood for that temperature and relative humidity.
is the oven-dry mass of wood (i.e. no moisture). If the wood is placed in an environment at a particular temperature and relative humidity, its moisture content will generally begin to change in time, until it is finally in equilibrium with its surroundings, and the moisture content no longer changes in time. This moisture content is the EMC of the wood for that temperature and relative humidity.
The Hailwood-Horrobin equation for two hydrates is often used to approximate the relationship between EMC, temperature (T), and relative humidity (h):
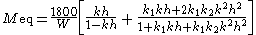
where Meq is the equilibrium moisture content (percent), T is the temperature (degrees Fahrenheit), h is the relative humidity (fractional) and:
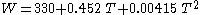
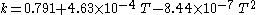
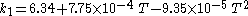
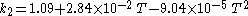
This equation does not account for the slight variations with wood species, state of mechanical stress, and/or hysteresis
. It is an empirical fit to tabulated data provided in the same reference, and closely agrees with the tabulated data. For example, at T=140 deg F, h=0.55, EMC=8.4% from the above equation, while EMC=8.0% from the tabulated data.
Moisture
Humidity is the amount of moisture the air can hold before it rains. Moisture refers to the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts...
content of wood below the fibre saturation point
Fibre saturation point
Fibre saturation point is a term used in wood mechanics and especially wood drying, to denote the point in the drying process at which only water bound in the cell walls remains - all other water, called free water, having been removed from the cell cavities. Further drying of the wood results in...
is a function of both relative humidity
Relative humidity
Relative humidity is a term used to describe the amount of water vapor in a mixture of air and water vapor. It is defined as the partial pressure of water vapor in the air-water mixture, given as a percentage of the saturated vapor pressure under those conditions...
and temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
of surrounding air. The equilibrium moisture content (EMC) is the moisture content at which the wood is neither gaining or losing moisture; this however, is a dynamic equilibrium and changes with relative humidity and temperature.
The moisture content (M) of wood is defined as:
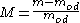
where m is the mass of the wood (with moisture) and
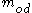 is the oven-dry mass of wood (i.e. no moisture). If the wood is placed in an environment at a particular temperature and relative humidity, its moisture content will generally begin to change in time, until it is finally in equilibrium with its surroundings, and the moisture content no longer changes in time. This moisture content is the EMC of the wood for that temperature and relative humidity.
is the oven-dry mass of wood (i.e. no moisture). If the wood is placed in an environment at a particular temperature and relative humidity, its moisture content will generally begin to change in time, until it is finally in equilibrium with its surroundings, and the moisture content no longer changes in time. This moisture content is the EMC of the wood for that temperature and relative humidity.The Hailwood-Horrobin equation for two hydrates is often used to approximate the relationship between EMC, temperature (T), and relative humidity (h):
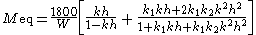
where Meq is the equilibrium moisture content (percent), T is the temperature (degrees Fahrenheit), h is the relative humidity (fractional) and:
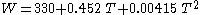
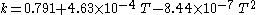
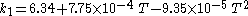
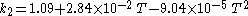
This equation does not account for the slight variations with wood species, state of mechanical stress, and/or hysteresis
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of a system not just on its current environment but also on its past. This dependence arises because the system can be in more than one internal state. To predict its future evolution, either its internal state or its history must be known. If a given input alternately...
. It is an empirical fit to tabulated data provided in the same reference, and closely agrees with the tabulated data. For example, at T=140 deg F, h=0.55, EMC=8.4% from the above equation, while EMC=8.0% from the tabulated data.

