Extraterrestrial atmospheres
Encyclopedia
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
s in the Solar System
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
have atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
s. These include all the gas giants
Gas Giants
Gas Giants were a pop rock band from Tempe, Arizona, formed as a successor project to the Gin Blossoms. The group was known as The Pharaohs when they formed in 1997, but changed their name after their label, A&M Records, merged with Universal Records and the band changed hands, re-signing with...
, as well as Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
and Venus
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
. Several moons
Natural satellite
A natural satellite or moon is a celestial body that orbits a planet or smaller body, which is called its primary. The two terms are used synonymously for non-artificial satellites of planets, of dwarf planets, and of minor planets....
and other bodies (notably Pluto
Pluto
Pluto, formal designation 134340 Pluto, is the second-most-massive known dwarf planet in the Solar System and the tenth-most-massive body observed directly orbiting the Sun...
) also have atmospheres, as do comet
Comet
A comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet...
s and the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. In addition, there is evidence that extrasolar planet
Extrasolar planet
An extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars...
s have atmospheres. Comparisons of these atmospheres to one another and to Earth's atmosphere broaden our basic understanding of atmospheric processes such as the greenhouse effect
Greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is re-radiated in all directions. Since part of this re-radiation is back towards the surface, energy is transferred to the surface and the lower atmosphere...
, aerosol
Aerosol
Technically, an aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in a gas. Examples are clouds, and air pollution such as smog and smoke. In general conversation, aerosol usually refers to an aerosol spray can or the output of such a can...
and cloud physics, and atmospheric chemistry
Atmospheric chemistry
Atmospheric chemistry is a branch of atmospheric science in which the chemistry of the Earth's atmosphere and that of other planets is studied. It is a multidisciplinary field of research and draws on environmental chemistry, physics, meteorology, computer modeling, oceanography, geology and...
and dynamics.
Mercury
Due to its small size (and thus its small gravity), MercuryMercury (planet)
Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in the Solar System, orbiting the Sun once every 87.969 Earth days. The orbit of Mercury has the highest eccentricity of all the Solar System planets, and it has the smallest axial tilt. It completes three rotations about its axis for every two orbits...
has no substantial atmosphere. Its extremely thin atmosphere mostly consists of a small amount of helium and traces of sodium, potassium, and oxygen. These gases derive from the solar wind
Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the Sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons with energies usually between 1.5 and 10 keV. The stream of particles varies in temperature and speed over time...
, radioactive decay, meteor impacts, and breakdown of Mercury's crust. Mercury's atmosphere is not stable and is constantly being refreshed because of its atoms escaping into space
Space
Space is the boundless, three-dimensional extent in which objects and events occur and have relative position and direction. Physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum...
as a result of the planet's heat.
Venus

Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
. It contains minor amounts of nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
and other trace elements, including compounds based on hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
, nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
, carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
, and oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
. The atmosphere of Venus is much hotter, denser, and deeper than that of Earth.
The troposphere
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere. It contains approximately 80% of the atmosphere's mass and 99% of its water vapor and aerosols....
begins at the surface and extends up to an altitude of 65 kilometres (an altitude at which the mesosphere
Mesosphere
The mesosphere is the layer of the Earth's atmosphere that is directly above the stratosphere and directly below the thermosphere. In the mesosphere temperature decreases with increasing height. The upper boundary of the mesosphere is the mesopause, which can be the coldest naturally occurring...
has already been reached on Earth). At the top of the troposphere, temperature and pressure reach Earth-like levels. Winds at the surface are a few metres per second, reaching 70 m/s or more in the upper troposphere. The stratosphere
Stratosphere
The stratosphere is the second major layer of Earth's atmosphere, just above the troposphere, and below the mesosphere. It is stratified in temperature, with warmer layers higher up and cooler layers farther down. This is in contrast to the troposphere near the Earth's surface, which is cooler...
and mesosphere extend from 65 km to 95 km in height. The thermosphere and exosphere begin at around 95 kilometres, eventually reaching the limit of the atmosphere at about 220 to 250 km.
The air pressure at Venus' surface is about 92 times that of the Earth. The enormous amount of CO2 in the atmosphere creates a strong greenhouse effect
Greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is re-radiated in all directions. Since part of this re-radiation is back towards the surface, energy is transferred to the surface and the lower atmosphere...
, raising the surface temperature to around 470 °C, hotter than that of any other planet in the solar system.
Mars
The Martian atmosphere is very thin and composed mainly of carbon dioxideCarbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, with some nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
and argon
Argon
Argon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide...
. The average surface pressure
Surface pressure
Surface pressure is the atmospheric pressure at a location on Earth's surface. It is directly proportional to the mass of air over that location....
on Mars is 0.6-0.9 kPa
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
, compared to about 101 kPa for Earth. This results in a much lower atmospheric thermal inertia
Volumetric heat capacity
Volumetric heat capacity , also termed volume-specific heat capacity, describes the ability of a given volume of a substance to store internal energy while undergoing a given temperature change, but without undergoing a phase change...
, and as a consequence Mars is subject to strong thermal tides
Atmospheric tide
Atmospheric tides are global-scale periodic oscillations of the atmosphere. In many ways they are analogous to ocean tides. Atmospheric tides can be excited by:*The regular day/night cycle in the insolation of the atmosphere...
that can change total atmospheric pressure by up to 10%. The thin atmosphere also increases the variability of the planet's temperature. Martian surface temperatures vary from lows of approximately −140 °C (−220 °F) during the polar winters to highs of up to 20 °C (70 °F) in summers.
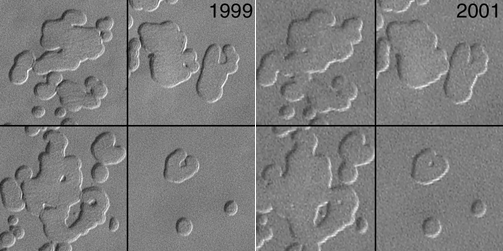
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
warmed by about 0.65 °C (1.2 °F) due to dust storms that made its surface darker so that it absorbed more sunlight. Changes in pits
Swiss cheese features
Swiss cheese features are curious pits in the south polar ice cap of Mars named from their similarity to the holes in Swiss cheese. They were first seen in 2000 using Mars Orbiter Camera imagery. They are typically a few hundred meters across and 8 metres deep, with a flat base and steep sides...
in the layer of frozen carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
at the Martian south pole observed between 1999 and 2001 suggest the south polar ice cap
Planum Australe
Planum Australe is the southern polar plain on Mars. It extends southward of roughly 75°S and is centered at . The geology of this region was to be explored by the failed NASA mission Mars Polar Lander, which lost contact on entry into the Martian atmosphere.-Ice cap:Planum Australe is partially...
is shrinking. More recent observations indicate that Mars' south pole is continuing to melt. "It's evaporating right now at a prodigious rate," says Michael Malin
Michael C. Malin
Michael C. Malin is an American astronomer, space-scientist, and CEO of Malin Space Science Systems. His cameras have been important scientific instruments in the Exploration of Mars....
, principal investigator for the Mars Orbiter Camera. The pits in the ice are growing by about 3 meters (9.8 ft) per year. Malin states that conditions on Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
are not currently conductive to the formation of new ice. NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
has suggested that this indicates a "climate change in progress" on Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
. One study suggests this may be a local phenomenon rather than a global one.
Colin Wilson has proposed that the observed variations are caused by irregularities in the orbit of Mars. William Feldman speculates the warming could be because Mars might be coming out of an ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
. Other scientists believe the warming may be a result albedo
Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
changes from dust storms. The study predicts the planet could continue to warm, as a result of positive feedback
Positive feedback
Positive feedback is a process in which the effects of a small disturbance on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A. In contrast, a system that responds to a perturbation in a way that reduces its effect is...
.
Gas giants
The four outer planets of the Solar System are gas giantsGas Giants
Gas Giants were a pop rock band from Tempe, Arizona, formed as a successor project to the Gin Blossoms. The group was known as The Pharaohs when they formed in 1997, but changed their name after their label, A&M Records, merged with Universal Records and the band changed hands, re-signing with...
. They share some atmospheric commonalities. All have atmospheres that are mostly hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
and that blend into the liquid interior at pressures greater than the critical pressure, so that there is no clear boundary between atmosphere and body.
Jupiter

Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
's upper atmosphere is composed of about 75% hydrogen and 24% helium by mass, with the remaining 1% consisting of other elements. The interior contains denser materials such that the distribution is roughly 71% hydrogen, 24% helium and 5% other elements by mass. The atmosphere contains trace amounts of methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
, water vapor
Water vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
, ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
, and silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
-based compounds. There are also traces of carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
, ethane
Ethane
Ethane is a chemical compound with chemical formula C2H6. It is the only two-carbon alkane that is an aliphatic hydrocarbon. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas....
, hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of expired eggs perceptible at concentrations as low as 0.00047 parts per million...
, neon
Neon
Neon is the chemical element that has the symbol Ne and an atomic number of 10. Although a very common element in the universe, it is rare on Earth. A colorless, inert noble gas under standard conditions, neon gives a distinct reddish-orange glow when used in either low-voltage neon glow lamps or...
, oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, phosphine
Phosphine
Phosphine is the compound with the chemical formula PH3. It is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas. Pure phosphine is odourless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like garlic or rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphine...
, and sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
. The outermost layer of the atmosphere contains crystal
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
s of frozen ammonia, possibly underlaid by a thin layer of water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
.
Jupiter is covered with a cloud layer about 50 km deep. The clouds are composed of ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
crystals and possibly ammonium hydrosulfide. The clouds are located in the tropopause
Tropopause
The tropopause is the atmospheric boundary between the troposphere and the stratosphere.-Definition:Going upward from the surface, it is the point where air ceases to cool with height, and becomes almost completely dry...
and are arranged into bands of different latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
s, known as tropical regions. These are sub-divided into lighter-hued zones and darker belts. The interactions of these conflicting circulation
Atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air, and the means by which thermal energy is distributed on the surface of the Earth....
patterns cause storms and turbulence
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
. The best-known feature of the cloud layer is the Great Red Spot, a persistent anticyclonic
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined by the United States' National Weather Service's glossary as "[a] large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere"...
storm
Storm
A storm is any disturbed state of an astronomical body's atmosphere, especially affecting its surface, and strongly implying severe weather...
located 22° south of the equator that is larger than Earth. In 2000, an atmospheric feature formed in the southern hemisphere that is similar in appearance to the Great Red Spot, but smaller in size. The feature was named Oval BA, and has been nicknamed Red Spot Junior.
Observations of the Red Spot Jr. storm suggest Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
could be in a period of global climate change. This is hypothesized to be part of an approximately 70 year global climate cycle, characterized by the relatively rapid forming and subsequent slow erosion and merging of cyclonic and anticyclonic vortices
Vortex
A vortex is a spinning, often turbulent,flow of fluid. Any spiral motion with closed streamlines is vortex flow. The motion of the fluid swirling rapidly around a center is called a vortex...
in Jupiter's atmosphere. These vortices facilitate the heat exchange between poles and equator. If they have sufficiently eroded, heat exchange is strongly reduced and regional temperatures may shift by as much as 10 K, with the poles cooling down and the equator region heating up. The resulting large temperature differential destabilizes the atmosphere and thereby leads to the creation of new vortices.
Saturn
The outer atmosphere of SaturnSaturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest planet in the Solar System, after Jupiter. Saturn is named after the Roman god Saturn, equated to the Greek Cronus , the Babylonian Ninurta and the Hindu Shani. Saturn's astronomical symbol represents the Roman god's sickle.Saturn,...
consists of about 93.2% hydrogen and 6.7% helium. Trace amounts of ammonia, acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
, ethane, phosphine, and methane have also been detected. As with Jupiter, the upper clouds on Saturn are composed of ammonia crystals, while the lower level clouds appear to be composed of either ammonium hydrosulfide (NH4SH) or water.
The Saturnian atmosphere is in several ways similar to that of Jupiter. It exhibits a banded pattern similar to Jupiter's, and occasionally exhibits long-lived ovals caused by storms. A storm formation analogous to Jupiter's Great Red Spot, the Great White Spot, is a short-lived phenomenon that forms with a roughly 30-year periodicity. It was last observed in 1990. However, the storms and the band pattern are less visible and active than those of Jupiter, due to the overlying ammonia hazes in Saturn's troposphere.
Saturn's atmosphere has several unusual features. Its winds are among the Solar System's fastest, with Voyager
Voyager program
The Voyager program is a U.S program that launched two unmanned space missions, scientific probes Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable planetary alignment of the late 1970s...
data indicating peak easterly winds of 500 m/s. It is also the only planet with a warm polar vortex, and is the only planet other than Earth where eyewall clouds have been observed in hurricane-like structures.
Uranus
The atmosphere of UranusUranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus...
is composed primarily of gas and various ices. It is about 83% hydrogen, 15% helium, 2% methane and traces of acetylene. Like Jupiter and Saturn, Uranus has a banded cloud layer, although this is not readily visible without enhancement of visual images of the planet. Unlike the larger gas giants, the low temperatures in the upper Uranian cloud layer, down to 50 K
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
, causes cloud formation from methane rather than ammonia.
Although in general less storm activity has been observed in the Uranian atmosphere than in those of Jupiter or Saturn, due to its overlying methane and acetylene hazes in its atmosphere making the planet look like a bland, baby blue globe. Images taken in 1997 with the Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
showed storm activity in that part of the atmosphere emerging from the 25-year long Uranian winter. The general lack of storm activity may be related to the lack of an internal energy generation mechanism for Uranus, a feature unique among the gas giants.
Neptune

Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Named for the Roman god of the sea, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third largest by mass. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times...
is similar to that of Uranus. It is about 80% hydrogen, 19% helium, and 1.5% methane. However the weather activity on Neptune is much more active, and its atmosphere is much bluer than that of Uranus. The upper levels of the atmosphere reach temperatures of about 55 K
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
, giving rise to methane clouds in its troposphere, which gives the planet its ultramarine color. Temperatures rise steadily deeper inside the atmosphere.
Neptune has extremely dynamic weather systems, including the highest wind speeds in the solar system, thought to be powered by the flow of internal heat. Typical winds in the banded equatorial region can possess speeds of around 350 m/s, while storm systems can have winds reaching up to around 900 m/s, nearly the speed of sound in Neptune's atmosphere. Several large storm systems have been identified, including the Great Dark Spot, a cyclonic storm system the size of Eurasia, the Scooter, a white cloud group further south than the Great Dark Spot, and the Wizard's eye/Dark Spot 2, a southern cyclonic storm.
Neptune
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Named for the Roman god of the sea, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third largest by mass. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times...
, the farthest planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
from Earth, has increased in brightness since 1980. Neptune's brightness is statistically correlated with its stratospheric temperature. Hammel and Lockwood hypothesize that the change in brightness includes a solar variation component as well as a seasonal component, though they did not find a statistically significant correlation with solar variation
Solar variation
Solar variation is the change in the amount of radiation emitted by the Sun and in its spectral distribution over years to millennia. These variations have periodic components, the main one being the approximately 11-year solar cycle . The changes also have aperiodic fluctuations...
. They propose that the resolution of this issue will be clarified by brightness observations in the next few years: forcing by a change in sub-solar latitude should be reflected in a flattening and decline of brightness, while solar forcing should be reflected in a flattening and then resumed rise of brightness.http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/2007/2006GL028764.shtml
Natural satellites
Seven of the many natural satellites in the solar system are known to have atmospheres: EuropaEuropa (moon)
Europa Slightly smaller than Earth's Moon, Europa is primarily made of silicate rock and probably has an iron core. It has a tenuous atmosphere composed primarily of oxygen. Its surface is composed of ice and is one of the smoothest in the Solar System. This surface is striated by cracks and...
, Io
Io (moon)
Io ) is the innermost of the four Galilean moons of the planet Jupiter and, with a diameter of , the fourth-largest moon in the Solar System. It was named after the mythological character of Io, a priestess of Hera who became one of the lovers of Zeus....
, Callisto
Callisto (moon)
Callisto named after the Greek mythological figure of Callisto) is a moon of the planet Jupiter. It was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei. It is the third-largest moon in the Solar System and the second largest in the Jovian system, after Ganymede. Callisto has about 99% the diameter of the...
, Enceladus
Enceladus (moon)
Enceladus is the sixth-largest of the moons of Saturn. It was discovered in 1789 by William Herschel. Until the two Voyager spacecraft passed near it in the early 1980s very little was known about this small moon besides the identification of water ice on its surface...
, Ganymede
Ganymede (moon)
Ganymede is a satellite of Jupiter and the largest moon in the Solar System. It is the seventh moon and third Galilean satellite outward from Jupiter. Completing an orbit in roughly seven days, Ganymede participates in a 1:2:4 orbital resonance with the moons Europa and Io, respectively...
, Titan
Titan (moon)
Titan , or Saturn VI, is the largest moon of Saturn, the only natural satellite known to have a dense atmosphere, and the only object other than Earth for which clear evidence of stable bodies of surface liquid has been found....
, and Triton
Triton (moon)
Triton is the largest moon of the planet Neptune, discovered on October 10, 1846, by English astronomer William Lassell. It is the only large moon in the Solar System with a retrograde orbit, which is an orbit in the opposite direction to its planet's rotation. At 2,700 km in diameter, it is...
. Ganymede and Europa both have very tenuous oxygen atmospheres, thought to be produced by radiation spliting the water ice present on the surface of these moons into hydrogen and oxygen. Io has an extremely thin atmosphere consisting mainly of sulfur dioxide , arising from volcanism and sunlight-driven sublimation of surface sulfur dioxide deposits. The atmosphere of Enceladus is also extremely thin and variable, consisting mainly of water vapor, nitrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide vented from the moon's interior through cryovolcanism. The extremely thin carbon dioxide atmosphere of Callisto is thought to be replenished by sublimation from surface deposits.
Titan

Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's, with a surface pressure of 147 kPa
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
, one and a half times that of the Earth. The atmosphere is 98.4% nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, with the remaining 1.6% composed of methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
and trace amounts of other gases such as hydrocarbons (including ethane
Ethane
Ethane is a chemical compound with chemical formula C2H6. It is the only two-carbon alkane that is an aliphatic hydrocarbon. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas....
, diacetylene
Diacetylene
Diacetylene , with the formula C4H2, is a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains three single bonds and two triple bonds. It is the first in the series of polyynes.-Occurrence:...
, methylacetylene
Methylacetylene
Methylacetylene is an alkyne with the chemical formula H3C≡CH. It is a component of MAPP gas along with its isomer 1,2-propadiene , which is commonly used in gas welding...
, cyanoacetylene
Cyanoacetylene
Cyanoacetylene is an organic compound with formula or H-C≡C-C≡N. It is the simplest cyanopolyyne. Cyanoacetylene has been detected by spectroscopic methods in interstellar clouds, in the coma of comet Hale–Bopp and in the atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan....
, acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
, propane
Propane
Propane is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula , normally a gas, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as a fuel for engines, oxy-gas torches, barbecues, portable stoves, and residential central...
), argon
Argon
Argon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide...
, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
, cyanogen
Cyanogen
Cyanogen is the chemical compound with the formula 2. It is a colorless, toxic gas with a pungent odor.The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules consist of two CN groups — analogous to diatomic halogen molecules, such as Cl2, but far less oxidizing...
, hydrogen cyanide and helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
. The hydrocarbons are thought to form in Titan's upper atmosphere in reactions resulting from the breakup of methane by the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
's ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
light, producing a thick orange smog. Titan has no magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
and sometimes orbits outside Saturn's magnetosphere
Magnetosphere
A magnetosphere is formed when a stream of charged particles, such as the solar wind, interacts with and is deflected by the intrinsic magnetic field of a planet or similar body. Earth is surrounded by a magnetosphere, as are the other planets with intrinsic magnetic fields: Mercury, Jupiter,...
, directly exposing it to the solar wind
Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the Sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons with energies usually between 1.5 and 10 keV. The stream of particles varies in temperature and speed over time...
. This may ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
ize and carry away some molecules from the top of the atmosphere.
Titan's atmosphere supports an opaque cloud layer that obscures Titan's surface features at visible wavelengths. The haze
Haze
Haze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon where dust, smoke and other dry particles obscure the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classification of horizontal obscuration into categories of fog, ice fog, steam fog, mist, haze, smoke, volcanic...
that can be seen in the picture to the right contributes to the moon's Anti-Greenhouse Effect
Anti-Greenhouse Effect
The anti-greenhouse effect is a neologism used to describe two different effects that describe a cooling effect an atmosphere has on the ambient temperature of the planet. Unlike the greenhouse effect, which is common, an anti-greenhouse effect is only known to exist in one situation in our Solar...
and lowers the temperature by reflecting sunlight away from the satellite. The thick atmosphere blocks most visible wavelength light from the Sun and other sources from reaching Titan's surface.
Triton
TritonTriton (moon)
Triton is the largest moon of the planet Neptune, discovered on October 10, 1846, by English astronomer William Lassell. It is the only large moon in the Solar System with a retrograde orbit, which is an orbit in the opposite direction to its planet's rotation. At 2,700 km in diameter, it is...
, Neptune's largest moon, has a tenuous nitrogen atmosphere with small amounts of methane. Tritonian atmospheric pressure is about 1Pa
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
. The surface temperature is at least 35.6 K, with the nitrogen atmosphere in equilibrium with nitrogen ice on Triton's surface.
Triton has increased in absolute temperature by 5% since 1989 to 1998. A similar rise of temperature on Earth would be equal to about 11 °C (20 °F) increase in temperature in nine years. "At least since 1989, Triton has been undergoing a period of global warming. Percentage-wise, it's a very large increase," said James L. Elliot
James L. Elliot
James Ludlow Elliot was an American astronomer and scientist who, as part of a team, discovered the rings around the planet Uranus. Elliot was also part of a team that observed global warming on Triton, the largest moon of Neptune....
, who published the report.
Triton is approaching an unusually warm summer season that only happens once every few hundred years. Elliot and his colleagues believe that Triton's warming trend could be driven by seasonal changes in the absorption of solar energy by its polar ice caps. One suggestion for this warming is that it is a result of frost patterns changing on its surface. Another is that ice albedo has changed, allowing for more heat from the Sun to be absorbed. Bonnie J. Buratti et al. argue the changes in temperature are a result of deposition of dark, red material from geological processes on the moon, such as massive venting. Because Triton's Bond albedo
Bond albedo
The Bond albedo, named after the American astronomer George Phillips Bond , who originally proposed it, is the fraction of power in the total electromagnetic radiation incident on an astronomical body that is scattered back out into space...
is among the highest within the Solar System
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
, it is sensitive to small variations in spectral albedo
Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
.
Pluto

Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
, and carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
, derived from the ices on its surface. The atmosphere is believed to completely freeze and collapse when Pluto moves further from the Sun on its extremely elliptical orbit
Elliptic orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics an elliptic orbit is a Kepler orbit with the eccentricity less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to zero. In a stricter sense, it is a Kepler orbit with the eccentricity greater than 0 and less than 1 . In a...
. Pluto needs 248 years for one complete orbit, and has been observed for less than one third of that time. It has an average distance of 39 AU
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
from the Sun, hence in-depth data from Pluto is sparse and difficult to gather. Temperature is inferred indirectly for Pluto; when it passes in front of a star, observers note how fast the light drops off. From this, they deduce the density of the atmosphere, and that is used as an indicator of temperature.
One such occultation
Occultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden by another object that passes between it and the observer. The word is used in astronomy . It can also refer to any situation wherein an object in the foreground blocks from view an object in the background...
events happened in 1988. Observations of a second occulation on August 20, 2002 suggest that Pluto's atmospheric pressure has tripled, indicating a warming of about 2 °C (3.6 °F). The warming is "likely not connected with that of the Earth," says Jay Pasachoff.
One astronomer has speculated the warming may be a result of eruptive activity, but it is more likely Pluto's temperature is heavily influenced by its elliptical orbit. It was closest to the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
in 1989 (perihelion
Apsis
An apsis , plural apsides , is the point of greatest or least distance of a body from one of the foci of its elliptical orbit. In modern celestial mechanics this focus is also the center of attraction, which is usually the center of mass of the system...
) and has slowly receded since. If it has any thermal inertia, it is expected to warm for a while after it passes perihelion. "This warming trend on Pluto could easily last for another 13 years," says David J. Tholen
David J. Tholen
David James Tholen is an American astronomer at the Institute for Astronomy of the University of Hawaii, who specializes in planetary and solar system astronomy.-Professional life:...
. It has also been suggested that a darkening of surface ice may also be the cause, but additional data and modeling is needed. Frost distribution on the surface of Pluto is significantly affected by the dwarf planet's high obliquity.
In January 2006, NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
launched New Horizons
New Horizons
New Horizons is a NASA robotic spacecraft mission currently en route to the dwarf planet Pluto. It is expected to be the first spacecraft to fly by and study Pluto and its moons, Charon, Nix, Hydra and S/2011 P 1. Its estimated arrival date at the Pluto-Charon system is July 14th, 2015...
, a spacecraft set to study Pluto. It is expected to pass by Pluto in 2015.
Comets

The coma of a comet is a very large but very tenuous atmosphere of dust and gas around the cometary nucleus. The coma can be larger than the sun. The coma is generally made of ice
Ice
Ice is water frozen into the solid state. Usually ice is the phase known as ice Ih, which is the most abundant of the varying solid phases on the Earth's surface. It can appear transparent or opaque bluish-white color, depending on the presence of impurities or air inclusions...
and dust, but the composition varies depending on the composition of the comet.
Extrasolar planets
Two planets outside the solar system have been observed to have atmospheres. The first observed extrasolar planetary atmosphere was made in 2001. Sodium in the atmosphere of the planet HD 209458 bHD 209458 b
HD 209458 b is an extrasolar planet that orbits the Solar analog star HD 209458 in the constellation Pegasus, some 150 light-years from Earth's solar system, with evidence of water vapor....
was detected during a set of four transits of the planet across its star. Later observations with the Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
showed an enormous ellipsoidal envelope of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
, carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
and oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
around the planet. This envelope reaches temperatures of 10,000 K. The planet is estimated to be losing (1-5)×108 kg of hydrogen per second. This type of atmosphere loss may be common to all planets orbiting Sun-like stars closer than around 0.1 AU.
In addition to hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen, HD 209458 b is thought to have water vapor
Water vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
in its atmosphere. Water vapour has also been observed in the atmosphere of HD 189733 b
HD 189733 b
HD 189733 b is an extrasolar planet approximately 63 light-years away in the constellation of Vulpecula . The planet was discovered orbiting the star HD 189733 on October 5, 2005, when astronomers in France observed the planet transiting across the face of the star. The planet is classified as a...
, another hot gas giant planet.

