
Geography of Indonesia
Encyclopedia
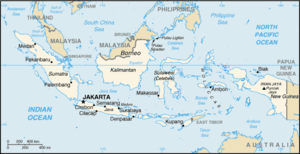
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
is an archipelagic
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
island country in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, lying between the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
and the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. It is in a strategic location astride or along major sea lanes from Indian Ocean to Pacific Ocean. The country's variations in culture have been shaped—although not specifically determined—by centuries of complex interactions with the physical environment. Although Indonesians are now less vulnerable to the effects of nature as a result of improved technology and social programs, to some extent their social diversity has emerged from traditionally different patterns of adjustment to their physical circumstances.
Regions
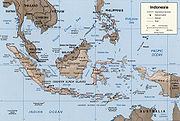
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, Java, Borneo
Borneo
Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is located north of Java Island, Indonesia, at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia....
(known as "Kalimantan
Kalimantan
In English, the term Kalimantan refers to the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo, while in Indonesian, the term "Kalimantan" refers to the whole island of Borneo....
" in Indonesia), Sulawesi
Sulawesi
Sulawesi is one of the four larger Sunda Islands of Indonesia and is situated between Borneo and the Maluku Islands. In Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger Indonesian populations.- Etymology :The Portuguese were the first to...
, and New Guinea
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
; two major archipelagos (Nusa Tenggara and the Maluku Islands
Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands are an archipelago that is part of Indonesia, and part of the larger Maritime Southeast Asia region. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone...
); and sixty smaller archipelagoes. Four of the islands are shared with other nations: Borneo is shared with Malaysia and Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
, Sebatik, located eastern coast of Kalimantan, shared with Malaysia, Timor
Timor
Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, north of the Timor Sea. It is divided between the independent state of East Timor, and West Timor, belonging to the Indonesian province of East Nusa Tenggara. The island's surface is 30,777 square kilometres...
is shared with East Timor
East Timor
The Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, commonly known as East Timor , is a state in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the nearby islands of Atauro and Jaco, and Oecusse, an exclave on the northwestern side of the island, within Indonesian West Timor...
, and the newly divided provinces of Papua
Papua (Indonesian province)
Papua comprises most of the western half of the island of New Guinea and nearby islands. Its capital is Jayapura. It's the largest and easternmost province of Indonesia. The province originally covered the entire western half of New Guinea...
and West Papua share the island of New Guinea
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
with Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea , officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania, occupying the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and numerous offshore islands...
. Indonesia's total land area is 1919317 square kilometres (741,052 sq mi). Included in Indonesia's total territory is another 93000 square kilometres (35,908 sq mi) of inland seas (straits, bay
Bay
A bay is an area of water mostly surrounded by land. Bays generally have calmer waters than the surrounding sea, due to the surrounding land blocking some waves and often reducing winds. Bays also exist as an inlet in a lake or pond. A large bay may be called a gulf, a sea, a sound, or a bight...
s, and other bodies of water). The additional surrounding sea areas bring Indonesia's generally recognized territory (land and sea) to about 5 million square kilometers. The government, however, also claims an exclusive economic zone, which brings the total to about 7.9 million square kilometers. Latitude = 5.00 S & Longitude = 120.00 W
Geology
Sumatra, Java, Madura, and Kalimantan lie on the Sunda ShelfSunda Shelf
Geologically, the Sunda Shelf is a south east extension of the continental shelf of Southeast Asia. Major landmasses on the shelf include the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Java, Madura, Bali and their surrounding smaller islands. It covers an area of approximately 1.85 million km2...
and geographers have conventionally grouped them, (along with Sulawesi), as the Greater Sunda Islands
Greater Sunda Islands
The Greater Sunda Islands are a group of large islands within the Malay archipelago. Jawa , smallest but by far the most populous and important; Sumatera in the west, directly across the Strait of Malacca from Malaysia; Kalimantan, the Indonesian sector of large, compact, minicontinent Borneo; and...
. At Indonesia's eastern extremity is western New Guinea, which lies on the Sahul Shelf. Sea depths in the Sunda and Sahul shelves average 200 metres (656 ft) or less. Between these two shelves lie Sulawesi, Nusa Tenggara (also known as the Lesser Sunda Islands
Lesser Sunda Islands
The Lesser Sunda Islands or Nusa Tenggara are a group of islands in the southern Maritime Southeast Asia, north of Australia. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up the Sunda Islands...
), and the Maluku Islands
Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands are an archipelago that is part of Indonesia, and part of the larger Maritime Southeast Asia region. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone...
(or the Moluccas), which form a second island group where the surrounding seas in some places reach 4500 metres (14,764 ft) in depth. The term "Outer Islands" is used inconsistently by various writers but it is usually taken to mean those islands other than Java and Madura.
Borneo montane rain forests
The Borneo montane rain forests are an ecoregion, of Cloud forest, within the Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests Biome, of the island of Borneo in south-east Asia .-Location and description:...
inland.
Nusa Tenggara consists of two strings of islands stretching eastward from Bali toward Papua. The inner arc of Nusa Tenggara is a continuation of the chain of mountains and volcanoes extending from Sumatra through Java, Bali, and Flores, and trailing off in the volcanic Banda Islands
Banda Islands
The Banda Islands are a volcanic group of ten small volcanic islands in the Banda Sea, about south of Seram Island and about east of Java, and are part of the Indonesian province of Maluku. The main town and administrative centre is Bandanaira, located on the island of the same name. They rise...
, which along with the Kai Islands
Kai Islands
The Kai Islands of Indonesia are in the south-eastern part of the Maluku Islands, in Maluku Province.-Geography:...
and the Tanimbar Islands
Tanimbar Islands
The Tanimbar Islands, also called Timor Laut, are a group of about 65 islands in the Maluku province of Indonesia, including Fordata, Larat, Maru, Molu, Nuswotar, Selaru, Selu, Seira, Wotap, Wuliaru and Yamdena.-Geography:...
and other small islands in the Banda Sea
Banda Sea
The Banda Sea is a sea in the Maluku Islands of Indonesia, technically part of the Pacific Ocean but separated from it by hundreds of islands, as well as the Halmahera and Ceram Seas...
are typical examples of the Wallacea
Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of Indonesian islands separated by deep water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores, Sumba, Timor, Halmahera, Buru, Seram, and...
mixture of Asian and Australasian plant and animal life. The outer arc of Nusa Tenggara is a geological extension of the chain of islands west of Sumatra that includes Nias, Mentawai, and Enggano. This chain resurfaces in Nusa Tenggara in the ruggedly mountainous islands of Sumba and Timor.
The Maluku Islands (or Moluccas) are geologically among the most complex of the Indonesian islands. They are located in the northeast sector of the archipelago, bounded by the Philippines to the north, Papua to the east, and Nusa Tenggara to the south. The largest of these islands include Halmahera
Halmahera
Halmahera is the largest island in the Maluku Islands. It is part of the North Maluku province of Indonesia.Halmahera has a land area of 17,780 km² and a population in 1995 of 162,728...
, Seram
Seram
Seram is an island in the Maluku province of Indonesia. It is located north of Ambon Island. The chief port/town is Masohi.- Geography and geology :...
and Buru
Buru
Buru is the third largest island within Maluku Islands of Malay Archipelago. It lies between the Banda Sea to the south and Seram Sea to the north, west of Ambon and Seram islands. The island belongs to Maluku province of Indonesia and includes the Buru and South Buru regencies...
, all of which rise steeply out of very deep seas and have unique Wallacea vegetation. This abrupt relief pattern from sea to high mountains means that there are very few level coastal plains. The islands of North Maluku
North Maluku
North Maluku is a province of northeastern Indonesia. It covers the northern part of the Maluku Islands, which are split between it and the province of Maluku. Maluku province used to cover the entire group...
are the original Spice Islands, a distinct rainforest
Rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by high rainfall, with definitions based on a minimum normal annual rainfall of 1750-2000 mm...
ecoregion
Ecoregion
An ecoregion , sometimes called a bioregion, is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than an ecozone and larger than an ecosystem. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural...
.
Geomorphologists
Geomorphology
Geomorphology is the scientific study of landforms and the processes that shape them...
believe that the island of New Guinea, of which Papua is a part, may once have been part of the Australian continent. The breakup and tectonic action created towering, snowcapped mountain peaks lining the island's central east-west spine and hot, humid alluvial plains along the coasts. The New Guinea Highlands
New Guinea Highlands
The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, are a chain of mountain ranges and intermountain river valleys, many of which support thriving agricultural communities, on the large island of New Guinea, which lies to the north of Australia...
range some 650 kilometres (404 mi) east to west along the island, forming a mountainous spine between the north and south coasts. A number of islands off the coast of New Guinea have their own distinctive habitats, including the limestone islands of Biak
Schouten Islands
The Indonesian Schouten Islands are an island group of Papua province, eastern Indonesia in the Cenderawasih Bay 50 km off the north-western coast of the island of New Guinea...
, in the entrance to the large Cenderawasih Bay
Cenderawasih Bay
Cenderawasih Bay , also Teluk Sarera , formerly Geelvink Bay is a large bay in northern Province of Papua and West Papua, New Guinea, Indonesia, at . The Dutch name comes after a Dutch ship and family called Geelvinck...
at the northwest end of the island.
Mountains and tectonics
Most of the larger islands are mountainous, with peaks ranging between 3000 and 3800 m (9,842.5 and 12,467.2 ) meters above sea level in Sumatra, Java, Bali, Lombok, Sulawesi, and Seram. The country's tallest mountains are located in the Jayawijaya MountainsJayawijaya Mountains
The Jayawijaya Mountains, formerly known as the Orange Range, are the eastern mountain range of the Maoke Mountains in the central highlands region of the Indonesian part of New Guinea. The range extends for 230 miles east of the Sudirman Range to the Star Mountains. Its highest point is Trikora...
and the Sudirman Range
Sudirman Range
The Sudirman Range or Dugunduguoo or Nassau Range is a mountain range in Papua province, Indonesia.Located at , it comprises a western portion of the Maoke Mountains. The highest peak in Oceania and Australasia, Puncak Jaya , is located here, as well as the large Grasberg copper and gold mine,...
in Papua. The highest peak, Puncak Jaya
Puncak Jaya
Puncak Jaya or Carstensz Pyramid is the highest summit of Mount Carstensz in the Sudirman Range of the western central highlands of Papua province, Indonesia . Other summits are East Carstensz Peak and Ngga Pulu...
(4884 metres (16,024 ft)), is located in the Sudirman Mountains.
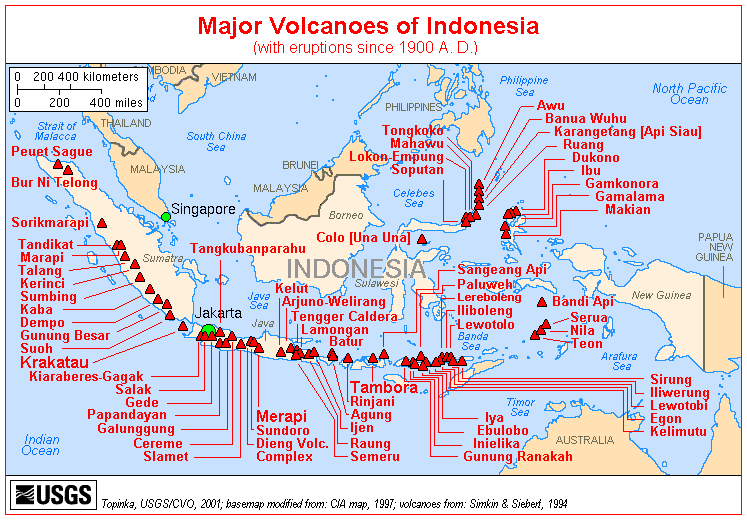
Tectonically, Indonesia is highly unstable. It lies on the Pacific Ring of Fire
Pacific Ring of Fire
The Pacific Ring of Fire is an area where large numbers of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur in the basin of the Pacific Ocean. In a horseshoe shape, it is associated with a nearly continuous series of oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and volcanic belts and/or plate movements...
where the Australian Plate and the Pacific Plate
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At 103 million square kilometres, it is the largest tectonic plate....
are pushed under the Eurasian plate
Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate which includes most of the continent of Eurasia , with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent, and the area east of the Chersky Range in East Siberia...
where they melt at about 100 km deep. A string of volcanoes stretches from Sumatra to the Banda Sea
Banda Sea
The Banda Sea is a sea in the Maluku Islands of Indonesia, technically part of the Pacific Ocean but separated from it by hundreds of islands, as well as the Halmahera and Ceram Seas...
. While the volcanic ash has resulted in fertile soils, it makes agricultural conditions unpredictable in some areas. A string of volcanoes runs through Sumatra, Java, Bali and Nusa Tenggara, and then loops around through to the Banda Islands
Banda Islands
The Banda Islands are a volcanic group of ten small volcanic islands in the Banda Sea, about south of Seram Island and about east of Java, and are part of the Indonesian province of Maluku. The main town and administrative centre is Bandanaira, located on the island of the same name. They rise...
of Maluku to northeastern Sulawesi. Of the 400 volcanoes, approximately 150 are active. Between 1972 and 1991, twenty-nine volcanic eruptions were recorded, mostly on Java. The two most violent volcanic eruptions in modern times occurred in Indonesia; in 1815 Mount Tambora
Mount Tambora
Mount Tambora is an active stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, on the island of Sumbawa, Indonesia. Sumbawa is flanked both to the north and south by oceanic crust, and Tambora was formed by the active subduction zone beneath it. This raised Mount Tambora as high as , making it...
in Sumbawa
Sumbawa
Sumbawa is an Indonesian island, located in the middle of the Lesser Sunda Islands chain, with Lombok to the west, Flores to the east, and Sumba further to the southeast. It is in the province of West Nusa Tenggara....
erupted killing 92,000 and in 1883, Krakatau, erupted killing 36,000.
Time zones
The keeping of standard time is divided into three time zoneTime zone
A time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
s:
- Western Indonesian Time/WIT (IndonesianIndonesian languageIndonesian is the official language of Indonesia. Indonesian is a normative form of the Riau Islands dialect of Malay, an Austronesian language which has been used as a lingua franca in the Indonesian archipelago for centuries....
: Waktu Indonesia Barat/WIB) (UTC+7UTC+7UTC+07:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +07:00. In ISO 8601 the associated time would be written as .Also known as Indochina Time , it is used in:-As standard time :*Australia...
)- WIB is observed in islands of SumatraSumatraSumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, Java, provinces of West KalimantanWest KalimantanWest Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia. It is one of four Indonesian provinces in Kalimantan, the Indonesian part of the island of Borneo. Its capital city Pontianak is located right on the Equator....
and Central KalimantanCentral KalimantanCentral Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia, one of four in Kalimantan - the Indonesian part of the island of Borneo. Its provincial capital is Palangka Raya.The province has a population of just over 2.2 million at the 2010 Census...
- WIB is observed in islands of Sumatra
- Central Indonesian Time/CIT (Waktu Indonesia Tengah/WITA) (UTC+8UTC+8UTC+08:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +08:00. In ISO 8601 the associated time would be written as .With an estimated population of 1.53 billion living within the time zone, roughly 22.5% of the world population, it is the most populous time zone in world, as well as a possible...
)- WITA is observed in islands of SulawesiSulawesiSulawesi is one of the four larger Sunda Islands of Indonesia and is situated between Borneo and the Maluku Islands. In Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger Indonesian populations.- Etymology :The Portuguese were the first to...
, BaliBaliBali is an Indonesian island located in the westernmost end of the Lesser Sunda Islands, lying between Java to the west and Lombok to the east...
, provinces of East Nusa TenggaraEast Nusa TenggaraEast Nusa Tenggara is a province of Indonesia, located in the eastern portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, including West Timor. The provincial capital is Kupang, located on West Timor...
, West Nusa TenggaraWest Nusa TenggaraWest Nusa Tenggara is a province in south-central Indonesia. The province encompasses the western portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, except for Bali as the Wallace line running the length of the Lombok Strait forms the western boundary of the province....
, East KalimantanEast KalimantanEast Kalimantan is the second largest Indonesian province, located on the Kalimantan region on the east of Borneo island. The resource-rich province has two major cities, Samarinda and Balikpapan...
and South KalimantanSouth KalimantanSouth Kalimantan/South Borneo is one of the thirty-three Provinces of Indonesia and one of four Indonesian provinces in the Indonesian part of Borneo. The provincial capital is Banjarmasin...
- WITA is observed in islands of Sulawesi
- Eastern Indonesian Time/EIT (Waktu Indonesia Timur/WIT) (UTC+9UTC+9UTC+09:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +09. This time is used in:-As standard time :*East Timor*Indonesia **Moluccas**Papua and West Papua *Japan - Japan Standard Time*North Korea...
).- WIT is observed in provinces of MalukuMaluku (Indonesian province)Maluku is a province of Indonesia, comprising, broadly, the central and southern parts of the Maluku Islands , which are culturally and geographically associated with Melanesia....
, North MalukuNorth MalukuNorth Maluku is a province of northeastern Indonesia. It covers the northern part of the Maluku Islands, which are split between it and the province of Maluku. Maluku province used to cover the entire group...
, PapuaPapua (Indonesian province)Papua comprises most of the western half of the island of New Guinea and nearby islands. Its capital is Jayapura. It's the largest and easternmost province of Indonesia. The province originally covered the entire western half of New Guinea...
and West Papua.
- WIT is observed in provinces of Maluku
Climate

Parts of Sulawesi and some islands closer to Australia, such as Sumba
Sumba
Sumba is an island in eastern Indonesia, is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, and is in the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Sumba has an area of 11,153 km², and the population was officially at 611,422 in 2005...
and Timor
Timor
Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, north of the Timor Sea. It is divided between the independent state of East Timor, and West Timor, belonging to the Indonesian province of East Nusa Tenggara. The island's surface is 30,777 square kilometres...
, are drier, however, these are exceptions. The almost uniformly warm waters that make up 81% of Indonesia's area ensure that temperatures on land remain fairly constant. The coastal plains averaging 28 °C (82.4 °F), the inland and mountain areas averaging 26 °C (78.8 °F), and the higher mountain regions, 23 °C (73.4 °F). The area's relative humidity ranges between 70 and 90%. Winds are moderate and generally predictable, with monsoons usually blowing in from the south and east in June through October and from the northwest in November through March. Typhoons and large scale storms pose little hazard to mariners in Indonesia waters; the major danger comes from swift currents in channels, such as the Lombok
Lombok Strait
The Lombok Strait is a strait connecting the Java Sea to the Indian Ocean, located between the islands of Bali and Lombok in Indonesia. The Gili Islands are on the Lombok side....
and Sape
Sape Strait
The Sape Strait The Sape Strait (Indonesian: Selat Sape) The Sape Strait (Indonesian: Selat Sape) (also Sapie Strait is a strait connecting the Flores Sea to the Sumba Strait. It separates the islands of Sumbawa and Komodo. It joins the Indondesian provinces of West Nusa Tenggara and East Nusa...
straits.
Environmental issues
For centuries, the geographical resources of the Indonesian archipelago have been exploited in ways that fall into consistent social and historical patterns. One cultural pattern consists of the formerly Indianized, rice-growing peasants in the valleys and plains of Sumatra, Java, and Bali; another cultural complex is composed of the largely Islamic coastal commercial sector; a third, more marginal sector consists of the upland forest farming communities which exist by means of subsistence swidden agriculture. To some degree, these patterns can be linked to the geographical resources themselves, with abundant shoreline, generally calm seas, and steady winds favoring the use of sailing vessels, and fertile valleys and plains—at least in the Greater Sunda Islands—permitting irrigated rice farming. The heavily forested, mountainous interior hinders overland communication by road or river, but fosters slash-and-burn agriculture.Indonesia's high population and rapid industrialisation present serious environmental issues
Environmental issues in Indonesia
Environmental issues in Indonesia are associated with the country's high population and rapid industrialisation, and they are often given a lower priority due to high poverty levels and weak, under-resourced governance...
, which are often given a lower priority due to high poverty levels and weak, under-resourced governance. Issues include large-scale deforestation
Deforestation in Indonesia
Deforestation in Indonesia has been a massive environmental impact on the country, home to some of the most biologically diverse forests in the world, ranking third behind Brazil and the Democratic Republic of Congo. As late as 1900, Indonesia was still a densely forested country with the total...
(much of it illegal
Illegal logging
Illegal logging is the harvest, transportation, purchase or sale of timber in violation of laws. The harvesting procedure itself may be illegal, including using corrupt means to gain access to forests; extraction without permission or from a protected area; the cutting of protected species; or the...
) and related wildfires causing heavy smog over parts of western Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore; over-exploitation of marine resources; and environmental problems associated with rapid urbanization
Urbanization
Urbanization, urbanisation or urban drift is the physical growth of urban areas as a result of global change. The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008....
and economic development
Economic development
Economic development generally refers to the sustained, concerted actions of policymakers and communities that promote the standard of living and economic health of a specific area...
, including air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
, traffic congestion
Traffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition on road networks that occurs as use increases, and is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. The most common example is the physical use of roads by vehicles. When traffic demand is great enough that the interaction...
, garbage management, and reliable water and waste water
Wastewater
Wastewater is any water that has been adversely affected in quality by anthropogenic influence. It comprises liquid waste discharged by domestic residences, commercial properties, industry, and/or agriculture and can encompass a wide range of potential contaminants and concentrations...
services. Deforestation and the destruction of peatlands make Indonesia the world's third largest emitter of greenhouse gases. Habitat destruction
Habitat destruction
Habitat destruction is the process in which natural habitat is rendered functionally unable to support the species present. In this process, the organisms that previously used the site are displaced or destroyed, reducing biodiversity. Habitat destruction by human activity mainly for the purpose of...
threatens the survival of indigenous and endemic species, including 140 species of mammals identified by the World Conservation Union
World Conservation Union
The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources is an international organization dedicated to finding "pragmatic solutions to our most pressing environment and development challenges." The organization publishes the IUCN Red List, compiling information from a network of...
(IUCN) as threatened
Threatened species
Threatened species are any speciesg animals, plants, fungi, etc.) which are vulnerable to endangerment in the near future.The World Conservation Union is the foremost authority on threatened species, and treats threatened species not as a single category, but as a group of three categories,...
, and 15 identified as critically endangered, including the Sumatran Orangutan.
In 1970, 15% of Indonesians lived in cities compared to over 30% today, and this increases pressure on the urban environment. Industrial pollution is increasing, particularly in Java, and the increasing affluence of the growing middle class drives a rapid increase in the number of motor vehicles and associated emissions. Garbage and waste water services are being placed under increasing pressure. Reliance on septic systems or effluent disposal in open canals and river systems remains the norm, and is a major polluter of water resources. Very few Indonesians have access to safe drinking water and must boil it before use.
Area and boundaries
Area:total land area: 1,919,440 km2 (land: 1,826,440 km2,
inland water: 93,000 km2)
territorial area: 5,193,250 km2
total area (including exclusive economic zone): around 7.9 million km2
Land boundaries:
total: 2,830 km
border countries: Malaysia 1,782 km, Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea , officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania, occupying the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and numerous offshore islands...
820 km, East Timor
East Timor
The Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, commonly known as East Timor , is a state in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the nearby islands of Atauro and Jaco, and Oecusse, an exclave on the northwestern side of the island, within Indonesian West Timor...
228 km
Other nearby countries: India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
NW of Aceh, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
, Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
.
Coastline: 54,716 km
Maritime claims: measured from claimed archipelagic baselines
exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (230.2 mi; 370.4 km)
territorial sea: 12 nmi (13.8 mi; 22.2 km)
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m(sea surface level), Wetar Basin in east of Banda Sea
Banda Sea
The Banda Sea is a sea in the Maluku Islands of Indonesia, technically part of the Pacific Ocean but separated from it by hundreds of islands, as well as the Halmahera and Ceram Seas...
at -7,440 m (northwest of Tanimbar Islands
Tanimbar Islands
The Tanimbar Islands, also called Timor Laut, are a group of about 65 islands in the Maluku province of Indonesia, including Fordata, Larat, Maru, Molu, Nuswotar, Selaru, Selu, Seira, Wotap, Wuliaru and Yamdena.-Geography:...
& southeast of Ceram Island), where subduction zone is
highest point: Puncak Jaya
Puncak Jaya
Puncak Jaya or Carstensz Pyramid is the highest summit of Mount Carstensz in the Sudirman Range of the western central highlands of Papua province, Indonesia . Other summits are East Carstensz Peak and Ngga Pulu...
(also known as Carstenz Pyramid) 4,884 m
Resources and land use
Natural resources: petroleumPetroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, tin
Tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4...
, natural gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
, nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
, timber
Timber
Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S...
, bauxite
Bauxite
Bauxite is an aluminium ore and is the main source of aluminium. This form of rock consists mostly of the minerals gibbsite Al3, boehmite γ-AlO, and diaspore α-AlO, in a mixture with the two iron oxides goethite and hematite, the clay mineral kaolinite, and small amounts of anatase TiO2...
, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, fertile soils, coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
, gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
, silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
Land use:
arable land: 9.9%
permanent crops: 7.2%
other: 82.9% (1998 est.)
Irrigated land: 48,150 km2 (1998 est.)

