
Geography of Papua New Guinea
Encyclopedia
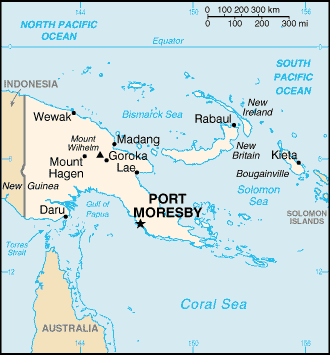
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
, the islands of New Ireland
New Ireland (island)
New Ireland is a large island in Papua New Guinea, approximately 7,404 km² in area. It is the largest island of the New Ireland Province, lying northeast of the island of New Britain. Both islands are part of the Bismarck Archipelago, named after Otto von Bismarck, and they are separated by...
, New Britain
New Britain
New Britain, or Niu Briten, is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from the island of New Guinea by the Dampier and Vitiaz Straits and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel...
and Bougainville
Bougainville Island
Bougainville Island is the main island of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville of Papua New Guinea. This region is also known as Bougainville Province or the North Solomons. The population of the province is 175,160 , which includes the adjacent island of Buka and assorted outlying islands...
, and smaller nearby islands. Together these make up the nation of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea , officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania, occupying the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and numerous offshore islands...
in tropical Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
, located at the western edge of the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
.
Papua New Guinea is largely mountainous, and much of it is covered with tropical rainforest
Rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by high rainfall, with definitions based on a minimum normal annual rainfall of 1750-2000 mm...
. The New Guinea Highlands
New Guinea Highlands
The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, are a chain of mountain ranges and intermountain river valleys, many of which support thriving agricultural communities, on the large island of New Guinea, which lies to the north of Australia...
runs the length of New Guinea, and the highest areas receive snowfall - a rarity in the tropics. Within Papua New Guinea Mount Wilhelm
Mount Wilhelm
Mount Wilhelm is the highest mountain in Papua New Guinea at . It is part of the Bismarck Range and the peak is the point where three provinces intersect, Simbu, Western Highlands and Madang...
is the highest peak, at 4 509 m. There are several major rivers, notably the Sepik River (1 126 km long), which winds through lowland swamp
Swamp
A swamp is a wetland with some flooding of large areas of land by shallow bodies of water. A swamp generally has a large number of hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates periodical inundation. The two main types of swamp are "true" or swamp...
plains to the north coast, and the Fly River
Fly River
The Fly at , is the second longest river, after the Sepik, in Papua New Guinea. The Fly is the largest river in Oceania, the largest in the world without a single dam in its catchment, and overall ranks as the twenty-fifth largest river in the world by volume of discharge...
(1 050 km long), which flows through one of the largest swampland
Swampland
In physics, the term swampland is used in contrast to the term "landscape," to indicate physical theories or aspects of such theories which could be true if gravity wasn't an issue, but which are not compatible with string theory...
s in the world to the south coast. The Highlands consist of a number of smaller ranges running west to east, such as the Finisterre Range
Finisterre Range
Finisterre Range is a mountain range in north-eastern Papua New Guinea, at . The unnamed highest point of the range , which is ranked 45th in the world by prominence, is usually quoted at 4,175 m, but SRTM data suggests that it is nearer to 4,120 m...
which dominates the Huon Peninsula
Huon Peninsula
Huon Peninsula is a large rugged peninsula on the island of New Guinea in Morobe Province, eastern Papua New Guinea. It is named after French explorer Jean-Michel Huon de Kermadec who discovered it along with his personal assistant and porter, Henry Ole. The peninsula is dominated by the steep...
to north of the city of Lae
Lae
Lae, the capital of Morobe Province, is the second-largest city in Papua New Guinea. It is located at the start of the Highlands Highway which is the main land transport corridor from the Highlands region to the coast...
.
Papua New Guinea has one land border - that which divides the island of New Guinea. Across the 820 km border, the western half of New Guinea is officially known as Papua province
Papua (Indonesian province)
Papua comprises most of the western half of the island of New Guinea and nearby islands. Its capital is Jayapura. It's the largest and easternmost province of Indonesia. The province originally covered the entire western half of New Guinea...
, governed by Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
. There are maritime borders with Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
to the south and Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is a sovereign state in Oceania, east of Papua New Guinea, consisting of nearly one thousand islands. It covers a land mass of . The capital, Honiara, is located on the island of Guadalcanal...
to the southeast.
Physical geography
Papua New Guinea has a total area of 462 840 km², of which 452 860 km² is land and 9 980 km² is water. Its coastline is 5 152 km long.The northernmost point is Mussau Island
Mussau Island
Mussau Island is the largest island of St. Matthias Islands, Papua New Guinea, at . It is one of the northernmost islands of Papua New Guinea....
(1°23' S), southernmost point is Hemenahei Island
Hemenahei Island
-References:...
(11°29' S), easternmost point is Olava, Bougainville
Bougainville Island
Bougainville Island is the main island of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville of Papua New Guinea. This region is also known as Bougainville Province or the North Solomons. The population of the province is 175,160 , which includes the adjacent island of Buka and assorted outlying islands...
(155°57' E) and the westernmost point is Mabudawan (140°54' E).
Papua New Guinea has several volcanoes, as it is situated along the Pacific's "Ring of Fire"
Pacific Ring of Fire
The Pacific Ring of Fire is an area where large numbers of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur in the basin of the Pacific Ocean. In a horseshoe shape, it is associated with a nearly continuous series of oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and volcanic belts and/or plate movements...
. Volcanic eruptions are not rare, and the area is prone to earthquakes and tsunamis because of this. The volcanic disturbance can often cause severe earthquakes, which in turn can also cause tsunamis. Papua New Guinea is also prone to landslides, often caused by deforestation in major forests. The mountainous regions of Papua New Guinea are the areas most susceptible to landslides causing damage.
Offshore islands include the small, forested Admiralty Islands
Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are a group of eighteen islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the south Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-covered islands form part of Manus Province, the smallest and...
, the largest of which is Manus
Manus
Manus, a masculine first name derived from the Latin meaning "hand" or "fist," and, less commonly, a "band of men," may refer to:*Manus Province, in Papua New Guinea**Manus Island, part of Manus Province...
, to the north of the main island of New Guinea. These have a distinct plant and animal life from the main island but the natural forest has been cleared in places for logging and agriculture.
Climate
Tropical; northwest monsoonMonsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
(December to March), southeast monsoon (May to October); slight seasonal temperature variation. In lower altitudes, the temperature is around 80°F (27°C) year round. But the higher altitudes are a constant 70°F (21°C).
Human geography
measured from claimed archipelagic baselines
continental shelf:
200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
exclusive fishing zone:
200 nautical miles (370 km)
territorial sea:
12 nautical miles (22 km)
Land use
Natural resources:gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
, natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, timber
Timber
Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S...
, oil
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, fisheries
Land use:
- arable land: 0.49%
- permanent crops: 1.4%
- other (forests, swamplands, etc.): 98.11% (2005 estimate)
Environmental issues
The rainforest is subject to deforestationDeforestation
Deforestation is the removal of a forest or stand of trees where the land is thereafter converted to a nonforest use. Examples of deforestation include conversion of forestland to farms, ranches, or urban use....
as a result of growing commercial demand for tropical timber; forest clearance, especially in coastal areas, for plantations; pollution
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
from mining projects. If the trend continues, more than half the forest that existed when Papua New Guinea became independent from Australia in 1975 will be gone by 2021.
party to
- Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the SeaLaw of the seaLaw of the sea may refer to:* United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea* Admiralty law* The Custom of the Sea...
, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands

