
Head (vessel)
Encyclopedia

Pressure vessel
A pressure vessel is a closed container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure.The pressure differential is dangerous and many fatal accidents have occurred in the history of their development and operation. Consequently, their design,...
are commonly known as heads.
Head shapes
The shape of the heads used can vary. The most common head shapes are:Hemispherical
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
head :A sphere is the ideal shape for a head, because the pressure in the vessel is divided equally across the surface of the head. The radius (r) of the head equals the radius of the cylindrical part of the vessel.
Ellipsoidal head :This is also called a 2:1 elliptical head. The shape of this head is more economical, because the height of the head is just a quarter of the diameter. Its radius varies between the major and minor axis.
Torispherical head :These heads have a dish with a fixed radius (r1), the size of which depends on the type of torispherical head. The transition between the cylinder and the dish is called the knuckle. The knuckle has a toroidal shape. The most common types of torispherical heads are:
-
- Klöpper head :This is a torispherical head. The dish has a radius that equals the diameter of the cylinder it is attached to (
 ). The knuckle has a radius that equals a tenth of the diameter of the cylinder (
). The knuckle has a radius that equals a tenth of the diameter of the cylinder (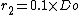 ), hence its alternative designation "Decimal head".
), hence its alternative designation "Decimal head".
- Klöpper head :This is a torispherical head. The dish has a radius that equals the diameter of the cylinder it is attached to (
Also other sizes are:
 ,(page13) rest of height (lets say
,(page13) rest of height (lets say  )
)  .
.
-
- Korbbogen head :This is a torispherical head. The radius of the dish is 80% of the diameter of the cylinder (
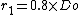 ). The radius of the knuckle is (
). The radius of the knuckle is (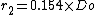 ).
).
- Korbbogen head :This is a torispherical head. The radius of the dish is 80% of the diameter of the cylinder (
Also other sizes are:
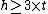 , rest of height (lets say
, rest of height (lets say 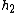 )
) 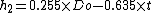 . This shape finds its origin in architecture.
. This shape finds its origin in architecture.Flat head :This is a head consisting of a toroidal knuckle connecting to a flat plate. This type of head is typically used for the bottom of cookware.

Conical head : This is a cone
Cone (geometry)
A cone is an n-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a base to a point called the apex or vertex. Formally, it is the solid figure formed by the locus of all straight line segments that join the apex to the base...
-shaped head.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatmentHeat treatment
Heat treating is a group of industrial and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are also used in the manufacture of many other materials, such as glass...
is usually required after cold forming, but not required by heads formed by hot forming:

