
Horizontal convective rolls
Encyclopedia

Planetary boundary layer
The planetary boundary layer , also known as the atmospheric boundary layer , is the lowest part of the atmosphere and its behavior is directly influenced by its contact with a planetary surface. On Earth it usually responds to changes in surface forcing in an hour or less...
. Although horizontal convective rolls, also known as cloud streets, have been clearly seen in satellite photographs for the last 30 years, their development is poorly understood due to a lack of observational data. Research has shown these eddies to be significant to the vertical transport of momentum, heat, moisture, and air pollutants within the boundary layer.
Characteristics
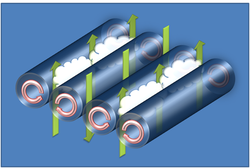
Horizontal convective rolls are counter-rotating vortex rolls that are nearly aligned with the mean wind of the convective boundary layer. Early theory on the features predict that the vortices may be aligned up to 30° to the left for stable environments, 18° to the left for neutral environments, and nearly parallel to the mean wind for unstable environments. This theory has been supported by aircraft observations from several field experiments.The depth of a vortex is usually the depth of the boundary layer, which is generally on the order of 1–2 km. A vortex pair usually has a lateral to vertical dimension ratio of 3:1. Experimental studies have shown that the aspect ratio (a ratio of roll wavelength to boundary layer depth) has been found to vary between 2.2:1 and 6.5:1, with an average aspect ratio of 5.7:1. However, in some situations, the aspect ratio may be as large as 10:1. Large aspect ratios for rolls are believed to be caused by non-linear interactions at small convective scales, which are not predicted by theoretical calculations. The lifetime of a convective roll can last from 1 to 72 hours.
If the environmental air is near saturation, condensation may occur in updrafts produced from the vortex rotation. The sinking motion produced between alternating pairs of rolls, combined with the updrafts, will produce cloud streets. Typical updraft and downdraft speeds are usually less than 1 m/s. Gliders often use the updrafts produced by the rolls to gain altitude while flying.
Development and required environmental conditions
The exact process that leads to the formation of horizontal convective rolls is not well understood, but most formation theories involve a combination of thermal or convective instability and dynamic instability. In thermal instabilities, turbulent energy that forms the rolls is produced from buoyancy. For this condition to be satisfied, a moderate surface heat fluxHeat flux
Heat flux or thermal flux is the rate of heat energy transfer through a given surface. The SI derived unit of heat rate is joule per second, or watt. Heat flux is the heat rate per unit area. In SI units, heat flux is measured in W/m2]. Heat rate is a scalar quantity, while heat flux is a vectorial...
is necessary to produce a slightly unstable environment; however, too much heat flux will cause the environment to be too unstable, and will lead to cellular, instead of roll convection.
Turbulent energy derived from dynamic instabilities is produced from wind shear energy. Dynamic conditions favorable for roll development generally have high speed shear, and very little directional shear. Low speed shear environments generally produce cellular convection. It has been suggested that dynamic instability requires an inflection point in the cross roll wind speed profile—that is, the wind speed profile is curved, reaching a maxima within the boundary layer. Although inflection points are common in many wind profiles of convective roll events, some events have been observed lacking inflection points, suggesting that this is not a requirement for roll convection.
The combination of convective and dynamic instability can be quantified in the ratio
 , where
, where  is the depth of the boundary layer and
is the depth of the boundary layer and  is the Monin-Obukhov length
is the Monin-Obukhov lengthMonin-Obukhov Length
The is used to describe the effects of buoyancy on turbulent flows, particularly in the lower tenth of the atmospheric boundary layer. It was first defined by Alexander Obukhov in 1946,...
. In the case of roll convection, the Monin-Obukhov length is the height at which turbulent energy production from buoyancy dominates that produced from wind shear. Roll convection is typically observed for
 values that are approximately greater than -5 and approximately less than -25. These conditions are most frequently observed in cold air outbreaks, and produce the combination of necessary dynamic and convective instabilities that produce roll convection. Roll convection is more frequently observed over water surfaces than land surfaces, due to the interactions of orography making the convection less distinct.
values that are approximately greater than -5 and approximately less than -25. These conditions are most frequently observed in cold air outbreaks, and produce the combination of necessary dynamic and convective instabilities that produce roll convection. Roll convection is more frequently observed over water surfaces than land surfaces, due to the interactions of orography making the convection less distinct.External links
- Dunlop, Storm (2002) The Weather Identification Handbook Guilford, Connecticut: The Lyons Press. ISBN 1-58574-857-9
- Scorer, Verkaik (1989) Spacious Skies David & Charles ISBN 0-7153-9139-9

