Mesosome
Encyclopedia
Invagination
Invagination means to fold inward or to sheath. In biology, this can refer to a number of processes.* Invagination is the morphogenetic processes by which an embryo takes form, and is the initial step of gastrulation, the massive reorganization of the embryo from a simple spherical ball of cells,...
s in the plasma membrane of bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
that are produced by the chemical fixation
Fixation (histology)
In the fields of histology, pathology, and cell biology, fixation is a chemical process by which biological tissues are preserved from decay, thereby preventing autolysis or putrefaction...
techniques used to prepare samples for electron microscopy. Although several functions were proposed for these structures in the 1960s, they were recognized as artifacts by the late 1970s and are no longer considered to be part of the normal structure of bacterial cells.
Initial observations
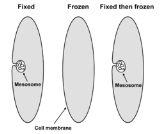
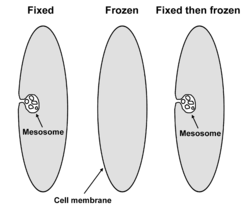
These structures are invaginations of the plasma membrane observed in gram-positiveGram-positive
Gram-positive bacteria are those that are stained dark blue or violet by Gram staining. This is in contrast to Gram-negative bacteria, which cannot retain the crystal violet stain, instead taking up the counterstain and appearing red or pink...
bacteria that have been chemically fixed
Fixation (histology)
In the fields of histology, pathology, and cell biology, fixation is a chemical process by which biological tissues are preserved from decay, thereby preventing autolysis or putrefaction...
to prepare them for electron microscopy. They were first observed in 1953 by George B. Chapman and James Hillier, who referred to them as "peripheral bodies." They were termed "mesosomes" by J. D. Robertson in 1959. Initially, it was thought that mesosomes might play a role in several cellular processes, such as cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
formation during cell division
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
, chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
replication, or as a site for oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate . Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP,...
.
Disproof of hypothesis
These models were called into question during the late 1970s when data accumulated suggesting that mesosomes are artifacts formed through damage to the membrane during the process of chemical fixation, and do not occur in cells that have not been chemically fixed. By the mid to late 1980s, with advances in cryofixation and freeze substitution methods for electron microscopy, it was generally concluded that mesosomes do not exist in living cells. However, a few researchers continue to argue that the evidence remains inconclusive, and that mesosomes might not be artifacts in all cases.Recently, similar folds in the membrane have been observed in bacteria that have been exposed to some classes of antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s, and antibacterial peptides (defensin
Defensin
Defensins are small cysteine-rich cationic proteins found in both vertebrates and invertebrates. They have also been reported in plants. They are, and function as, host defense peptides. They are active against bacteria, fungi and many enveloped and nonenveloped viruses. They consist of 18-45 amino...
s). The appearance of these mesosome-like structures may be the result of these chemicals damaging the plasma membrane and/or cell wall.
The case of the proposal and then disproof of the mesosome hypothesis
Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. The term derives from the Greek, ὑποτιθέναι – hypotithenai meaning "to put under" or "to suppose". For a hypothesis to be put forward as a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it...
has been discussed from the viewpoint of the philosophy of science
Philosophy of science
The philosophy of science is concerned with the assumptions, foundations, methods and implications of science. It is also concerned with the use and merit of science and sometimes overlaps metaphysics and epistemology by exploring whether scientific results are actually a study of truth...
as an example of how a scientific idea can be falsified
Falsifiability
Falsifiability or refutability of an assertion, hypothesis or theory is the logical possibility that it can be contradicted by an observation or the outcome of a physical experiment...
and the hypothesis then rejected, and analyzed to explore how the scientific community
Scientific community
The scientific community consists of the total body of scientists, its relationships and interactions. It is normally divided into "sub-communities" each working on a particular field within science. Objectivity is expected to be achieved by the scientific method...
carries out this testing process.

