Outline of Belarus
Encyclopedia
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
. Belarus borders Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
to the north and east, Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
to the south, Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
to the west, and Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
and Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
to the north. A third of the country is forest
Forest
A forest, also referred to as a wood or the woods, is an area with a high density of trees. As with cities, depending where you are in the world, what is considered a forest may vary significantly in size and have various classification according to how and what of the forest is composed...
ed, and agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
and manufacturing
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
are its strongest economic sectors.
Until the 20th century, the Belarusians
Belarusians
Belarusians ; are an East Slavic ethnic group who populate the majority of the Republic of Belarus. Introduced to the world as a new state in the early 1990s, the Republic of Belarus brought with it the notion of a re-emerging Belarusian ethnicity, drawn upon the lines of the Old Belarusian...
lacked the opportunity to evolve a distinctive national identity, since the lands of modern-day Belarus belonged to several countries, including the Duchy of Polatsk
Duchy of Polatsk
The Principality of Polotsk, also known as the Kingdom of Polotsk or the Duchy of Polotsk was a medieval principality of the Early East Slavs, and was considered one of the constituent principalities within the Kievan Rus', although with a wide degree of autonomy. It was established around the...
, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a dualistic state of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century...
, and the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
. After the short-lived Belarusian People's Republic (1918–19), Belarus became a constituent republic of the Soviet Union
Republics of the Soviet Union
The Republics of the Soviet Union or the Union Republics of the Soviet Union were ethnically-based administrative units that were subordinated directly to the Government of the Soviet Union...
, the Byelorussian SSR
Byelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic was one of fifteen constituent republics of the Soviet Union. It was one of the four original founding members of the Soviet Union in 1922, together with the Ukrainian SSR, the Transcaucasian SFSR and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic...
. The parliament of the republic declared the sovereignty of Belarus on July 27, 1990, and following the collapse of the Soviet Union, Belarus declared independence on August 25, 1991. Alexander Lukashenko
Alexander Lukashenko
Alexander Grigoryevich Lukashenko has been serving as the President of Belarus since 20 July 1994. Before his career as a politician, Lukashenko worked as director of a state-owned agricultural farm. Under Lukashenko's rule, Belarus has come to be viewed as a state whose conduct is out of line...
has been the country's president since 1994. During his presidency, Lukashenko has implemented Soviet-era policies, such as state ownership of the economy, despite objections from Western governments. Since 1996, Belarus has been negotiating with Russia to unify into a single state called the Union of Russia and Belarus
Union of Russia and Belarus
The Union State , semi-officially known as Union State of Russia and Belarus , is a supranational entity consisting of the Russian Federation and the Republic of Belarus.- Creation :...
.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Belarus:
General reference
- Pronunciation: bɛləˈruːs
- Common English country name: BelarusBelarusBelarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
- Official English country name: The Republic of Belarus
- Common endonym(s):
- Official endonym(s):
- Adjectival(s): BelarusianBelarusianBelarusian may refer to:* Something of, or related to Belarus* Belarusians . See also Demographics of Belarus and Culture of Belarus. For specific Belarusians, see List of Belarusians.* Belarusian language...
- Demonym(s):
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Belarus - International rankings of BelarusInternational rankings of Belarus-International rankings:...
- ISO country codes: BY, BLR, 112
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:BYISO 3166-2:BYISO 3166-2:BY is the entry for Belarus in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Belarus, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .by.by.by is the Internet country code top-level domain for Belarus. It is administered by The Operative-analytical center of the Republic of Belarus . The code "BY" originates from an alternative spelling of Belarus, Byelorussia, which was used during their inclusion in the Soviet Union...
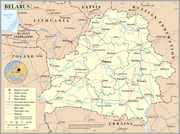
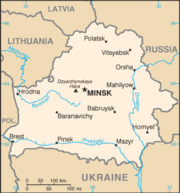
Geography of Belarus
- Belarus is: a landlocked country
- Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes... - EurasiaEurasiaEurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
- Eastern EuropeEastern EuropeEastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
- Eastern Europe
- Europe
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Eastern European TimeEastern European TimeEastern European Time is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in some European countries that also use Eastern European Summer Time as a summer daylight saving time.- Usage :...
(UTC+02), Eastern European Summer TimeEastern European Summer TimeEastern European Summer Time is one of the names of UTC+3 time zone, 3 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in some European, North African, and Middle Eastern countries...
(UTC+03) - Extreme points of Belarus
- High: Dzyarzhynskaya HaraDzyarzhynskaya HaraDzyarzhynskaya Hara is the highest point in Belarus. The hill is 345 meters above sea level and is located west of Minsk, near Dzyarzhynsk, in the village Skirmuntava. The original name of the hill was Svyataya Hara...
346 m (1,135 ft) - Low: Neman RiverNeman RiverNeman or Niemen or Nemunas, is a major Eastern European river rising in Belarus and flowing through Lithuania before draining into the Curonian Lagoon and then into the Baltic Sea at Klaipėda. It is the northern border between Lithuania and Russia's Kaliningrad Oblast in its lower reaches...
90 m (295 ft)
- High: Dzyarzhynskaya Hara
- Land boundaries: 3,306 km
- Northern Hemisphere
Environment of Belarus

- Climate of Belarus
- Environmental issues in Belarus
- Ecoregions in Belarus
- Renewable energy in Belarus
- Geology of Belarus
- Protected areas of Belarus
- Biosphere reserves in Belarus
- National parks of Belarus
- Wildlife of Belarus
- Flora of Belarus
- Fauna of Belarus
Natural geographic features of Belarus
- Rivers of Belarus
- World Heritage Sites in Belarus
Administrative divisions of Belarus
- Main article: Administrative divisions of BelarusAdministrative divisions of BelarusAt the top level of administration, the Eastern European country of Belarus is divided into six voblasts and the city of Minsk, which has a special status being the capital of Belarus...
- Provinces of Belarus
Provinces of Belarus
- MinskMinsk- Ecological situation :The ecological situation is monitored by Republican Center of Radioactive and Environmental Control .During 2003–2008 the overall weight of contaminants increased from 186,000 to 247,400 tons. The change of gas as industrial fuel to mazut for financial reasons has worsened...
- Brest ProvinceBrest VoblastBrest Voblast or Brest Oblast is a province of Belarus with its administrative center being Brest.Important cities within the voblast' include: Baranovichi, Brest, and Pinsk.-Geography:...
- Homyel ProvinceHomiel VoblastHomiel Voblast or Gomel Oblast is a province of Belarus with its administrative center being Homyel.Important cities within the voblasts include: Gomel, Mazyr, Zhlobin, Svetlahorsk, Rechytsia, Kalinkavichy, Rahachow, Dobrush...
- Hrodna ProvinceHrodna VoblastHrodna Voblast or Grodno Oblast is a voblast in northwestern Belarus.The capital - Grodno is the biggest city of the province. It lies on the Neman River. Grodno's existence is attested to from 1127. Two castles dating from the 14th - 18th centuries are located here on the steep right bank of...
- Mahilyow ProvinceMahilyow VoblastMahilyow Voblasts or Mogilyov Oblast is a province of Belarus with its administrative center being Mogilyov ....
- Minsk Province
- Vitsebsk ProvinceVitsebsk VoblastVitsebsk Voblast or Vitebsk Oblast is a province of Belarus with its administrative center being Vitebsk .As of a 2009 estimate, the voblast has a population of 1,230,800...
Government and politics of Belarus
- Main article: Government of BelarusGovernment of BelarusThe Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus is the executive branch of state power in Belarus, and it is appointed by the President of Belarus...
and Politics of BelarusPolitics of BelarusThe politics of Belarus takes place in a framework of a presidential republic, where by the President of Belarus is the head of state. Executive power is exercised by the government, in its top sits a prime minister, appointed by the President...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: presidentialPresidential systemA presidential system is a system of government where an executive branch exists and presides separately from the legislature, to which it is not responsible and which cannot, in normal circumstances, dismiss it....
republicRepublicA republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of... - Capital of Belarus: Minsk
- Elections in BelarusElections in BelarusBelarus elects on national level a head of state - the president - and a legislature. The president is elected for a five year term by the people. The National Assembly has two chambers...
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Belarus
- Political scandals of Belarus
- Taxation in Belarus
Executive branch of the government of Belarus
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: President of BelarusPresident of BelarusThe office of President of Belarus is the head of state of Belarus. The office was created in 1994 with the passing of the Constitution of Belarus by the Supreme Soviet. This replaced the office of Chairman of the Supreme Soviet as the head of state...
, - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of Belarus, - Cabinet of Belarus
Legislative branch of the government of Belarus
- Parliament of Belarus (bicameral)
- Upper houseUpper houseAn upper house, often called a senate, is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house; a legislature composed of only one house is described as unicameral.- Possible specific characteristics :...
: Council of the RepublicCouncil of the RepublicCouncil of the Republic may refer to:* Council of the Republic of the Soviet Union* Council of the Republic of Belarus* Council of the Republic of Russia... - Lower houseLower houseA lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house.Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide the lower house has come to wield more power...
: House of Representatives of Belarus
- Upper house
Judicial branch of the government of Belarus
- Supreme Court of BelarusSupreme Court of BelarusThe Supreme Court of the Republic of Belarus is the highest-tier court inside of Belarus and acts as the final "court of review." Its general tasks include the oversight of lower-tier courts and can render justice in areas of general civil and criminal law...
Foreign relations of Belarus
- Diplomatic missions in Belarus
- Diplomatic missions of Belarus
- United States-Belarus relations
International organization membership
The Republic of Belarus is a member of:- Black Sea Economic Cooperation Zone (BSEC) (observer)
- Central European InitiativeCentral European InitiativeThe Central European Initiative is a forum of regional cooperation in Central, Eastern and South Eastern Europe, counting 18 member states. It was formed in Budapest in 1989.-History:...
(CEI) - Collective Security Treaty OrganizationCollective Security Treaty OrganizationThe Collective Security Treaty Organization is an intergovernmental military alliance which was signed on 15 May 1992. On 7 October 2002, the Presidents of Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan signed a charter in Tashkent founding the CSTO.Nikolai Bordyuzha was appointed...
(CSTO) - Commonwealth of Independent StatesCommonwealth of Independent StatesThe Commonwealth of Independent States is a regional organization whose participating countries are former Soviet Republics, formed during the breakup of the Soviet Union....
(CIS) - Eurasian Economic CommunityEurasian Economic CommunityThe Eurasian Economic Community originated from the Commonwealth of Independent States customs union between Belarus, Russia and Kazakhstan on 29 March 1996...
(EAEC) - Euro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilEuro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilThe Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council , a NATO institution, is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and those parts of Asia on the European periphery. The member states meet to cooperate and consult on a range of political and security issues...
(EAPC) - European Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentEuropean Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentFounded in 1991, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development uses the tools of investment to help build market economies and democracies in 30 countries from central Europe to central Asia. Its mission was to support the formerly communist countries in the process of establishing their...
(EBRD) - Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - General Confederation of Trade UnionsGeneral Confederation of Trade UnionsThe General Confederation of Trade Unions or GCTU is an international trade union confederation. It was founded April 16, 1992 and incorporates members from the Commonwealth of Independent States....
(GCTU) - International Atomic Energy AgencyInternational Atomic Energy AgencyThe International Atomic Energy Agency is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. The IAEA was established as an autonomous organization on 29 July 1957...
(IAEA) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Development AssociationInternational Development AssociationThe International Development Association , is the part of the World Bank that helps the world’s poorest countries. It complements the World Bank's other lending arm — the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — which serves middle-income countries with capital investment and...
(IDA) - International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Mobile Satellite OrganizationInternational Mobile Satellite OrganizationThe International Mobile Satellite Organization is the intergovernmental organization that oversees certain public satellite safety and security communication services provided via the Inmarsat satellites...
(IMSO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for MigrationInternational Organization for MigrationThe International Organization for Migration is an intergovernmental organization. It was initially established in 1951 as the Intergovernmental Committee for European Migration to help resettle people displaced by World War II....
(IOM) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) - International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM)
- International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Trade Union ConfederationInternational Trade Union ConfederationThe International Trade Union Confederation is the world's largest trade union federation. It was formed on November 1, 2006 out of the merger of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions and the World Confederation of Labour...
(ITUC) - Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - Nonaligned Movement (NAM)
- Nuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers Group is a multinational body concerned with reducing nuclear proliferation by controlling the export and re-transfer of materials that may be applicable to nuclear weapon development and by improving safeguards and protection on existing materials.- History :It was founded in...
(NSG) - Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Partnership for PeacePartnership for PeacePartnership for Peace is a North Atlantic Treaty Organisation program aimed at creating trust between NATO and other states in Europe and the former Soviet Union; 22 States are members...
(PFP) - Permanent Court of ArbitrationPermanent Court of ArbitrationThe Permanent Court of Arbitration , is an international organization based in The Hague in the Netherlands.-History:The court was established in 1899 as one of the acts of the first Hague Peace Conference, which makes it the oldest institution for international dispute resolution.The creation of...
(PCA) - United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations Industrial Development OrganizationUnited Nations Industrial Development OrganizationThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization , French/Spanish acronym ONUDI, is a specialized agency in the United Nations system, headquartered in Vienna, Austria...
(UNIDO) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Tourism OrganizationWorld Tourism OrganizationThe World Tourism Organization , based in Madrid, Spain, is a United Nations agency dealing with questions relating to tourism. It compiles the World Tourism rankings. The World Tourism Organization is a significant global body, concerned with the collection and collation of statistical information...
(UNWTO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO) (observer)
Law and order in Belarus
- Main article: Law of Belarus
- Capital punishment in BelarusCapital punishment in BelarusThe provision for Capital Punishment in Belarus has been a part of the country since gaining independence from the Soviet Union. The current national constitution prescribes this punishment for "grave crimes." Later laws have clarified the specific crimes for which capital punishment can be used...
- Constitution of BelarusConstitution of BelarusThe Constitution of the Republic of Belarus is the ultimate law of Belarus. Adopted in 1994, three years after the country declared its independence from the Soviet Union, this formal document establishes the framework of the Belarusian state and government and enumerates the rights and freedoms...
- Crime in Belarus
- Human rights in BelarusHuman rights in BelarusSince the election of the country's first president, Aleksandr Lukashenko in July 1994, Lukashenko has steadily consolidated his power through authoritarian means. Government restrictions on freedom of speech and the press, peaceful assembly, and religion remain in place...
- Censorship in BelarusCensorship in BelarusCensorship in Belarus, although prohibited by the country's constitution, is enforced by a number of laws. These include a law that makes insulting the president punishable by up to five years in prison, and another that makes criticizing Belarus abroad punishable by up to two years in prison.-...
- LGBT rights in Belarus
- Freedom of religion in BelarusFreedom of religion in BelarusThe Constitution provides for freedom of religion; however, the Government restricted this right in practice.Respect for religious freedom has recently worsened...
- Censorship in Belarus
- Law enforcement in BelarusLaw enforcement in BelarusAs well as the Militsiya, law enforcement in Belarus is also the responsibility of other agencies such as the Presidential Guard and the State Security Agency of the Republic of Belarus, all under the authority of the country's Ministry of Internal Affairs....
Military of Belarus
- Main article: Military of Belarus
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
:- Ministry of Defence of Belarus
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Belarus
- Navy of Belarus
- Air Force of Belarus
- Special forces of Belarus
- Military history of Belarus
- Military ranks of Belarus
History of Belarus
- Main article: History of BelarusHistory of BelarusThis article describes the history of Belarus. The Belarusian ethnos is traced at least as far in time as other East Slavs.After an initial period of independent feudal consolidation, Belarusian lands were incorporated into the Kingdom of Lithuania, Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and later in the...
, Timeline of the history of Belarus, and Current events of Belarus
- Economic history of Belarus
- Military history of Belarus
Culture of Belarus
- Main article: Culture of BelarusCulture of BelarusThe culture of Belarus is the product of a millennium of development under the impact of a number of diverse factors. These include the physical environment; the ethnographic background of Belarusians ; the paganism of the early settlers and their hosts; Byzantine Christianity as a link to the...
- Architecture of Belarus
- Cuisine of Belarus
- Ethnic minorities in Belarus
- Festivals in Belarus
- Humor in Belarus
- Languages of BelarusLanguages of BelarusBelarusian and Russian are the official languages according to the Constitution of Belarus . The constitution guarantees preservation of the cultural heritage of all ethnic minorities, including their languages ....
- Media in Belarus
- National symbols of BelarusNational symbols of BelarusUpon the independence of Belarus from the Soviet Union, the country resurrected national symbols that were used before the Soviet era. These included a flag of red and white stripes and a coat of arms consisting of a charging knight on horseback. These national symbols were replaced by Soviet-era...
- Coat of arms of Belarus
- Flag of BelarusFlag of BelarusThe current national flag of Belarus was formally adopted on June 7, 1995, following the result of a referendum voted on by the Belarusian people in the previous month. This new design replaced a historical flag used by the Belarusian People's Republic of 1918, before Belarus became a Soviet...
- National anthem of Belarus
- People of Belarus
- Prostitution in Belarus
- Public holidays in BelarusPublic holidays in BelarusNational holidays in Belarus are classified into state holidays and other holidays and commemorative days, including religious holidays. Nine of them are non-working days. Other holidays and commemorative days...
- Records of Belarus
- Religion in BelarusReligion in BelarusBefore 1917 Belarus had 2,466 religious communities, including 1,650 Orthodox, 127 Roman Catholic, 657 Jewish, 32 Protestant, and several Muslim communities. Under the communists , the activities of these communities were severely restricted...
- Buddhism in Belarus
- Christianity in BelarusChristianity in BelarusThe majority of the population of Belarus is Eastern Orthodox. The majority of Orthodox Christians in Belarus belong to the Belarusian Orthodox Church, which remains a unit of the Russian Orthodox Church. There is a Belarusian Autocephalous Orthodox Church which is not officially registered.There...
- Hinduism in BelarusHinduism in BelarusHinduism in Belarus has a very small following. There are three main Hindu groups in country. They are ISKCON, Brahmakumaris and The Light of Kailasa...
- Islam in BelarusIslam in BelarusIslam in Belarus has long history. It was introduced into the lands which now constitute Belarus by Lipka Tatars in the 14th -16th centuries. Today Muslim immigrants contribute to Islam in the country.-History:...
- Judaism in Belarus
- Sikhism in Belarus
- World Heritage Sites in Belarus
Art in Belarus
- Art in Belarus
- Cinema of Belarus
- Literature of Belarus
- Music of BelarusMusic of BelarusBelarus is an Eastern European country with a rich tradition of folk and religious music. The country's folk music traditions can be traced back to the times of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. In the 20th century, the Soviet control of the country somewhat limited musical development because...
- Television in BelarusTelevision in Belarus- Television channels :-See also:*Eastern Bloc information dissemination...
- Theatre in Belarus
Sports in Belarus
- Main article: Sports in Belarus
- Football in BelarusFootball in BelarusIn Belarus, a country that gained independence in 1991, football is the most popular sport, closely followed by ice hockey. The national association takes part in all competitions organized by FIFA and UEFA at senior and youth level, as well as in women’s football...
- Belarus at the OlympicsBelarus at the OlympicsAthletes from Belarus began their Olympic participation at the 1952 Summer Games in Helsinki, Finland as part of the Soviet Union . After the Soviet Union disbanded in 1991, Belarus, along with four of the other fourteen former Soviet republics, competed in the 1992 Winter Olympics as the Unified...
Economy and infrastructure of Belarus
- Main article: Economy of BelarusEconomy of BelarusRecently, the Belarusian economy has shifted into sustained high gear, along with Ukraine, Russia, and many other Commonwealth of Independent States economies. The economic boom provided by mineral wealth of Russia and other CIS nations and its key location as a transit route between the EU and...
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 69th (sixty-ninth)
- Agriculture in BelarusAgriculture in BelarusAgriculture in Belarus is a shrinking sector of the Belarusian economy. The share of agriculture in GDP declined from 11.6% in 2000 to 7.4% in 2007, while the share of agriculture in total employment dropped from 14.1% to 9.9% over the same period...
- Banking in BelarusBanking in BelarusThe banking system in Belarus is highly regulated and mostly state-owned. Banks are used as a tool of the government to support different programs. The National Bank of Bealrus, the country's Central bank, is the regulator of the system...
- National Bank of Belarus
- Communications in BelarusCommunications in BelarusThe Media and telecommunications in Belarus are dominated by the state which owns most of the corporations and infrastructure.-Telephone system:Telephone lines in use: 3.969 million Mobile/cellular: 9.686 million...
- Internet in Belarus
- Internet censorship in Belarus
- Internet in Belarus
- Companies of Belarus
- Currency of BelarusCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: RubleBelarusian rubleThe ruble is the currency of Belarus. The symbol for the ruble is Br and the ISO 4217 code is BYR.-First ruble, 1992–2000:The breakup of supply chain in the former Soviet enterprises demanded that goods be bought and sold on the market, often requiring cash settlement...
- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: BYRByrByr was formerly used in English-language geology and astronomy as a unit of one billion years. The "B" is an abbreviation for "billion" , with "yr" simply an abbreviation for "year". Today, the term gigaannum is also used, but Gy or Gyr are still sometimes used in English-language works...
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Belarus
- Energy in BelarusEnergy in BelarusEnergy in Belarus describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Belarus. Energy policy of Belarus will describe the politics of Belarus related to energy more in detail. Belarus is net energy importer. According to IEA the energy import exceeded the energy use in 2008...
- Energy policy of Belarus
- Oil industry in Belarus
- Health care in Belarus
- Mining in Belarus
- Belarus Stock Exchange
- Tourism in Belarus
- Transport in BelarusTransport in BelarusThis article is about transport in Belarus. For Soviet transportation, see Transport in the Soviet Union.- Railways :Rail transport in Belarus is operated by Belarusskaya Chyhunkatotal:5,512 kmcountry comparison to the world: 32...
- Airports in Belarus
- Rail transport in BelarusRail transport in BelarusRail transport in Belarus is owned by the national rail company BŽD / BČ . The railway network consists of 5,512 km, its gauge is 1,520 mm and 874 km are electrified.-History:...
- Roads in BelarusRoads in BelarusAutomobile roads in Belarus are classified into several categories.-State-owned common access roads:The state-owned roads of common access are managed by the Belavtodor department of the Ministry of Transport and Communications of Belarus...
- Water supply and sanitation in Belarus
Education in Belarus
- Main article: Education in BelarusEducation in BelarusEducation in Belarus is free at all levels except higher education. The government ministry that oversees the running of the school systems is the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Belarus. Each of the regions inside Belarus have oversight of the education systems, and students have the...
The 2 leading establishments in the national education system:
- Academy of Public Administration under the aegis of the President of the Republic of BelarusAcademy of Public Administration (Belarus)The Academy of Public Administration under the aegis of the President of the Republic of Belarus , Minsk, is the leading higher educational establishment in a national education system of the Republic of Belarus and head establishment of education in system of training, retraining and in-service...
- Belarusian State UniversityBelarusian State UniversityBelarusian State University , Minsk, Belarus, was founded on October 30, 1921. The BSU is a higher education establishment in the Republic of Belarus.-History:...
See also
- Index of Belarus-related articles
- List of Belarus-related topics
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Europe
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
External links
MediaGovernmental websites
- President's official site
- Government of Belarus
- Embassy of Belarus in the United States
- E-Government in Belarus
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs
Informational/cultural
- A Belarus Miscellany
- The Virtual Guide to Belarus
- Belarus Tourism and Travel Information
- The 1st Belarusian Art Gallery
- Contemporary Belarusian Art and Painting
- Media in Belarus
- The World Bank in Belarus
- The health resort of Belarus
- Photos of Belarus
City and country maps






