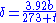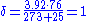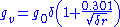Peek's law
Encyclopedia
In physics
, Peek's law is a description of the conditions necessary for corona discharge
between two wires:
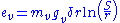
ev is the "visual critical corona voltage" or "corona inception voltage" (CIV), the voltage (in kilovolts) required to initiate a visible corona discharge between the wires.
mv is an irregularity factor to account for the condition of the wires. For smooth, polished wires, mv = 1. For roughened, dirty or weathered wires, 0.98 to 0.93, and for cable
s, 0.87 to 0.83.
r is the radius
of the wires
S is the distance between the wires
δ is the air density factor. It is calculated by the equation:
gv is the "visual critical" potential gradient
, and is calculated by the equation:
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, Peek's law is a description of the conditions necessary for corona discharge
Corona discharge
In electricity, a corona discharge is an electrical discharge brought on by the ionization of a fluid surrounding a conductor that is electrically energized...
between two wires:
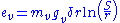
ev is the "visual critical corona voltage" or "corona inception voltage" (CIV), the voltage (in kilovolts) required to initiate a visible corona discharge between the wires.
mv is an irregularity factor to account for the condition of the wires. For smooth, polished wires, mv = 1. For roughened, dirty or weathered wires, 0.98 to 0.93, and for cable
Cable
A cable is two or more wires running side by side and bonded, twisted or braided together to form a single assembly. In mechanics cables, otherwise known as wire ropes, are used for lifting, hauling and towing or conveying force through tension. In electrical engineering cables are used to carry...
s, 0.87 to 0.83.
r is the radius
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
of the wires
S is the distance between the wires
δ is the air density factor. It is calculated by the equation:
-
- where
- b = pressure in centimeters of mercury
- t = temperature in degrees Celsius
- At SATPStandard conditions for temperature and pressureStandard condition for temperature and pressure are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data...
(25°C and 76 cmHg):
gv is the "visual critical" potential gradient
Potential gradient
A potential gradient is the local space rate of change of the potential with respect to displacement.In electrostatics then, it is the local space rate of change of the electric potential:Units are volts per meter...
, and is calculated by the equation:
-
- where g0 is the "disruptive critical" potential gradient, about 30 kV/cm for air