
Quorum (Distributed Systems)
Encyclopedia
A quorum is the minimum number of votes that a distributed transaction has to obtain in order to be allowed to perform an operation in a distributed system. A quorum-based technique is implemented to enforce consistent operation in a distributed system.
, as well as a commit method to ensure transaction
atomicity in the presence of network partitioning.
or abort
) at every site. In case of network partitioning, sites are partitioned and the partitions may not be able to communicate with each other. This is where a quorum-based technique comes in. The fundamental idea is that a transaction is executed if the majority of sites vote to execute it.
Every site in the system is assigned a vote Vi. Let us assume that the total number of votes in the system is V, and the abort and commit quorums are Va and Vc, respectively. Then the following rules must be obeyed in the implementation of the commit protocol:
The first rule ensures that a transaction cannot be committed and aborted at the same time. The next two rules indicate the votes that a transaction has to obtain before it can terminate one way or the other.
, no two transactions should be allowed to read or write a data item concurrently. In case of replicated databases, a quorum-based replica control protocol can be used to ensure that no two copies of a data item are read or written by two transactions concurrently.
The quorum-based voting for replica control is due to [Gifford, 1979]
. Each copy of a replicated data item is assigned a vote. Each operation then has to obtain a read quorum (Vr) or a write quorum (Vw) to read or write a data item, respectively. If a given data item has a total of V votes, the quorums have to obey the following rules:
The first rule ensures that a data item is not read and written by two transactions concurrently. The second rule ensures that two write operations from two transactions cannot occur concurrently on the same data item. The two rules ensure that one-copy serializability is maintained.
Quorum-based techniques in distributed database systems
Quorum-based voting can be used as a replica control method, as well as a commit method to ensure transaction
Database transaction
A transaction comprises a unit of work performed within a database management system against a database, and treated in a coherent and reliable way independent of other transactions...
atomicity in the presence of network partitioning.
Quorum-based voting in commit protocols
In a distributed database system, a transaction could be executing its operations at multiple sites. Since atomicity requires every distributed transaction to be atomic, the transaction must have the same fate (commitCommit (data management)
In the context of computer science and data management, commit refers to the idea of making a set of tentative changes permanent. A popular usage is at the end of a transaction. A commit is an act of committing.-Data management:...
or abort
Rollback (data management)
In database technologies, a rollback is an operation which returns the database to some previous state. Rollbacks are important for database integrity, because they mean that the database can be restored to a clean copy even after erroneous operations are performed...
) at every site. In case of network partitioning, sites are partitioned and the partitions may not be able to communicate with each other. This is where a quorum-based technique comes in. The fundamental idea is that a transaction is executed if the majority of sites vote to execute it.
Every site in the system is assigned a vote Vi. Let us assume that the total number of votes in the system is V, and the abort and commit quorums are Va and Vc, respectively. Then the following rules must be obeyed in the implementation of the commit protocol:
- Va + Vc > V, where 0
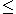 Va, Vc
Va, Vc 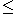 V.
V. - Before a transaction commits, it must obtain a commit quorum Vc.
- Before a transaction aborts, it must obtain an abort quorum Va.
The first rule ensures that a transaction cannot be committed and aborted at the same time. The next two rules indicate the votes that a transaction has to obtain before it can terminate one way or the other.
Quorum-based voting for replica control
In replicated databases, a data object has copies present at several sites. To ensure serializabilitySerializability
In concurrency control of databases, transaction processing , and various transactional applications , both centralized and distributed, a transaction schedule is serializable, has the serializability property, if its outcome In concurrency control of databases, transaction processing (transaction...
, no two transactions should be allowed to read or write a data item concurrently. In case of replicated databases, a quorum-based replica control protocol can be used to ensure that no two copies of a data item are read or written by two transactions concurrently.
The quorum-based voting for replica control is due to [Gifford, 1979]
. Each copy of a replicated data item is assigned a vote. Each operation then has to obtain a read quorum (Vr) or a write quorum (Vw) to read or write a data item, respectively. If a given data item has a total of V votes, the quorums have to obey the following rules:
- Vr + Vw > V
- Vw > V/2
The first rule ensures that a data item is not read and written by two transactions concurrently. The second rule ensures that two write operations from two transactions cannot occur concurrently on the same data item. The two rules ensure that one-copy serializability is maintained.
See also
- Database transactionDatabase transactionA transaction comprises a unit of work performed within a database management system against a database, and treated in a coherent and reliable way independent of other transactions...
- Replication (computer science)Replication (computer science)Replication is the process of sharing information so as to ensure consistency between redundant resources, such as software or hardware components, to improve reliability, fault-tolerance, or accessibility. It could be data replication if the same data is stored on multiple storage devices, or...
- Atomicity (database systems)

