
Roman numeral analysis
Encyclopedia
In music
, roman numeral analysis is the use of roman numeral symbols in the musical analysis
of chords
. In music theory
related to or derived from the common practice period
, arabic numerals with caret
s are used to designate scale degree
s themselves (), whereas in theory related to or derived from jazz
or modern popular music
uses numbers (1, 2, 3, etc...) to represent scale degrees (See also diatonic function
). In both theories, the roman numeral, number, or careted number, refers to a chord built upon that scale degree. For example, I,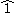 , or 1, all refer to the chord upon the first scale
, or 1, all refer to the chord upon the first scale
step.
Gottfried Weber
's Versuch einer geordneten Theorie der Tonsetzkunst (Theory of Musical Composition) (Mainz, B. Schott, 1817-21) introduced for the first time the analytical symbol by which a chord is identified by the Roman numeral of the scale-degree number of its root.
The current system used today to study and analyze tonal music comes about initially from the work and writings of Rameau’s fundamental bass. The dissemination of Rameau’s concepts could only have come about during the significant waning of the study of harmony for the purpose of the basso continuo and its implied improvisational properties in the later 18th century. The use of Roman numerals in describing fundamentals as “scale degrees in relation to a tonic” was brought about by John Trydell’s writing Two Essays in 1766. Alternatives include the functional hybrid Nashville number system
and macro analysis
.
, all triads are represented by upper case numerals, followed by a symbol to indicate if it is not a major chord (e.g. "-" for minor or "ø" for half-diminished):
E Major:
, are often denoted by Roman numerals, with higher numbers denoting lower strings. For example I signifies the E string on the violin and the A string on the viola
and cello
, these being the highest strings, respectively, on each instrument. They are also sometimes used to signify position. In this case, the number in Roman numerals corresponds with the position number. For example, III means third position and V means fifth.
Music
Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
, roman numeral analysis is the use of roman numeral symbols in the musical analysis
Musical analysis
Musical analysis is the attempt to answer the question how does this music work?. The method employed to answer this question, and indeed exactly what is meant by the question, differs from analyst to analyst, and according to the purpose of the analysis. According to Ian Bent , analysis is "an...
of chords
Chord (music)
A chord in music is any harmonic set of two–three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may for many practical and theoretical purposes be understood as chords...
. In music theory
Music theory
Music theory is the study of how music works. It examines the language and notation of music. It seeks to identify patterns and structures in composers' techniques across or within genres, styles, or historical periods...
related to or derived from the common practice period
Common practice period
The common practice period, in the history of Western art music , spanning the Baroque, Classical, and Romantic periods, lasted from c. 1600 to c. 1900.-General characteristics:...
, arabic numerals with caret
Caret
Caret usually refers to the spacing symbol ^ in ASCII and other character sets. In Unicode, however, the corresponding character is , whereas the Unicode character named caret is actually a similar but lowered symbol: ....
s are used to designate scale degree
Degree (music)
In music theory, a scale degree or scale step is the name of a particular note of a scale in relation to the tonic...
s themselves (), whereas in theory related to or derived from jazz
Jazz
Jazz is a musical style that originated at the beginning of the 20th century in African American communities in the Southern United States. It was born out of a mix of African and European music traditions. From its early development until the present, jazz has incorporated music from 19th and 20th...
or modern popular music
Popular music
Popular music belongs to any of a number of musical genres "having wide appeal" and is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. It stands in contrast to both art music and traditional music, which are typically disseminated academically or orally to smaller, local...
uses numbers (1, 2, 3, etc...) to represent scale degrees (See also diatonic function
Diatonic function
In tonal music theory, a diatonic function is the specific, recognized role of each of the 7 notes and their chords in relation to the diatonic key...
). In both theories, the roman numeral, number, or careted number, refers to a chord built upon that scale degree. For example, I,
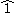 , or 1, all refer to the chord upon the first scale
, or 1, all refer to the chord upon the first scaleMusical scale
In music, a scale is a sequence of musical notes in ascending and descending order. Most commonly, especially in the context of the common practice period, the notes of a scale will belong to a single key, thus providing material for or being used to conveniently represent part or all of a musical...
step.
Gottfried Weber
Gottfried Weber
Jacob Gottfried Weber , was a prominent German writer on music , composer, and jurist....
's Versuch einer geordneten Theorie der Tonsetzkunst (Theory of Musical Composition) (Mainz, B. Schott, 1817-21) introduced for the first time the analytical symbol by which a chord is identified by the Roman numeral of the scale-degree number of its root.
Common practice numerals
| Roman numeral analysis symbols | ||
|---|---|---|
| Roman Numeral | Triad quality | Example (tonic) |
| Uppercase | Major triad Major chord In music theory, a major chord is a chord having a root, a major third, and a perfect fifth. When a chord has these three notes alone, it is called a major triad... |
I |
| Lowercase | Minor triad Minor chord In music theory, a minor chord is a chord having a root, a minor third, and a perfect fifth.When a chord has these three notes alone, it is called a minor triad.... |
i |
| Lowercase o | Diminished triad Diminished chord A diminished triad chord or diminished chord is a triad consisting of two minor thirds above the root — if built on C, a diminished chord would have a C, an E and a G. It resembles a minor triad with a lowered fifth.... |
io |
| Uppercase + | Augmented triad Augmented triad In music, an augmented triad is a triad, or chord, consisting of two major thirds . The term augmented triad arises from an augmented triad being a three note chord, or triad, whose top note is raised, or augmented... |
I+ |
The current system used today to study and analyze tonal music comes about initially from the work and writings of Rameau’s fundamental bass. The dissemination of Rameau’s concepts could only have come about during the significant waning of the study of harmony for the purpose of the basso continuo and its implied improvisational properties in the later 18th century. The use of Roman numerals in describing fundamentals as “scale degrees in relation to a tonic” was brought about by John Trydell’s writing Two Essays in 1766. Alternatives include the functional hybrid Nashville number system
Nashville number system
The Nashville Number System is an informal method of transcribing music by denoting the scale degree on which a chord is built. It was developed by Neal Matthews, Jr. in the late '50s as a simplified system for The Jordanaires to use in the studio and further developed by Charlie McCoy...
and macro analysis
Macro analysis
In music theory, macro analysis is a method of transcribing, or writing down chords that may be used along with or instead of conventional musical analysis...
.
Jazz and pop numerals
In music theory aimed towards jazz and popular musicJazz harmony
Jazz harmony is the theory and practice of how chords are used in jazz music. Jazz bears certain similarities to other practices in the tradition of Western harmony, such as many chord progressions, and the incorporation of the major and minor scales as a basis for chordal construction, but...
, all triads are represented by upper case numerals, followed by a symbol to indicate if it is not a major chord (e.g. "-" for minor or "ø" for half-diminished):
E Major:
- E maj7 becomes I maj7
- F# -7 becomes II -7
- G# -7 becomes III -7
- A maj7 becomes IV maj7
- B7 becomes V7
- C# -7 becomes VI -7
- D#ø7 becomes VIIø7
Major
| Traditional Notation | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii° |
| Alternate Notation | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII |
| Chord Symbol | I Maj | II min | III min | IV Maj | V Maj | VI min | VII dim |
| Scale degree (major mode) |
tonic Tonic (music) In music, the tonic is the first scale degree of the diatonic scale and the tonal center or final resolution tone. The triad formed on the tonic note, the tonic chord, is thus the most significant chord... |
supertonic Supertonic In music or music theory, the supertonic is the second degree or note of a diatonic scale, one step above the tonic. In music theory, the supertonic chord is symbolized by the Roman numeral ii in a major scale, indicating that the chord is a minor chord , or ii in a natural minor scale, indicating... |
mediant Mediant In music, the mediant is the third scale degree of the diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant. Similarly, the submediant is halfway between the tonic and subdominant... |
subdominant Subdominant In music, the subdominant is the technical name for the fourth tonal degree of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance "below" the tonic as the dominant is above the tonic - in other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdominant. It is also the note immediately... |
dominant Dominant (music) In music, the dominant is the fifth scale degree of the diatonic scale, called "dominant" because it is next in importance to the tonic,and a dominant chord is any chord built upon that pitch, using the notes of the same diatonic scale... |
submediant Submediant In music, the submediant is the sixth scale degree of the diatonic scale, the 'lower mediant' halfway between the tonic and the subdominant or 'lower dominant'... |
leading tone |
Minor
| Traditional Notation | i | ii° | III | iv | v | VI | VII | vii° |
| Alternate Notation | I | ii | iii | iv | v | vi | vii | |
| Chord Symbol | I min | II dim | III Maj | IV min | V min | VI Maj | VII Maj | VII dim |
| Scale degree (minor mode) |
tonic | supertonic | mediant | subdominant | dominant | submediant | subtonic Subtonic In music, the subtonic or flattened seventh is the lowered or minor seventh degree of the scale, a whole step below the tonic, as opposed to the leading tone... |
leading tone |
Performance practice
In performance practice, individual strings of stringed instruments, such as the violinViolin
The violin is a string instrument, usually with four strings tuned in perfect fifths. It is the smallest, highest-pitched member of the violin family of string instruments, which includes the viola and cello....
, are often denoted by Roman numerals, with higher numbers denoting lower strings. For example I signifies the E string on the violin and the A string on the viola
Viola
The viola is a bowed string instrument. It is the middle voice of the violin family, between the violin and the cello.- Form :The viola is similar in material and construction to the violin. A full-size viola's body is between and longer than the body of a full-size violin , with an average...
and cello
Cello
The cello is a bowed string instrument with four strings tuned in perfect fifths. It is a member of the violin family of musical instruments, which also includes the violin, viola, and double bass. Old forms of the instrument in the Baroque era are baryton and viol .A person who plays a cello is...
, these being the highest strings, respectively, on each instrument. They are also sometimes used to signify position. In this case, the number in Roman numerals corresponds with the position number. For example, III means third position and V means fifth.

