
Savart
Encyclopedia
The savart is a unit of measurement for musical interval
s . One savart is equal to one thousandth of a decade
. Today the savart has largely been replaced by the cent
and the millioctave
. Another name for the savart is the eptaméride.
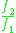 is the ratio of frequencies
is the ratio of frequencies
of a given interval, the corresponding measure in savarts is given by:
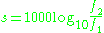
or
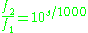
Like the more common cent, the savart is a logarithmic measure, and thus intervals can be added by simply adding their savart values, instead of multiplying them as you would frequencies. The number of savarts in an octave is 1000 times the base-10 logarithm of 2, or nearly 301.03. Sometimes this is rounded to 300, which makes the unit more useful for equal temperament
.
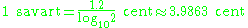

(1791–1841), but it was devised earlier by the French acoustician Joseph Sauveur
(1653–1716), who named it the eptaméride or heptaméride, as one seventh of a méride
, the earliest logarithmic interval measure. The name was changed to savart in the 20th century.
Interval (music)
In music theory, an interval is a combination of two notes, or the ratio between their frequencies. Two-note combinations are also called dyads...
s . One savart is equal to one thousandth of a decade
Decade (log scale)
One decade is a factor of 10 difference between two numbers measured on a logarithmic scale. It is especially useful when referring to frequencies and when describing frequency response of electronic systems, such as audio amplifiers and filters.-Calculations:The factor-of-ten in a decade can be...
. Today the savart has largely been replaced by the cent
Cent (music)
The cent is a logarithmic unit of measure used for musical intervals. Twelve-tone equal temperament divides the octave into 12 semitones of 100 cents each...
and the millioctave
Millioctave
The millioctave is a unit of measurement for musical intervals. As is expected from the prefix milli-, an octave is defined as 1000 millioctaves...
. Another name for the savart is the eptaméride.
Definition
If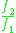 is the ratio of frequencies
is the ratio of frequenciesFrequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
of a given interval, the corresponding measure in savarts is given by:
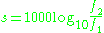
or
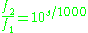
Like the more common cent, the savart is a logarithmic measure, and thus intervals can be added by simply adding their savart values, instead of multiplying them as you would frequencies. The number of savarts in an octave is 1000 times the base-10 logarithm of 2, or nearly 301.03. Sometimes this is rounded to 300, which makes the unit more useful for equal temperament
Equal temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament, or a system of tuning, in which every pair of adjacent notes has an identical frequency ratio. As pitch is perceived roughly as the logarithm of frequency, this means that the perceived "distance" from every note to its nearest neighbor is the same for...
.
Conversion
The conversion from savarts into cents or millioctaves is rather simple: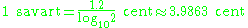

History
The savart is named after the French physicist and doctor Félix SavartFélix Savart
Félix Savart became a professor at Collège de France in 1836 and was the co-originator of the Biot-Savart Law, along with Jean-Baptiste Biot. Together, they worked on the theory of magnetism and electrical currents. Their law was developed about 1820. The Biot-Savart Law relates magnetic fields to...
(1791–1841), but it was devised earlier by the French acoustician Joseph Sauveur
Joseph Sauveur
Joseph Sauveur was a French mathematician and physicist. He was a professor of mathematics and in 1696 became a member of the French Academy of Sciences.-Life:Joseph Sauveur was the son of a provincial notary...
(1653–1716), who named it the eptaméride or heptaméride, as one seventh of a méride
Meride
Meride is a municipality in the district of Mendrisio in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland.-History:Meride is first mentioned in 852 as Melede. In 1430 it was mentioned as Merede....
, the earliest logarithmic interval measure. The name was changed to savart in the 20th century.

