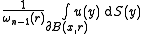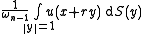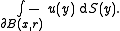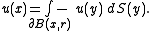Spherical mean
Encyclopedia
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, the spherical mean of a function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
around a point is the average of all values of that function on a sphere of given radius centered at that point.
Definition
Consider an open setOpen set
The concept of an open set is fundamental to many areas of mathematics, especially point-set topology and metric topology. Intuitively speaking, a set U is open if any point x in U can be "moved" a small amount in any direction and still be in the set U...
U in the Euclidean space
Euclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
Rn and a continuous function
Continuous function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function for which, intuitively, "small" changes in the input result in "small" changes in the output. Otherwise, a function is said to be "discontinuous". A continuous function with a continuous inverse function is called "bicontinuous".Continuity of...
u defined on U with real
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
or complex
Complex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
values. Let x be a point in U and r > 0 be such that the closed
Closed set
In geometry, topology, and related branches of mathematics, a closed set is a set whose complement is an open set. In a topological space, a closed set can be defined as a set which contains all its limit points...
ball
Ball (mathematics)
In mathematics, a ball is the space inside a sphere. It may be a closed ball or an open ball ....
B(x, r) of center x and radius r is contained in U. The spherical mean over the sphere of radius r centered at x is defined as
where ∂B(x, r) is the (n−1)-sphere forming the boundary
Boundary (topology)
In topology and mathematics in general, the boundary of a subset S of a topological space X is the set of points which can be approached both from S and from the outside of S. More precisely, it is the set of points in the closure of S, not belonging to the interior of S. An element of the boundary...
of B(x, r), dS denotes integration with respect to spherical measure
Spherical measure
In mathematics — specifically, in geometric measure theory — spherical measure σn is the “natural” Borel measure on the n-sphere Sn. Spherical measure is often normalized so that it is a probability measure on the sphere, i.e...
and ωn−1(r) is the "surface area" of this (n−1)-sphere.
Equivalently, the spherical mean is given by
where ωn−1 is the area of the (n−1)-sphere of radius 1.
The spherical mean is often denoted as
Properties and uses
- From the continuity of
 it follows that the function
it follows that the function
- is continuous, and its limitLimit of a functionIn mathematics, the limit of a function is a fundamental concept in calculus and analysis concerning the behavior of that function near a particular input....
as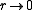 is
is 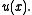
- Spherical means are used in finding the solution of the wave equationWave equationThe wave equation is an important second-order linear partial differential equation for the description of waves – as they occur in physics – such as sound waves, light waves and water waves. It arises in fields like acoustics, electromagnetics, and fluid dynamics...
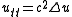 for
for 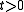 with prescribed boundary conditions at
with prescribed boundary conditions at 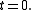
- If
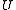 is an open set in
is an open set in 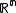 and
and  is a C2Smooth functionIn mathematical analysis, a differentiability class is a classification of functions according to the properties of their derivatives. Higher order differentiability classes correspond to the existence of more derivatives. Functions that have derivatives of all orders are called smooth.Most of...
is a C2Smooth functionIn mathematical analysis, a differentiability class is a classification of functions according to the properties of their derivatives. Higher order differentiability classes correspond to the existence of more derivatives. Functions that have derivatives of all orders are called smooth.Most of...
function defined on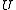 , then
, then  is harmonicHarmonic functionIn mathematics, mathematical physics and the theory of stochastic processes, a harmonic function is a twice continuously differentiable function f : U → R which satisfies Laplace's equation, i.e....
is harmonicHarmonic functionIn mathematics, mathematical physics and the theory of stochastic processes, a harmonic function is a twice continuously differentiable function f : U → R which satisfies Laplace's equation, i.e....
if and only if for all in
in 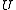 and all
and all 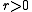 such that the closed ball
such that the closed ball 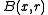 is contained in
is contained in 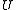 one has
one has
- This result can be used to prove the maximum principleMaximum principleIn mathematics, the maximum principle is a property of solutions to certain partial differential equations, of the elliptic and parabolic types. Roughly speaking, it says that the maximum of a function in a domain is to be found on the boundary of that domain...
for harmonic functions.