
Spin contamination
Encyclopedia
In computational chemistry
, spin contamination is the artificial mixing of different electron
ic spin
-states. This can occur when an approximate orbital-based wave function is represented in an unrestricted form – that is, when the spatial parts of α and β spin-orbitals are permitted to differ. Approximate wave functions with a high degree of spin contamination are undesirable. In particular, they are not eigenfunctions of the total spin-squared operator, Ŝ2, but can formally be expanded in terms of pure spin states of higher multiplicities
(the contaminants).
of spin-orbitals. For an open-shell system, the mean-field approach of Hartree–Fock theory gives rise to different equations for the α and β orbitals. Consequently there are two approaches that can be taken – either to force double occupation of the lowest orbitals by constraining the α and β spatial distributions to be the same (restricted open-shell Hartree–Fock, ROHF) or permit complete variational freedom (unrestricted Hartree–Fock UHF). In general, an N-electron Hartree–Fock wave function composed of Nα α-spin orbitals and Nβ β-spin orbitals can be written as
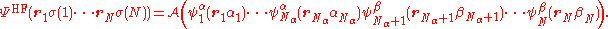
where is the antisymmetrization operator. This wave function is an eigenfunction of the total spin projection operator, Ŝz, with eigenvalue (Nα − Nβ)/2 (assuming Nα ≥ Nβ). For a ROHF wave function, the first 2Nβ spin-orbitals are forced to have the same spatial distribution:
is the antisymmetrization operator. This wave function is an eigenfunction of the total spin projection operator, Ŝz, with eigenvalue (Nα − Nβ)/2 (assuming Nα ≥ Nβ). For a ROHF wave function, the first 2Nβ spin-orbitals are forced to have the same spatial distribution:
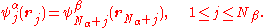
There is no such constraint in an UHF approach.
so it is desirable that any approximate wave function is an eigenfunction of Ŝ2. The eigenvalues of Ŝ2 are S(S + 1) where S can take the values 0 (singlet), 1/2 (doublet), 1 (triplet
), 3/2 (quartet), and so forth.
The ROHF wave function is an eigenfunction of Ŝ2: the expectation value Ŝ2 for a ROHF wave function is

However, the UHF wave function is not: the expectation value of Ŝ2 for an UHF wave function is

The sum of the last two terms is a measure of the extent of spin contamination in the unrestricted Hartree–Fock approach and is always non-negative – the wave function is usually contaminated to some extent by higher order spin eigenstates unless a ROHF approach is taken. Naturally, there is no contamination if all electrons are the same spin. Also, there
is often no contamination if the number of α and β electrons is the same. A small basis set could also constrain the
wavefunction sufficiently to prevent spin contamination.
Such contamination is a manifestation of the different treatment of α and β electrons that would otherwise occupy the same molecular orbital. It is also present in Møller–Plesset perturbation theory calculations that employ an unrestricted wave function as a reference state and, to a much lesser extent, in the unrestricted Kohn–Sham approach to density functional theory
using approximate exchange-correlation functionals.
. Given this, several approaches to remove or minimize spin contamination from UHF wave functions have been proposed.
The annihilated UHF (AUHF) approach involves the annihilation of first spin contaminant of the density matrix at each step in the self-consistent solution of the Hartree–Fock equations using a state-specific Löwdin annihilator. The resulting wave function, while not completely free of contamination, dramatically improves upon the UHF approach especially in the absence of high order contamination.
Projected UHF (PUHF) annihilates all spin contaminants from the self consistent UHF wave function. The projected energy is evaluated as the expectation of the projected wave function.
The spin-constrained UHF (SUHF) introduces a constraint in to the Hartree–Fock equations of the form λ(Ŝ2 − S(S + 1)), which as λ tends to infinity reproduces the ROHF solution.
All of these approach are readily applicable to unrestricted Møller–Plesset perturbation theory.
were Hartree-Fock orbitals, this is not necessarily correct.
Computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses principles of computer science to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses the results of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and solids...
, spin contamination is the artificial mixing of different electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
ic spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
-states. This can occur when an approximate orbital-based wave function is represented in an unrestricted form – that is, when the spatial parts of α and β spin-orbitals are permitted to differ. Approximate wave functions with a high degree of spin contamination are undesirable. In particular, they are not eigenfunctions of the total spin-squared operator, Ŝ2, but can formally be expanded in terms of pure spin states of higher multiplicities
Multiplicity (chemistry)
Multiplicity in quantum chemistry is used to distinguish between several degenerate wavefunctions that differ only in the orientation of their angular spin momenta. It is defined as 2S+1, where S is the angular spin momentum....
(the contaminants).
Open-shell wave functions
Within Hartree–Fock theory, the wave function is approximated as a Slater determinantSlater determinant
In quantum mechanics, a Slater determinant is an expression that describes the wavefunction of a multi-fermionic system that satisfies anti-symmetry requirements and consequently the Pauli exclusion principle by changing sign upon exchange of fermions . It is named for its discoverer, John C...
of spin-orbitals. For an open-shell system, the mean-field approach of Hartree–Fock theory gives rise to different equations for the α and β orbitals. Consequently there are two approaches that can be taken – either to force double occupation of the lowest orbitals by constraining the α and β spatial distributions to be the same (restricted open-shell Hartree–Fock, ROHF) or permit complete variational freedom (unrestricted Hartree–Fock UHF). In general, an N-electron Hartree–Fock wave function composed of Nα α-spin orbitals and Nβ β-spin orbitals can be written as
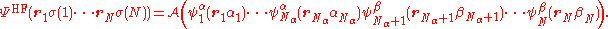
where
 is the antisymmetrization operator. This wave function is an eigenfunction of the total spin projection operator, Ŝz, with eigenvalue (Nα − Nβ)/2 (assuming Nα ≥ Nβ). For a ROHF wave function, the first 2Nβ spin-orbitals are forced to have the same spatial distribution:
is the antisymmetrization operator. This wave function is an eigenfunction of the total spin projection operator, Ŝz, with eigenvalue (Nα − Nβ)/2 (assuming Nα ≥ Nβ). For a ROHF wave function, the first 2Nβ spin-orbitals are forced to have the same spatial distribution: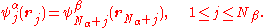
There is no such constraint in an UHF approach.
Contamination
The total spin-squared operator commutes with the nonrelativistic molecular HamiltonianMolecular Hamiltonian
In atomic, molecular, and optical physics as well as in quantum chemistry, molecular Hamiltonian is the name given to the Hamiltonian representing the energy of the electrons and nuclei in a molecule...
so it is desirable that any approximate wave function is an eigenfunction of Ŝ2. The eigenvalues of Ŝ2 are S(S + 1) where S can take the values 0 (singlet), 1/2 (doublet), 1 (triplet
Triplet state
A spin triplet is a set of three quantum states of a system, each with total spin S = 1 . The system could consist of a single elementary massive spin 1 particle such as a W or Z boson, or be some multiparticle state with total spin angular momentum of one.In physics, spin is the angular momentum...
), 3/2 (quartet), and so forth.
The ROHF wave function is an eigenfunction of Ŝ2: the expectation value Ŝ2 for a ROHF wave function is

However, the UHF wave function is not: the expectation value of Ŝ2 for an UHF wave function is

The sum of the last two terms is a measure of the extent of spin contamination in the unrestricted Hartree–Fock approach and is always non-negative – the wave function is usually contaminated to some extent by higher order spin eigenstates unless a ROHF approach is taken. Naturally, there is no contamination if all electrons are the same spin. Also, there
is often no contamination if the number of α and β electrons is the same. A small basis set could also constrain the
wavefunction sufficiently to prevent spin contamination.
Such contamination is a manifestation of the different treatment of α and β electrons that would otherwise occupy the same molecular orbital. It is also present in Møller–Plesset perturbation theory calculations that employ an unrestricted wave function as a reference state and, to a much lesser extent, in the unrestricted Kohn–Sham approach to density functional theory
Density functional theory
Density functional theory is a quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics and chemistry to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. With this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by...
using approximate exchange-correlation functionals.
Elimination
Although the ROHF approach does not suffer from spin contamination, it is far less commonly available in quantum chemistry computer programsQuantum chemistry computer programs
Quantum chemistry computer programs are used in computational chemistry to implement the methods of quantum chemistry. Most include the Hartree–Fock and some post-Hartree–Fock methods. They may also include density functional theory , molecular mechanics or semi-empirical quantum...
. Given this, several approaches to remove or minimize spin contamination from UHF wave functions have been proposed.
The annihilated UHF (AUHF) approach involves the annihilation of first spin contaminant of the density matrix at each step in the self-consistent solution of the Hartree–Fock equations using a state-specific Löwdin annihilator. The resulting wave function, while not completely free of contamination, dramatically improves upon the UHF approach especially in the absence of high order contamination.
Projected UHF (PUHF) annihilates all spin contaminants from the self consistent UHF wave function. The projected energy is evaluated as the expectation of the projected wave function.
The spin-constrained UHF (SUHF) introduces a constraint in to the Hartree–Fock equations of the form λ(Ŝ2 − S(S + 1)), which as λ tends to infinity reproduces the ROHF solution.
All of these approach are readily applicable to unrestricted Møller–Plesset perturbation theory.
Density Functional Theory (DFT)
Although many DFT codes simply calculate spin-contamination using the Kohn-Sham orbitals as if theywere Hartree-Fock orbitals, this is not necessarily correct.

