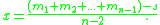Thymaridas
Encyclopedia
Thymaridas of Paros was an ancient Greek
mathematician and Pythagorean
noted for his work on prime numbers and simultaneous linear equations.
in order to help Thymaridas with the money that was collected for him.
Iamblichus states that Thymaridas called prime number
s "rectilinear" since they can only be represented on a one-dimensional line. Non-prime numbers, on the other hand, can be represented on a two-dimensional plane as a rectangle with sides that, when multiplied, produce the non-prime number in question. He further called the number one a "limiting quantity", or as we might say a "limit of fewness".
Iamblichus in Introductio arithmetica tells us that Thymaridas also worked with simultaneous linear equations. In particular, he created the then famous rule that was known as the "bloom of Thymaridas" or as the "flower of Thymaridas", which states that:
or using modern notation, the solution of the following system of n linear equations in n unknowns,
is given by
Iamblichus goes on to describe how some systems of linear equations that are not in this form can be placed into this form.
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
mathematician and Pythagorean
Pythagoreanism
Pythagoreanism was the system of esoteric and metaphysical beliefs held by Pythagoras and his followers, the Pythagoreans, who were considerably influenced by mathematics. Pythagoreanism originated in the 5th century BCE and greatly influenced Platonism...
noted for his work on prime numbers and simultaneous linear equations.
Life and work
Although little is known about the life of Thymaridas, it is believed that he was a rich man who fell into poverty. It is said that Thestor of Poseidonia traveled to ParosParos
Paros is an island of Greece in the central Aegean Sea. One of the Cyclades island group, it lies to the west of Naxos, from which it is separated by a channel about wide. It lies approximately south-east of Piraeus. The Municipality of Paros includes numerous uninhabited offshore islets...
in order to help Thymaridas with the money that was collected for him.
Iamblichus states that Thymaridas called prime number
Prime number
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. A natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number is called a composite number. For example 5 is prime, as only 1 and 5 divide it, whereas 6 is composite, since it has the divisors 2...
s "rectilinear" since they can only be represented on a one-dimensional line. Non-prime numbers, on the other hand, can be represented on a two-dimensional plane as a rectangle with sides that, when multiplied, produce the non-prime number in question. He further called the number one a "limiting quantity", or as we might say a "limit of fewness".
Iamblichus in Introductio arithmetica tells us that Thymaridas also worked with simultaneous linear equations. In particular, he created the then famous rule that was known as the "bloom of Thymaridas" or as the "flower of Thymaridas", which states that:
If the sum of n quantities be given, and also the sum of every pair containing a particular quantity, then this particular quantity is equal to 1/(n + 2) of the difference between the sums of these pairs and the first given sum.
or using modern notation, the solution of the following system of n linear equations in n unknowns,
x + x1 + x2 + … + xn−1 = s
x + x1 = m1
x + x2 = m2
.
.
.
x + xn−1 = mn−1
is given by
Iamblichus goes on to describe how some systems of linear equations that are not in this form can be placed into this form.