
Victoria class battleship
Encyclopedia
The Royal Navy
's Victoria class (or Sans Pareil class) battleships of the 1880s was the first class which used triple expansion steam engines, previous battleships having used compound engines.
There were only two ships in this class. The lead ship
, , was sunk in an accidental collision with another Royal Navy battleship in the Mediterranean with the loss of half of her crew. Her sister, survived until scrapped in April 1907.
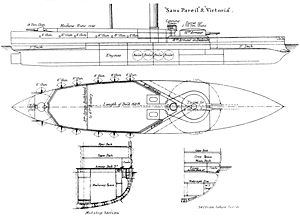 This class was intended to be an improved version of , and it was originally called the new Conquerors.
This class was intended to be an improved version of , and it was originally called the new Conquerors.
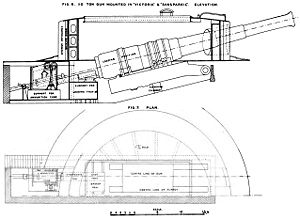 The original intention had been to fit 13.5 inch (343 mm), 67-ton guns in place of the Conquerors 12 inch (305 mm) guns in the single forward turret but late during the design it was decided to enlarge them to take the 16.25 inch (413 mm), 110-ton gun. Similar guns had been supplied by the manufacturer, Sir W. G. Armstrong, Whitworth & Co., Ltd., to the Italian
The original intention had been to fit 13.5 inch (343 mm), 67-ton guns in place of the Conquerors 12 inch (305 mm) guns in the single forward turret but late during the design it was decided to enlarge them to take the 16.25 inch (413 mm), 110-ton gun. Similar guns had been supplied by the manufacturer, Sir W. G. Armstrong, Whitworth & Co., Ltd., to the Italian
Regia Marina
and fitted in the Andrea Doria
and the 1,800 pound (816 kg) projectile could penetrate any thickness of armour afloat at that time. At a period when naval supremacy of the Mediterranean was seen as a crucial part of British policy, the Victoria class was intended for service as part of the British Mediterranean Fleet. The same model of gun had been fitted in the last Admiral class battleship
, which had a single example in each of its two barbettes instead of pairs of 13.5 inch (343 mm) guns and was the only other British warship to carry them.
The gun was not successful in service since it took four or five minutes to load and fire. The barrel only had a 75-round life and the muzzle tended to droop.
The rear turret contained a smaller 10 inch (254 mm) gun of similar design, and which weighed 26 tons.
gunboat
. The principal benefit was the improved efficiency of the engine meant a reduced displacement because less coal was needed; for example, trials with which had been re-engined with triple-expansion engines in 1889–1891 had shown that the coal consumption at 80% power was roughly halved.
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
's Victoria class (or Sans Pareil class) battleships of the 1880s was the first class which used triple expansion steam engines, previous battleships having used compound engines.
There were only two ships in this class. The lead ship
Lead ship
The lead ship or class leader is the first of a series or class of ships all constructed according to the same general design. The term is applicable military ships and larger civilian craft.-Overview:...
, , was sunk in an accidental collision with another Royal Navy battleship in the Mediterranean with the loss of half of her crew. Her sister, survived until scrapped in April 1907.
Design

Armament

Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
Regia Marina
Regia Marina
The Regia Marina dates from the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy in 1861 after Italian unification...
and fitted in the Andrea Doria
Italian battleship Andrea Doria (1885)
The Andrea Doria was an Italian battleship, the first named after Andrea Doria, launched in 1885. She was the third and final ship of the Ruggiero di Lauria-class pre-dreadnoughts, and served in the Regia Marina during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.-Design:The Ruggiero di Lauria class was...
and the 1,800 pound (816 kg) projectile could penetrate any thickness of armour afloat at that time. At a period when naval supremacy of the Mediterranean was seen as a crucial part of British policy, the Victoria class was intended for service as part of the British Mediterranean Fleet. The same model of gun had been fitted in the last Admiral class battleship
Admiral class battleship
The British Royal Navy's pre-dreadnought Admiral class battleships of the 1880s followed the pattern of the Devastation class in having the main armament on centre-line mounts with the superstructure in between. This pattern was followed by most following British designs until in 1906...
, which had a single example in each of its two barbettes instead of pairs of 13.5 inch (343 mm) guns and was the only other British warship to carry them.
The gun was not successful in service since it took four or five minutes to load and fire. The barrel only had a 75-round life and the muzzle tended to droop.
The rear turret contained a smaller 10 inch (254 mm) gun of similar design, and which weighed 26 tons.
Seakeeping
This class was one of the last of this period to have very low freeboard, of around 10 feet (3 m). This was done to reduce target area in a naval engagement but had a deleterious effect upon seaworthiness, and was an important factor in Victoria sinking within fifteen minutes following a collision since it allowed the water to quickly reach the gun turret ports.Propulsion
The most successful innovation of the class was the introduction of triple expansion steam engines into Royal Navy battleships. These engines had been developed as a result of the introduction of steel in boiler manufacture, which in turn had led to higher steam pressures. The Royal Navy had originally tried them with great success in the torpedoTorpedo
The modern torpedo is a self-propelled missile weapon with an explosive warhead, launched above or below the water surface, propelled underwater towards a target, and designed to detonate either on contact with it or in proximity to it.The term torpedo was originally employed for...
gunboat
Gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies.-History:...
. The principal benefit was the improved efficiency of the engine meant a reduced displacement because less coal was needed; for example, trials with which had been re-engined with triple-expansion engines in 1889–1891 had shown that the coal consumption at 80% power was roughly halved.

