Administrative divisions of the Peoples' Republic of Romania
Encyclopedia
Communist Romania
Communist Romania was the period in Romanian history when that country was a Soviet-aligned communist state in the Eastern Bloc, with the dominant role of Romanian Communist Party enshrined in its successive constitutions...
(later Socialist Republic of Romania
Communist Romania
Communist Romania was the period in Romanian history when that country was a Soviet-aligned communist state in the Eastern Bloc, with the dominant role of Romanian Communist Party enshrined in its successive constitutions...
), between 1950 and 1968.
History
The administrative reorganisation was followed by a new territorial division of RomaniaRomania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
. Preparations began in January 1949, with the opportunity of discussing the law about the so-called (People's Councils), when the leaders of the PMR
Romanian Communist Party
The Romanian Communist Party was a communist political party in Romania. Successor to the Bolshevik wing of the Socialist Party of Romania, it gave ideological endorsement to communist revolution and the disestablishment of Greater Romania. The PCR was a minor and illegal grouping for much of the...
decided to call on the help of the Soviet counselors for the raion
Raion
A raion is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet countries. The term, which is from French rayon 'honeycomb, department,' describes both a type of a subnational entity and a division of a city, and is commonly translated in English as "district"...
ation of the territory of RPR. Until then, Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
had been divided into judeţ
Judet
A județ is an administrative division in Romania, and was also used for some time in Moldova, before that country switched to raions.Județ translates into English as jurisdiction, but is commonly mistranslated as county .The territory of Romania is divided for administrative purposes into 41...
e (counties), organised into plăşi
Plasa
The Professional Lighting And Sound Association or PLASA is a UK-based trade organisation representing over 500 members worldwide.In addition to providing members with expert advice on a wide range of business and technical issues, PLASA also monitors legislative developments, alerting members to...
and rural and urban (communes). The county, as a local administration form, has its origins in the medieval
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
divisions of Wallachia
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians...
. After the formation of modern-day Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
, the name extended over Moldavia
Moldavia
Moldavia is a geographic and historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester river...
also (1859), following Dobrudja (1878) and Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
(1923). In the period of King Carol's
Carol II of Romania
Carol II reigned as King of Romania from 8 June 1930 until 6 September 1940. Eldest son of Ferdinand, King of Romania, and his wife, Queen Marie, a daughter of Prince Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh, the second eldest son of Queen Victoria...
dictatorship (1938–1940), the counties were abolished by forming 10 ţinuturi (lands).
The chiaburi (the Romanian equivalent of kulaks) were the direct "target" of the administrative reforms. Discussions regarding the raion
Raion
A raion is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet countries. The term, which is from French rayon 'honeycomb, department,' describes both a type of a subnational entity and a division of a city, and is commonly translated in English as "district"...
ation were retaken at the Plenara CC (the Session of the Central Committee of the Communist Party) between 15 and 17 May 1950, in the context of preparing the elections for the People's Councils. Some members of the CC were of the opinion that the division into counties should be maintained, because Romania didn't have the territory of the USSR
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
to be divided into regions. But Miron Constantinescu
Miron Constantinescu
Miron Constantinescu was a Romanian communist politician, a leading member of the Romanian Communist Party , as well as a Marxist sociologist, historian, academic, and journalist...
sustained that: "the term of raionation is the correct one, because it underlines the characteristic of this reorganisation and the expression used in Stalin's quote is raionation". Also, he presented the Report regarding the raionation to the Session, where he underlined the fact that "all of the content of the criteria proposed here is drawn up after the study of the Soviet material, on the basis of the Soviet teachings and on the basis of the concrete support that the Soviet counselors gave to us, to whom we thank for their help." At the end of July a central commission of the Communist Party (including Soviet counselors) was established to prepare the raionation of the territory.
The raionation Law was published on September 6, radically changing the administrative division of Romania. Instead of the 58 counties, 424 plăşi and 6,276 communes, the territory of the RPR was divided into 28 regions, 177 raion
Raion
A raion is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet countries. The term, which is from French rayon 'honeycomb, department,' describes both a type of a subnational entity and a division of a city, and is commonly translated in English as "district"...
s, 148 cities and towns and 4,052 communes. The process of raionation once finished, the governors organised the elections for the People's Councils on December 3, 1950.
Timeline
- September 6, 1950 - By Law nr. 5 the 58 counties (including the 424 plăşi and 6,276 rural and urban communes) were abolished, being replaced by 28 regions (composed of 177 raions, 148 cities and towns and 4,052 communes)
- September 19, 1952 - Decree nr.331. By merging, the number of regions was reduced to 18: Arad, Bacău, Baia Mare, Bârlad, Bucureşti, Cluj, Constanţa, Craiova, Galaţi, Hunedoara, Iaşi, Oradea, Piteşti, Ploieşti, Stalin, Suceava, Timişoara and, for the first time after the Great UnionUnion of Transylvania with RomaniaUnion of Transylvania with Romania was declared on by the assembly of the delegates of ethnic Romanians held in Alba Iulia.The national holiday of Romania, the Great Union Day occurring on December 1, commemorates this event...
, an administrative entity created on ethnic criteria, Regiunea Autonomă Maghiară (The Magyar Autonomous Region); - 1956 - An intermediary step through which the regions Arad and Bârlad were abolished
- 1960 - The final step, with territory redistribution and region renamings. The Magyar administrative entity was renamed Regiunea Mureş-Autonomă Maghiară (Mureş Region - Magyar Autonomous), also modifying its territory. In the end, the number of region was reduced to 16
- February 1968 - By the law adopted by Marea Adunare Naţională (The Great National AssemblyGreat National AssemblyThe Great National Assembly was the legislature of the Romanian People's Republic and the Socialist Republic Romania. When Communism was overthrown in Romania in December 1989, the National Assembly was replaced by a bicameral parliament, made up of the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate.The Great...
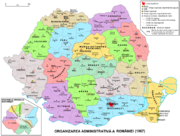
) the old county administrative and territorial division came into act. On January 14, 1968 a project-map was published and was discussed within the organisations of the Communist Party, subsequently undergoing some changes. The final result, substantially different from the original territorial organisation prior to 1950, comprised 39 countiesAdministrative divisions of RomaniaRomania's administration is relatively centralised and administrative subdivisions are therefore fairly simplified.According to the Constitution of Romania, its territory is organized administratively into communes, towns and counties:...
, the BucharestBucharestBucharest is the capital municipality, cultural, industrial, and financial centre of Romania. It is the largest city in Romania, located in the southeast of the country, at , and lies on the banks of the Dâmbovița River....
municipality, 236 cities and towns, of which 47 municipalities and 2,706 communes having 13,149 villages.
Regions of 1950
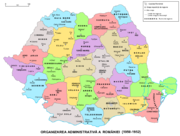
- Regiunea AradRegiunea AradRegiunea Arad was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation...
(Ar.) - Regiunea ArgeşRegiunea ArgesRegiunea Argeş was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation. It existed until 1952, when its territory merged with Vâlcea region to form Piteşti region...
(Ptş.) - Regiunea BacăuRegiunea BacauRegiunea Bacău was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(Bc.) - Regiunea Baia MareRegiunea Baia MareRegiunea Baia Mare was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(B.Mr.) - Regiunea BârladRegiunea BârladRegiunea Bârlad was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(Bd.) - Regiunea BihorRegiunea BihorRegiunea Bihor was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(Ord.) - Regiunea BotoşaniRegiunea BotosaniBotoşani Region was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation. It existed until 1952 when it was merged into Suceava region.-History:The capital of the region was Botoşani, and its territory...
(Bt.) - Regiunea BucureştiRegiunea BucurestiRegiunea Bucureşti was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation..-History:...
(R.B.) - Regiunea BuzăuRegiunea BuzauRegiunea Buzău was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(Bz.) - Regiunea ClujRegiunea ClujRegiunea Cluj was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, set after the soviet style.-History:...
(Clj.) - Regiunea ConstanţaRegiunea ConstantaRegiunea Constanţa was one of the 1950 new administrative Soviet-style divisions of the People's Republic of Romania.-History:...
(Cţa.) - Regiunea DoljRegiunea DoljRegiunea Dolj was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(Cv.) - Regiunea Galaţi (Gl.)
- Regiunea Gorj (Tg.J.)
- Regiunea Hunedoara (Dv.)
- Regiunea Ialomiţa (Cl.)
- Regiunea Iaşi (Iş.)
- Regiunea Mureş (Tg.M.)
- Regiunea Prahova (Pl.)
- Regiunea Putna (Fş.)
- Regiunea Rodna (Btr.)
- Regiunea Satu Mare (St.M.)
- Regiunea Severin (Lgş.)
- Regiunea Sibiu (Sb.)
- Regiunea Stalin (O.S.)
- Regiunea Suceava (Sv.)
- Regiunea Teleorman (R.Vd.)
- Regiunea Timişoara (Tmş.)
- Regiunea Vâlcea (Rm.V.)
Regions of 1952
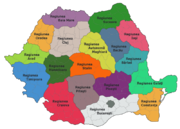
- Regiunea AradRegiunea AradRegiunea Arad was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation...
(Ar.) - Regiunea BacăuRegiunea BacauRegiunea Bacău was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(Bc.) - Regiunea Baia MareRegiunea Baia MareRegiunea Baia Mare was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(B.Mr.) - Regiunea BârladRegiunea BârladRegiunea Bârlad was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(Bd.) - Regiunea BucureştiRegiunea BucurestiRegiunea Bucureşti was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation..-History:...
(R.B.) (BucharestBucharestBucharest is the capital municipality, cultural, industrial, and financial centre of Romania. It is the largest city in Romania, located in the southeast of the country, at , and lies on the banks of the Dâmbovița River....
City - B.) - Regiunea ClujRegiunea ClujRegiunea Cluj was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, set after the soviet style.-History:...
(Clj.) - Regiunea ConstanţaRegiunea ConstantaRegiunea Constanţa was one of the 1950 new administrative Soviet-style divisions of the People's Republic of Romania.-History:...
(Cţa.) - Regiunea Craiova (Cv.)
- Regiunea Galaţi (Gl.)
- Regiunea Hunedoara (Dv.)
- Regiunea Iaşi (Iş.)
- Regiunea Autonomă Maghiară (Magyar Autonomous Region) (Tg.M.)
- Regiunea OradeaRegiunea BihorRegiunea Bihor was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(Ord.) - Regiunea PiteştiRegiunea ArgesRegiunea Argeş was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation. It existed until 1952, when its territory merged with Vâlcea region to form Piteşti region...
(Ptş.) - Regiunea Ploieşti (Pl.)
- Regiunea Stalin (O.S.)
- Regiunea Suceava (Sv.)
- Regiunea Timişoara (Tmş.)
Regions of 1956
1956 - An intermediary step through which there were abolished the regions Arad and Bârlad.- Regiunea ArgeşRegiunea ArgesRegiunea Argeş was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation. It existed until 1952, when its territory merged with Vâlcea region to form Piteşti region...
(AG) - Regiunea BacăuRegiunea BacauRegiunea Bacău was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(BC) - Regiunea Baia MareRegiunea Baia MareRegiunea Baia Mare was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(BM) - Regiunea BucureştiRegiunea BucurestiRegiunea Bucureşti was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation..-History:...
(B, Bucharest City - OB) - Regiunea ClujRegiunea ClujRegiunea Cluj was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, set after the soviet style.-History:...
(CJ) - Regiunea ConstanţaRegiunea ConstantaRegiunea Constanţa was one of the 1950 new administrative Soviet-style divisions of the People's Republic of Romania.-History:...
(CT) - Regiunea Craiova (CR)
- Regiunea Galaţi (GL)
- Regiunea Hunedoara (HD)
- Regiunea Iaşi (IS)
- Regiunea Autonomă Maghiară (Magyar Autonomous Region) (RAM, AM)
- Regiunea OradeaRegiunea BihorRegiunea Bihor was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(OR) - Regiunea Ploieşti (PL)
- Regiunea Stalin (ST, Braşov City/Oraşul Stalin - OS)
- Regiunea Suceava (SV)
- Regiunea Timişoara (TM)
Regions of 1960
- Regiunea ArgeşRegiunea ArgesRegiunea Argeş was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation. It existed until 1952, when its territory merged with Vâlcea region to form Piteşti region...
(AG) - Regiunea BacăuRegiunea BacauRegiunea Bacău was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(BC) - Regiunea Braşov (BV)
- Regiunea BucureştiRegiunea BucurestiRegiunea Bucureşti was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation..-History:...
(B, including Bucharest City) - Regiunea ClujRegiunea ClujRegiunea Cluj was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, set after the soviet style.-History:...
(CJ) - Regiunea CrişanaRegiunea BihorRegiunea Bihor was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(CR) - Regiunea DobrogeaRegiunea ConstantaRegiunea Constanţa was one of the 1950 new administrative Soviet-style divisions of the People's Republic of Romania.-History:...
(DB) - Regiunea Galaţi (GL)
- Regiunea Hunedoara (HD)
- Regiunea Iaşi (IS)
- Regiunea MaramureşRegiunea Baia MareRegiunea Baia Mare was one of the newly established administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Romania, copied after the Soviet style of territorial organisation.-History:...
(MR) - Regiunea Mureş-Autonomă Maghiară (Mureş Region-Magyar Autonomous) (MS)
- Regiunea Oltenia (OL)
- Regiunea Ploieşti (PL)
- Regiunea Suceava (SV)
- Regiunea Banat (BT)

