
Algorithmic version for Szemerédi regularity partition
Encyclopedia
A Simple Algorithm for Constructing Szemerédi's Regularity Partition is a paper by Alan M. Frieze
and Ravi Kannan giving an algorithm
ic version of the Szemerédi regularity lemma
to find an ε-regular partition of a given graph.
where E(X,Y) denotes the set of edges having one end vertex in X and one in Y. For ε>0, a pair of vertex sets X and Y is called ε-regular, if for all subsets A⊆X and B⊆Y satisfying |A| ≥ε |X| and |B| ≥ ε |Y|, we have |d(X,Y)-d(A,B)| ≤ ε.
A partition of the vertex set of G into k sets, V1,...,Vk, is called an equitable partition if for all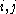 , ||Vi|-|Vj||≤1. An equitable partition is an
, ||Vi|-|Vj||≤1. An equitable partition is an  -regular partition, if for all but at most
-regular partition, if for all but at most 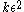 pairs (i,j) the pair
pairs (i,j) the pair 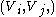 is
is  -regular.
-regular.
Now we are ready to state the regularity lemma.
Regularity lemma. For every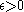 and positive integer
and positive integer 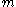 there exist integers
there exist integers 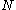 and
and 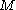 such that if
such that if 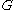 is a graph with at least
is a graph with at least 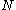 vertices, there exists an integer
vertices, there exists an integer 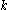 in the range
in the range 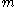 ≤
≤ 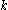 ≤
≤ 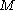 and an
and an  -regular partition of the vertex set of
-regular partition of the vertex set of 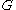 into
into 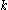 sets.
sets.
It is a common variant in the definition of an -regular partition to require that the vertex sets all have the same size, while collecting the leftover vertices in an "error"-set
-regular partition to require that the vertex sets all have the same size, while collecting the leftover vertices in an "error"-set 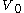 whose size is at most an
whose size is at most an  -fraction of the size of the vertex set of
-fraction of the size of the vertex set of 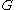 .
.
Szemerédi's regularity lemma is one of the most powerful tools of extremal graph theory. It says that, in some sense,
all graphs can be approximated by random-looking graphs. Therefore the lemma helps in proving theorems for arbitrary graphs whenever the corresponding result is easy for random graphs. The first constructive version was provided by Alon, Duke, Leffman, Rödl
and Yuster . Subsequently Frieze and Kannan gave a different version and extended it to hypergraphs . The paper
is a nice survey on regularity lemma and its various applications. Here we will briefly describe a different construction due to Alan Frieze and Ravi Kannan that uses singular values of matrices.
Lemma 1:
Fix k and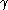 and let
and let 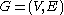 be a graph with
be a graph with  vertices. Let
vertices. Let 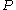 be an equitable partition of
be an equitable partition of 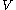 in classes
in classes 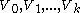 . Assume
. Assume 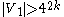 and
and 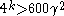 . Given proofs that more than
. Given proofs that more than 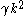 pairs
pairs 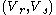 are not
are not 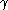 -regular, it is possible to find in O(n) time an equitable partition
-regular, it is possible to find in O(n) time an equitable partition 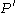 (which is a refinement of
(which is a refinement of 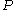 ) into
) into 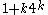 classes, with an exceptional class of cardinality at most
classes, with an exceptional class of cardinality at most 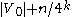 and such that
and such that 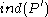 ≥
≥ 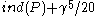
Lemma 2:
Let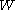 be a
be a 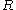 ×
×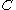 matrix with
matrix with 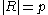 ,
, 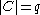 and
and 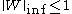 and
and 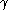 be a positive real.
be a positive real.
(a) If there exist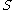 ⊆
⊆ 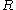 ,
, 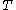 ⊆
⊆ 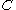 such that
such that  ≥
≥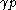 ,
, 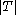 ≥
≥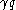 and
and 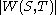 ≥
≥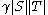 then
then 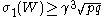
(b) If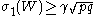 , then there exist
, then there exist 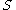 ⊆
⊆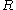 ,
,  ⊆
⊆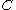 such that
such that  ≥
≥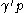 ,
, 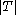 ≥
≥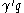 and
and 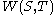 ≥
≥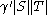 where
where 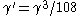 . Furthermore
. Furthermore 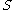 ,
, 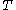 can be constructed in polynomial time.
can be constructed in polynomial time.
These two lemmas are combined in the following algorithmic construction of the Szemerédi regularity lemma
.
[Step 1] Arbitrarily divide the vertices of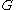 into an equitable partition
into an equitable partition 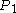 with classes
with classes 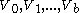 where
where 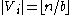 and hence
and hence 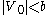 . denote
. denote 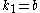 .
.
[Step 2] For every pair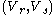 of
of 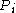 , compute
, compute 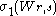 . If the pair
. If the pair 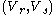 are not
are not 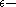 regular then by Lemma 2 we obtain a proof that they are not
regular then by Lemma 2 we obtain a proof that they are not 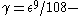 regular.
regular.
[Step 3] If there are at most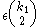 pairs that produce proofs of non
pairs that produce proofs of non 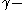 regularity that halt.
regularity that halt. 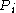 is
is 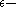 regular.
regular.
[Step 4] Apply Lemma 1 where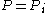 ,
, 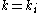 ,
, 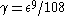 and obtain
and obtain 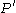 with
with 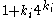 classes
classes
[Step 5] Let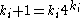 ,
, 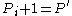 ,
, 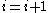 and go to Step 2.
and go to Step 2.
The algorithm will terminate with an -regular partition in
-regular partition in 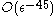 steps since the improvement at each step is
steps since the improvement at each step is 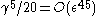 .
.
Alan M. Frieze
Alan M. Frieze is a professor in the Department of Mathematical Sciences at Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, United States. He graduated from the University of Oxford in 1966, and obtained his PhD from the University of London in 1975. His research interests lie in combinatorics, discrete...
and Ravi Kannan giving an algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
ic version of the Szemerédi regularity lemma
Szemerédi regularity lemma
In mathematics, the Szemerédi regularity lemma states that every large enough graph can be divided into subsets of about the same size so that the edges between different subsets behave almost randomly. introduced a weaker version of this lemma, restricted to bipartite graphs, in order to prove ...
to find an ε-regular partition of a given graph.
Formal statement of the regularity lemma
The formal statement of Szemerédi's regularity lemma requires some definitions. Let G be a graph. The density d(X,Y) of a pair of disjoint vertex sets X, Y is defined as d(X,Y)=|E(X,Y)|/|X||Y|where E(X,Y) denotes the set of edges having one end vertex in X and one in Y. For ε>0, a pair of vertex sets X and Y is called ε-regular, if for all subsets A⊆X and B⊆Y satisfying |A| ≥ε |X| and |B| ≥ ε |Y|, we have |d(X,Y)-d(A,B)| ≤ ε.
A partition of the vertex set of G into k sets, V1,...,Vk, is called an equitable partition if for all
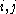 , ||Vi|-|Vj||≤1. An equitable partition is an
, ||Vi|-|Vj||≤1. An equitable partition is an  -regular partition, if for all but at most
-regular partition, if for all but at most 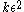 pairs (i,j) the pair
pairs (i,j) the pair 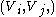 is
is  -regular.
-regular.Now we are ready to state the regularity lemma.
Regularity lemma. For every
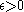 and positive integer
and positive integer 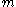 there exist integers
there exist integers 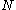 and
and 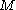 such that if
such that if 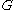 is a graph with at least
is a graph with at least 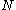 vertices, there exists an integer
vertices, there exists an integer 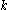 in the range
in the range 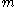 ≤
≤ 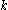 ≤
≤ 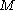 and an
and an  -regular partition of the vertex set of
-regular partition of the vertex set of 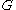 into
into 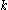 sets.
sets.It is a common variant in the definition of an
 -regular partition to require that the vertex sets all have the same size, while collecting the leftover vertices in an "error"-set
-regular partition to require that the vertex sets all have the same size, while collecting the leftover vertices in an "error"-set 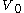 whose size is at most an
whose size is at most an  -fraction of the size of the vertex set of
-fraction of the size of the vertex set of 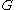 .
.Szemerédi's regularity lemma is one of the most powerful tools of extremal graph theory. It says that, in some sense,
all graphs can be approximated by random-looking graphs. Therefore the lemma helps in proving theorems for arbitrary graphs whenever the corresponding result is easy for random graphs. The first constructive version was provided by Alon, Duke, Leffman, Rödl
Vojtěch Rödl
Vojtěch Rödl is a Czech mathematician, currently the Samuel Candler Dobbs Professor at Emory University, Atlanta, known for his work in combinatorics. He received his PhD from Charles University, Prague in 1976...
and Yuster . Subsequently Frieze and Kannan gave a different version and extended it to hypergraphs . The paper
is a nice survey on regularity lemma and its various applications. Here we will briefly describe a different construction due to Alan Frieze and Ravi Kannan that uses singular values of matrices.
Constructive version of Szemerédi regularity lemma by Frieze and Kannan
The algorithm is based on two crucial lemmas:Lemma 1:
Fix k and
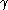 and let
and let 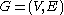 be a graph with
be a graph with  vertices. Let
vertices. Let 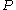 be an equitable partition of
be an equitable partition of 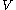 in classes
in classes 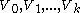 . Assume
. Assume 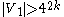 and
and 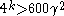 . Given proofs that more than
. Given proofs that more than 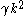 pairs
pairs 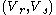 are not
are not 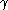 -regular, it is possible to find in O(n) time an equitable partition
-regular, it is possible to find in O(n) time an equitable partition 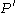 (which is a refinement of
(which is a refinement of 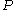 ) into
) into 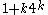 classes, with an exceptional class of cardinality at most
classes, with an exceptional class of cardinality at most 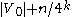 and such that
and such that 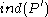 ≥
≥ 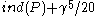
Lemma 2:
Let
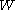 be a
be a 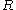 ×
×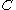 matrix with
matrix with 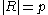 ,
, 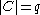 and
and 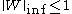 and
and 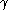 be a positive real.
be a positive real.(a) If there exist
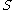 ⊆
⊆ 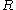 ,
, 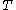 ⊆
⊆ 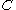 such that
such that  ≥
≥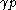 ,
,  ≥
≥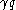 and
and 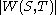 ≥
≥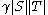 then
then 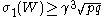
(b) If
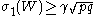 , then there exist
, then there exist 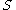 ⊆
⊆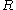 ,
,  ⊆
⊆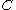 such that
such that  ≥
≥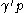 ,
,  ≥
≥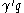 and
and 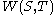 ≥
≥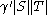 where
where 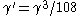 . Furthermore
. Furthermore 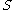 ,
, 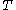 can be constructed in polynomial time.
can be constructed in polynomial time.These two lemmas are combined in the following algorithmic construction of the Szemerédi regularity lemma
Szemerédi regularity lemma
In mathematics, the Szemerédi regularity lemma states that every large enough graph can be divided into subsets of about the same size so that the edges between different subsets behave almost randomly. introduced a weaker version of this lemma, restricted to bipartite graphs, in order to prove ...
.
[Step 1] Arbitrarily divide the vertices of
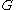 into an equitable partition
into an equitable partition 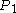 with classes
with classes 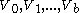 where
where 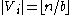 and hence
and hence 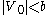 . denote
. denote 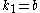 .
.[Step 2] For every pair
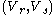 of
of 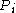 , compute
, compute 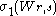 . If the pair
. If the pair 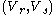 are not
are not 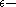 regular then by Lemma 2 we obtain a proof that they are not
regular then by Lemma 2 we obtain a proof that they are not 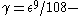 regular.
regular.[Step 3] If there are at most
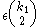 pairs that produce proofs of non
pairs that produce proofs of non 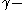 regularity that halt.
regularity that halt. 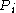 is
is 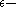 regular.
regular.[Step 4] Apply Lemma 1 where
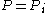 ,
, 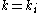 ,
, 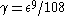 and obtain
and obtain 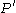 with
with 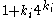 classes
classes[Step 5] Let
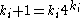 ,
, 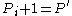 ,
, 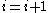 and go to Step 2.
and go to Step 2.The algorithm will terminate with an
 -regular partition in
-regular partition in 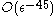 steps since the improvement at each step is
steps since the improvement at each step is 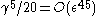 .
.

