
Battle of Eltham's Landing
Encyclopedia
The Battle of Eltham's Landing, also known as the Battle of Barhamsville, or West Point, took place on May 7, 1862, in New Kent County, Virginia
, as part of the Peninsula Campaign
of the American Civil War
. Brig. Gen.
William B. Franklin
's Union
division
landed at Eltham's Landing and was attacked by two brigade
s of Brig. Gen. G. W. Smith
's command, reacting to the threat to the Confederate army
's trains on the Barhamsville Road. Franklin's movement occurred while the Confederate army was withdrawing from the Williamsburg
line, but he was unable to interfere with the Confederate movement.
unexpectedly withdrew his forces from the Warwick Line
at the Battle of Yorktown
the night of May 3, Union Maj. Gen.
George B. McClellan
was taken by surprise and was unprepared to mount an immediate pursuit. On May 4, he ordered cavalry commander Brig. Gen. George Stoneman
to pursue Johnston's rearguard and sent approximately half of his Army of the Potomac
along behind Stoneman, under the command of Brig. Gen. Edwin V. Sumner. These troops fought in the inconclusive Battle of Williamsburg
on May 5, after which the Confederates continued to move northwest in the direction of Richmond
.
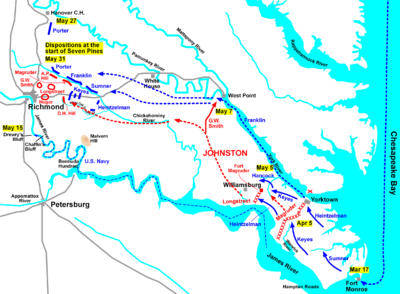 McClellan also ordered Brig. Gen. William B. Franklin's division to board transport ships on the York River
McClellan also ordered Brig. Gen. William B. Franklin's division to board transport ships on the York River
in an attempt to land and cut off Johnston's retreat. It took two days just to board the men and equipment onto the ships, so Franklin was of no assistance to the Williamsburg action. But McClellan had high hopes for his turning movement, planning to send other divisions (those of Brig. Gens. Fitz John Porter
, John Sedgwick
, and Israel B. Richardson
) by river after Franklin's. Their destination was Eltham's Landing on the south bank of the Pamunkey River
across from West Point
, a port on the York River, which was the terminus of the Richmond and York River Railroad
. From the landing, it was about 5 miles (8 km) south to the small town of Barhamsville, where a key intersection on the road to New Kent Court House was being used by Johnston's army on the afternoon of May 6.
Franklin's men came ashore in light pontoon boats and a 400 feet (121.9 m) long floating wharf was then built from pontoons, canal boats, and lumber, so that artillery and supplies could be unloaded. The work was continued by torchlight through the night and the only enemy resistance was a few random shots fired by Confederate pickets on the bluff above the landing, ending at about 10 p.m.
to protect the road to Barhamsville and Smith assigned the division of Brig. Gen. William H. C. Whiting
and Hampton's Legion
, under Colonel Wade Hampton
, to the task. On May 7, Franklin posted Brig. Gen. John Newton
's brigade in the woods on either side of the landing road, supported in the rear by portions of two more brigades (Brig. Gens. Henry W. Slocum and Philip Kearny
). Newton's skirmish line was pushed back as Brig. Gen. John Bell Hood
's Texas Brigade
advanced, with Hampton to his right. Hood was concerned about casualties from friendly fire
in the thick woods, so he ordered his men to advance with unloaded rifles. Encountering a Union picket line 15 paces away, Hood wrote, "A corporal of the enemy drew down his musket upon me as I stood in front of my line." Fortunately for Hood, Private John Deal of the 4th Texas Infantry had disobeyed his orders and carried a loaded rifle; he managed to shoot the Union corporal before the latter could fire.
As a second brigade followed Hood on his left, the Union troops retreated from the woods to the plain before the landing, seeking cover from the fire of Federal gunboats. Whiting employed artillery fire against the gunboats, but his guns had insufficient range, so he disengaged around 2 p.m. Union troops moved back into the woods after the Confederates left, but made no further attempt to advance.
Johnston was pleased with the outcome. Considering the success his men enjoyed in executing the order "to feel the enemy gently and fall back," he humorously asked General Hood, "What would your Texans have done, sir, if I had ordered them to charge and drive back the enemy?" Hood replied, "I suppose, General, they would have driven them into the river, and tried to swim out and capture the gunboats."
New Kent County, Virginia
At the 2000 census, there were 13,462 people, 4,925 households and 3,895 families residing in the county. The population density was 64 per square mile . There were 5,203 housing units at an average density of 25 per square mile...
, as part of the Peninsula Campaign
Peninsula Campaign
The Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War was a major Union operation launched in southeastern Virginia from March through July 1862, the first large-scale offensive in the Eastern Theater. The operation, commanded by Maj. Gen. George B...
of the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
. Brig. Gen.
Brigadier general (United States)
A brigadier general in the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, is a one-star general officer, with the pay grade of O-7. Brigadier general ranks above a colonel and below major general. Brigadier general is equivalent to the rank of rear admiral in the other uniformed...
William B. Franklin
William B. Franklin
William Buel Franklin was a career United States Army officer and a Union Army general in the American Civil War. He rose to the rank of a corps commander in the Army of the Potomac, fighting in several notable early battles in the Eastern Theater.-Early life:William B. Franklin was born in York,...
's Union
Union Army
The Union Army was the land force that fought for the Union during the American Civil War. It was also known as the Federal Army, the U.S. Army, the Northern Army and the National Army...
division
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or formation usually consisting of between 10,000 and 20,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades, and in turn several divisions typically make up a corps...
landed at Eltham's Landing and was attacked by two brigade
Brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that is typically composed of two to five battalions, plus supporting elements depending on the era and nationality of a given army and could be perceived as an enlarged/reinforced regiment...
s of Brig. Gen. G. W. Smith
Gustavus Woodson Smith
Gustavus Woodson Smith , more commonly known as G.W. Smith, was a career United States Army officer who fought in the Mexican-American War, a civil engineer, and a major general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War.-Early life and Mexico:Smith was born in Georgetown,...
's command, reacting to the threat to the Confederate army
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
's trains on the Barhamsville Road. Franklin's movement occurred while the Confederate army was withdrawing from the Williamsburg
Williamsburg, Virginia
Williamsburg is an independent city located on the Virginia Peninsula in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area of Virginia, USA. As of the 2010 Census, the city had an estimated population of 14,068. It is bordered by James City County and York County, and is an independent city...
line, but he was unable to interfere with the Confederate movement.
Background
When Confederate General Joseph E. JohnstonJoseph E. Johnston
Joseph Eggleston Johnston was a career U.S. Army officer, serving with distinction in the Mexican-American War and Seminole Wars, and was also one of the most senior general officers in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War...
unexpectedly withdrew his forces from the Warwick Line
Warwick Line
The Warwick Line was a defensive works across the Virginia Peninsula maintained along the Warwick River by Confederate General John B. Magruder against much larger Union forces under General George B...
at the Battle of Yorktown
Battle of Yorktown (1862)
The Battle of Yorktown or Siege of Yorktown was fought from April 5 to May 4, 1862, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. Marching from Fort Monroe, Union Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan's Army of the Potomac encountered Maj. Gen. John B. Magruder's small Confederate force...
the night of May 3, Union Maj. Gen.
Major general (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, and United States Air Force, major general is a two-star general-officer rank, with the pay grade of O-8. Major general ranks above brigadier general and below lieutenant general...
George B. McClellan
George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan was a major general during the American Civil War. He organized the famous Army of the Potomac and served briefly as the general-in-chief of the Union Army. Early in the war, McClellan played an important role in raising a well-trained and organized army for the Union...
was taken by surprise and was unprepared to mount an immediate pursuit. On May 4, he ordered cavalry commander Brig. Gen. George Stoneman
George Stoneman
George Stoneman, Jr. was a career United States Army officer, a Union cavalry general in the American Civil War, and the 15th Governor of California between 1883 and 1887.-Early life:...
to pursue Johnston's rearguard and sent approximately half of his Army of the Potomac
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
along behind Stoneman, under the command of Brig. Gen. Edwin V. Sumner. These troops fought in the inconclusive Battle of Williamsburg
Battle of Williamsburg
The Battle of Williamsburg, also known as the Battle of Fort Magruder, took place on May 5, 1862, in York County, James City County, and Williamsburg, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War...
on May 5, after which the Confederates continued to move northwest in the direction of Richmond
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond is the capital of the Commonwealth of Virginia, in the United States. It is an independent city and not part of any county. Richmond is the center of the Richmond Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Greater Richmond area...
.

York River (Virginia)
The York River is a navigable estuary, approximately long, in eastern Virginia in the United States. It ranges in width from at its head to near its mouth on the west side of Chesapeake Bay. Its watershed drains an area including portions of 17 counties of the coastal plain of Virginia north...
in an attempt to land and cut off Johnston's retreat. It took two days just to board the men and equipment onto the ships, so Franklin was of no assistance to the Williamsburg action. But McClellan had high hopes for his turning movement, planning to send other divisions (those of Brig. Gens. Fitz John Porter
Fitz John Porter
Fitz John Porter was a career United States Army officer and a Union General during the American Civil War...
, John Sedgwick
John Sedgwick
John Sedgwick was a teacher, a career military officer, and a Union Army general in the American Civil War. He was the highest ranking Union casualty in the Civil War, killed by a sniper at the Battle of Spotsylvania Court House.-Early life:Sedgwick was born in the Litchfield Hills town of...
, and Israel B. Richardson
Israel B. Richardson
Israel Bush Richardson was a United States Army officer during the Mexican-American War and American Civil War, where he was a major general in the Union Army...
) by river after Franklin's. Their destination was Eltham's Landing on the south bank of the Pamunkey River
Pamunkey River
The Pamunkey River is a tributary of the York River, about long, in eastern Virginia in the United States. Via the York River it is part of the watershed of Chesapeake Bay.-Course:...
across from West Point
West Point, Virginia
West Point is an incorporated town in King William County, Virginia, United States. The population was 2,867 at the 2000 census.-Geography:West Point is located at...
, a port on the York River, which was the terminus of the Richmond and York River Railroad
Richmond and York River Railroad
Richmond and York River Railroad was completed between Richmond, Virginia and West Point, Virginia in 1861. The western terminus was adjacent to Richmond's Tobacco Row...
. From the landing, it was about 5 miles (8 km) south to the small town of Barhamsville, where a key intersection on the road to New Kent Court House was being used by Johnston's army on the afternoon of May 6.
Franklin's men came ashore in light pontoon boats and a 400 feet (121.9 m) long floating wharf was then built from pontoons, canal boats, and lumber, so that artillery and supplies could be unloaded. The work was continued by torchlight through the night and the only enemy resistance was a few random shots fired by Confederate pickets on the bluff above the landing, ending at about 10 p.m.
Battle
Johnston ordered Maj. Gen. G. W. SmithGustavus Woodson Smith
Gustavus Woodson Smith , more commonly known as G.W. Smith, was a career United States Army officer who fought in the Mexican-American War, a civil engineer, and a major general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War.-Early life and Mexico:Smith was born in Georgetown,...
to protect the road to Barhamsville and Smith assigned the division of Brig. Gen. William H. C. Whiting
William H. C. Whiting
William Henry Chase Whiting was an United States Army officer who resigned after 16 years of service in the Army Corps of Engineers to serve in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War...
and Hampton's Legion
Hampton's Legion
Hampton's Legion was an American Civil War military unit of the Confederate States of America, organized and partially financed by wealthy South Carolina plantation owner Wade Hampton III...
, under Colonel Wade Hampton
Wade Hampton III
Wade Hampton III was a Confederate cavalry leader during the American Civil War and afterward a politician from South Carolina, serving as its 77th Governor and as a U.S...
, to the task. On May 7, Franklin posted Brig. Gen. John Newton
John Newton
John Henry Newton was a British sailor and Anglican clergyman. Starting his career on the sea at a young age, he became involved with the slave trade for a few years. After experiencing a religious conversion, he became a minister, hymn-writer, and later a prominent supporter of the abolition of...
's brigade in the woods on either side of the landing road, supported in the rear by portions of two more brigades (Brig. Gens. Henry W. Slocum and Philip Kearny
Philip Kearny
Philip Kearny, Jr., was a United States Army officer, notable for his leadership in the Mexican-American War and American Civil War. He was killed in action in the 1862 Battle of Chantilly.-Early life and career:...
). Newton's skirmish line was pushed back as Brig. Gen. John Bell Hood
John Bell Hood
John Bell Hood was a Confederate general during the American Civil War. Hood had a reputation for bravery and aggressiveness that sometimes bordered on recklessness...
's Texas Brigade
Texas Brigade
The Texas Brigade, also often referred to as Hood's Brigade, was an infantry brigade in the Confederate States Army that distinguished itself for its fierce tenacity and fighting capability during the American Civil War.-Organization:...
advanced, with Hampton to his right. Hood was concerned about casualties from friendly fire
Friendly fire
Friendly fire is inadvertent firing towards one's own or otherwise friendly forces while attempting to engage enemy forces, particularly where this results in injury or death. A death resulting from a negligent discharge is not considered friendly fire...
in the thick woods, so he ordered his men to advance with unloaded rifles. Encountering a Union picket line 15 paces away, Hood wrote, "A corporal of the enemy drew down his musket upon me as I stood in front of my line." Fortunately for Hood, Private John Deal of the 4th Texas Infantry had disobeyed his orders and carried a loaded rifle; he managed to shoot the Union corporal before the latter could fire.
As a second brigade followed Hood on his left, the Union troops retreated from the woods to the plain before the landing, seeking cover from the fire of Federal gunboats. Whiting employed artillery fire against the gunboats, but his guns had insufficient range, so he disengaged around 2 p.m. Union troops moved back into the woods after the Confederates left, but made no further attempt to advance.
Aftermath
The Battle at Eltham's Landing was little more than a heavy skirmish. There were 194 Union casualties and 48 Confederate. Franklin told McClellan, "I congratulate myself that we have maintained our position." Although the action was tactically inconclusive, Franklin missed an opportunity to intercept the Confederate retreat from Williamsburg, allowing it to pass unmolested.Johnston was pleased with the outcome. Considering the success his men enjoyed in executing the order "to feel the enemy gently and fall back," he humorously asked General Hood, "What would your Texans have done, sir, if I had ordered them to charge and drive back the enemy?" Hood replied, "I suppose, General, they would have driven them into the river, and tried to swim out and capture the gunboats."

