Behr's syndrome
Encyclopedia
Behr syndrome is an autosomal
recessive genetic disorder
named after Carl Behr
, who first described it in 1909.
Although it is an autosomal recessive disorder, heterozygotes may still manifest much attenuated symptoms.
of optic and neurological complications for both sexes. The disorder begins from early childhood with disturbance to vision, and loss or reduction in body control and co-ordination.
It includes a partial and increasing loss of vision, and/or blind spot
s. Eyesight degeneration is particularly prevalent in males. Symptom
s can also include rapid involuntary eye movements (nystagmus), ataxia
, progressive damage to nerves, nerve inflammation
, mental retardation, urinary incontinence, and unusual foot reflexes when the sole is stimulated (positive Babinski sign).
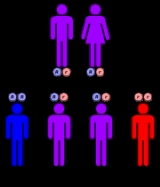
 Behr syndrome is autosomal recessive, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
Behr syndrome is autosomal recessive, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the gene - one inherited from each parent - are required to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry one copy of the defective gene, but are usually not affected by the disorder.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
recessive genetic disorder
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes, especially a condition that is present from before birth. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions....
named after Carl Behr
Carl Behr
Carl Julius Peter Behr was a German ophthalmologist born in Hamburg. In 1909 he described an hereditary syndrome of optic and neurologic disorders now known as Behr's syndrome....
, who first described it in 1909.
Although it is an autosomal recessive disorder, heterozygotes may still manifest much attenuated symptoms.
Diagnosis
Behr syndrome results in a spectrumSpectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
of optic and neurological complications for both sexes. The disorder begins from early childhood with disturbance to vision, and loss or reduction in body control and co-ordination.
It includes a partial and increasing loss of vision, and/or blind spot
Blind spot (vision)
A blind spot, also known as a scotoma, is an obscuration of the visual field. A particular blind spot known as the blindspot, or physiological blind spot, or punctum caecum in medical literature, is the place in the visual field that corresponds to the lack of light-detecting photoreceptor cells on...
s. Eyesight degeneration is particularly prevalent in males. Symptom
Symptom
A symptom is a departure from normal function or feeling which is noticed by a patient, indicating the presence of disease or abnormality...
s can also include rapid involuntary eye movements (nystagmus), ataxia
Ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign and symptom that consists of gross lack of coordination of muscle movements. Ataxia is a non-specific clinical manifestation implying dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum...
, progressive damage to nerves, nerve inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
, mental retardation, urinary incontinence, and unusual foot reflexes when the sole is stimulated (positive Babinski sign).
Genetics

Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the gene - one inherited from each parent - are required to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry one copy of the defective gene, but are usually not affected by the disorder.

