
Black's equation
Encyclopedia
Black's Equation is a mathematical model for the mean time to failure (MTTF) of a semiconductor circuit due to electromigration
: a phenomenon of molecular
rearrangement (movement) in the solid phase caused by an electromagnetic field
.
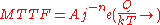
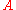 is a constant
is a constant
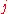 is the current density
is the current density
 is a model parameter
is a model parameter
 is the activation energy
is the activation energy
in eV (electron volts)
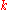 is Boltzmann constant
is Boltzmann constant
 is the absolute temperature in K
is the absolute temperature in K
The model is abstract, not based on a specific physical model, but flexibly describes the failure rate dependence on the temperature, the electrical stress, and the specific technology and materials. More adequately described as descriptive than prescriptive, the values for A, n, and Q are found by fitting the model to experimental data.
The model's value is that it maps experimental data taken at elevated temperature and stress levels in short periods of time to expected component failure rates under actual operating conditions. This data is obtained by running high temperature operating life (HTOL) testing.
Predicted semiconductor failure rates of millions or billions of hours should be used with caution because experimental correlation is all but impossible due to the predominance of other failure modes.
Electromigration
Electromigration is the transport of material caused by the gradual movement of the ions in a conductor due to the momentum transfer between conducting electrons and diffusing metal atoms. The effect is important in applications where high direct current densities are used, such as in...
: a phenomenon of molecular
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
rearrangement (movement) in the solid phase caused by an electromagnetic field
Electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field is a physical field produced by moving electrically charged objects. It affects the behavior of charged objects in the vicinity of the field. The electromagnetic field extends indefinitely throughout space and describes the electromagnetic interaction...
.
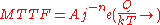
 is a constant
is a constant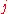 is the current density
is the current densityCurrent density
Current density is a measure of the density of flow of a conserved charge. Usually the charge is the electric charge, in which case the associated current density is the electric current per unit area of cross section, but the term current density can also be applied to other conserved...
 is a model parameter
is a model parameter is the activation energy
is the activation energyActivation energy
In chemistry, activation energy is a term introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius that is defined as the energy that must be overcome in order for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy may also be defined as the minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction...
in eV (electron volts)
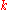 is Boltzmann constant
is Boltzmann constant is the absolute temperature in K
is the absolute temperature in KKelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
The model is abstract, not based on a specific physical model, but flexibly describes the failure rate dependence on the temperature, the electrical stress, and the specific technology and materials. More adequately described as descriptive than prescriptive, the values for A, n, and Q are found by fitting the model to experimental data.
The model's value is that it maps experimental data taken at elevated temperature and stress levels in short periods of time to expected component failure rates under actual operating conditions. This data is obtained by running high temperature operating life (HTOL) testing.
Predicted semiconductor failure rates of millions or billions of hours should be used with caution because experimental correlation is all but impossible due to the predominance of other failure modes.

