
Bühlmann model
Encyclopedia
The Bühlmann model is a random effects model (or "variance components model" or hierarchical linear model
) used in credibility theory
in actuarial science
to determine the appropriate premium for a group of insurance contracts.
A simplified form of the classical Bühlmann model where the components are assumed independent and the variances are equal for all observations, as well as the number of policies in each cell, is called the balanced Bühlmann model. In this model the claim statistics are determined by
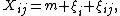
where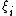 and
and 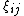 are independent random variables for which
are independent random variables for which
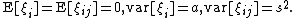
Here the interpretation of the random effects components is as follows:
Hierarchical linear modeling
In statistics, hierarchical linear modeling , a form of multi-level analysis, is a more advanced form of simple linear regression and multiple linear regression. Multilevel analysis allows variance in outcome variables to be analysed at multiple hierarchical levels, whereas in simple linear and...
) used in credibility theory
Credibility Theory
Credibility theory is a branch of actuarial science. It was developed originally as a method to calculate the risk premium by combining the individual risk experience with the class risk experience....
in actuarial science
Actuarial science
Actuarial science is the discipline that applies mathematical and statistical methods to assess risk in the insurance and finance industries. Actuaries are professionals who are qualified in this field through education and experience...
to determine the appropriate premium for a group of insurance contracts.
A simplified form of the classical Bühlmann model where the components are assumed independent and the variances are equal for all observations, as well as the number of policies in each cell, is called the balanced Bühlmann model. In this model the claim statistics are determined by
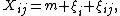
where
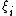 and
and 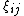 are independent random variables for which
are independent random variables for which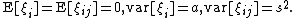
Here the interpretation of the random effects components is as follows:
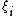 represents the departure of the true mean for all possible samples of members in group i from the overall mean m;
represents the departure of the true mean for all possible samples of members in group i from the overall mean m;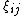 represents the departure of the jth selected individual in group i from the true mean,
represents the departure of the jth selected individual in group i from the true mean, 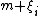 , for that group.
, for that group.

