
Carroll's paradox
Encyclopedia
In physics
, Carroll's paradox arises when considering the motion of a falling rigid rod that is specially constrained. Considered one way, the angular momentum
stays constant; considered in a different way, it changes. It is named after Michael M. Carroll who first published it in 1984.
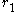 and
and 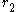 as might be drawn on the face of a wall clock. Suppose a uniform rigid heavy rod of length
as might be drawn on the face of a wall clock. Suppose a uniform rigid heavy rod of length 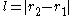 is somehow constrained between these two circles so that one end of the rod remains on the inner circle and the other remains on the outer circle. Motion of the rod along these circles, acting as guides, is frictionless. The rod is held in the three o'clock position so that it is horizontal, then released.
is somehow constrained between these two circles so that one end of the rod remains on the inner circle and the other remains on the outer circle. Motion of the rod along these circles, acting as guides, is frictionless. The rod is held in the three o'clock position so that it is horizontal, then released.
Now consider the angular momentum about the centre of the rod:
An apparent resolution of this paradox is that the physical situation cannot occur. To maintain the rod in a radial position the circles have to exert an infinite force. In real life it would not be possible to construct guides that do not exert a significant reaction force perpendicular to the rod. Victor Namias, however, disputed that infinite forces occur, and argued that a finitely thick rod experiences torque about its center of mass even in the limit as it approaches zero width.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, Carroll's paradox arises when considering the motion of a falling rigid rod that is specially constrained. Considered one way, the angular momentum
Angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
stays constant; considered in a different way, it changes. It is named after Michael M. Carroll who first published it in 1984.
Explanation
Consider two concentric circles of radius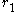 and
and 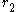 as might be drawn on the face of a wall clock. Suppose a uniform rigid heavy rod of length
as might be drawn on the face of a wall clock. Suppose a uniform rigid heavy rod of length 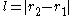 is somehow constrained between these two circles so that one end of the rod remains on the inner circle and the other remains on the outer circle. Motion of the rod along these circles, acting as guides, is frictionless. The rod is held in the three o'clock position so that it is horizontal, then released.
is somehow constrained between these two circles so that one end of the rod remains on the inner circle and the other remains on the outer circle. Motion of the rod along these circles, acting as guides, is frictionless. The rod is held in the three o'clock position so that it is horizontal, then released.Now consider the angular momentum about the centre of the rod:
- After release, the rod falls. Being constrained, it must rotate as it moves. When it gets to a vertical six o'clock position, it has lost potential energyPotential energyIn physics, potential energy is the energy stored in a body or in a system due to its position in a force field or due to its configuration. The SI unit of measure for energy and work is the Joule...
and, because the motion is frictionless, will have gained kinetic energyKinetic energyThe kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
. It therefore possesses angular momentum. - The reaction force on the rod from either circular guide is frictionless, so it must be directed along the rod; there can be no component of the reaction force perpendicular to the rod. Taking momentsMoment (physics)In physics, the term moment can refer to many different concepts:*Moment of force is the tendency of a force to twist or rotate an object; see the article torque for details. This is an important, basic concept in engineering and physics. A moment is valued mathematically as the product of the...
about the center of the rod, there can be no moment acting on the rod, so its angular momentum remains constant. Because the rod starts with zero angular momentum, it must continue to have zero angular momentum for all time.
An apparent resolution of this paradox is that the physical situation cannot occur. To maintain the rod in a radial position the circles have to exert an infinite force. In real life it would not be possible to construct guides that do not exert a significant reaction force perpendicular to the rod. Victor Namias, however, disputed that infinite forces occur, and argued that a finitely thick rod experiences torque about its center of mass even in the limit as it approaches zero width.

