
Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railroad
Encyclopedia
.svg.png)
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
of Illinois
Illinois
Illinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,...
that operated a main line between Pekin (near Peoria) and Madison (near St. Louis) via Springfield. Its property was sold at foreclosure
Foreclosure
Foreclosure is the legal process by which a mortgage lender , or other lien holder, obtains a termination of a mortgage borrower 's equitable right of redemption, either by court order or by operation of law...
to several new companies in the 1920s; the portion north of Springfield has since become the Illinois and Midland Railroad, while the remainder has been abandoned, except for a portion near St. Louis that is now owned by the Norfolk Southern Railway
Norfolk Southern Railway
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I railroad in the United States, owned by the Norfolk Southern Corporation. With headquarters in Norfolk, Virginia, the company operates 21,500 route miles in 22 eastern states, the District of Columbia and the province of Ontario, Canada...
.
History
The earliest predecessor of the CP&StL was the Illinois River Railroad, chartered by the Illinois General AssemblyIllinois General Assembly
The Illinois General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Illinois and comprises the Illinois House of Representatives and the Illinois Senate. The General Assembly was created by the first state constitution adopted in 1818. Illinois has 59 legislative districts, with two...
in February 1853 to build a line from Jacksonville north-northeasterly to La Salle through the valley of the Illinois River
Illinois River
The Illinois River is a principal tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately long, in the State of Illinois. The river drains a large section of central Illinois, with a drainage basin of . This river was important among Native Americans and early French traders as the principal water route...
. The line was opened from Virginia to Pekin in 1859, and in May 1864 the property was sold at foreclosure
Foreclosure
Foreclosure is the legal process by which a mortgage lender , or other lien holder, obtains a termination of a mortgage borrower 's equitable right of redemption, either by court order or by operation of law...
to the Peoria, Pekin and Jacksonville Railroad, which had been incorporated in June 1863 for this purpose. The company bought a line from Pekin to Peoria from the Peoria and Hannibal Railroad in May 1868, and in 1869 the road was extended southwest to the Toledo, Wabash and Western Railway (Wabash) at Jacksonville. The segment beyond Pekin acquired in 1868 was sold in November 1880 to the Peoria and Pekin Union Railway
Peoria and Pekin Union Railway
The Peoria and Pekin Union Railway is a switching and terminal railroad in Illinois that began operating in 1881 and was leased to the Tazewell and Peoria Railroad in 2004. Its main yard and roundhouse are in East Peoria, Illinois, and it owns track on both sides of the Illinois River...
, a terminal railroad
Terminal Railroad
Terminal Railroad or Terminal Railway may refer to:*Terminal railroad, a railroad that operates a terminal facility*Terminal Railway Alabama State Docks*Terminal Railway of Buffalo, predecessor of the New York Central Railroad...
serving those cities.
A second line was chartered in March 1869 as the Springfield and Northwestern Railroad, to build from Springfield north-northwesterly to Rock Island. It was completed in December 1874 from Springfield (also on the line of the Wabash) to Havana, where trains entered the Peoria, Pekin and Jacksonville Railroad to reach Peoria via trackage rights
Trackage rights
Trackage rights , running rights or running powers is an agreement whereby a railway company has the right to run its trains on tracks owned by another railway company....
. On opening, the road was leased to the Indianapolis, Bloomington and Western Railway (which had lines east from Havana and Pekin), but the lease was forfeited in 1875, and the Springfield and Northwestern Railroad was soon reorganized as the Springfield and Northwestern Railway, incorporated in May 1878.
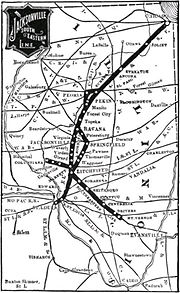
The system was broken up in 1893, as the Jacksonville, Louisville and St. Louis and Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis were placed under separate receivers. The latter's lease of the St. Louis and Chicago expired in December 1895, and that company soon became part of the new St. Louis, Peoria and Northern Railway. This left the Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railway, reorganized in January 1896 as the Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railroad of Illinois, with its original lines from Pekin to Jacksonville and Springfield and an isolated branch between Litchfield and Madison. Unable to use the direct line from Springfield to Litchfield, the CP&StL acquired trackage rights
Trackage rights
Trackage rights , running rights or running powers is an agreement whereby a railway company has the right to run its trains on tracks owned by another railway company....
over the St. Louis, Chicago and St. Paul Railroad ("Bluff Line") to Waverly and the Jacksonville Southeastern to Litchfield; the route was modified in July 1896 to use the latter line from Jacksonville to Litchfield. Several years later, the CP&StL would acquire the Bluff Line as its St. Louis connection, and sell off the Litchfield-Madison line.
The Bluff Line began as the St. Louis, Jerseyville and Springfield Railroad, incorporated in November 1880 to build from Springfield to the Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
near Grafton. The line was completed in 1882 from Bates, on the Wabash west of Springfield, through Jerseyville to Dow
Dow, Illinois
Dow is an unincorporated community in Jersey County, Illinois, United States.-Education:Dow is served by the public K-12 Jersey Community Unit School District 100. District schools in Dow include ....
, where it descended the Mississippi River's bluffs to Elsah and followed the shoreline to Grafton. After a lease to the St. Louis and Central Illinois Railroad, begun in December 1886, the line was reorganized in November 1888 as the St. Louis, Alton and Springfield Railroad, which had been incorporated in June 1887. In 1889, that company built a branch from Dow to the river at Lockhaven, and then along the Mississippi to Alton, as well as a connection from Elsah to Lockhaven. (The Dow-Elsah segment would later be abandoned.) Another reorganization, in September 1892, created the St. Louis, Chicago and St. Paul Railroad which built a direct entrance to Springfield from Loami (south of Bates), as well as an extension from Alton to Granite City in July 1894. The company was reorganized yet again in October 1897, forming the St. Louis, Chicago and St. Paul Railway of Illinois. Finally, in March 1900, the Bluff Line was merged into the Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railway of Illinois, a reorganization of the Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railroad of Illinois, and at the same time the Litchfield-Madison line was split off as a new Litchfield and Madison Railway
Litchfield and Madison Railway
The Litchfield and Madison Railway was a Class I railroad in Illinois in the United States. Its nickname was the St. Louis Gateway Route. The railroad operated of track from its creation in 1900 until it was absorbed by the Chicago and North Western Railway in 1958.- History :In 1889-1890, the...
, which the CP&StL continued to operate under lease until June 1904.
This consolidated company, with a main line from Pekin to Granite City/Madison, and branches to Jacksonville and Grafton, continued to have financial problems, and the final company to bear the name, the Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railroad, was incorporated in December 1909 and took over the property of the Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railway of Illinois in January 1913. Operations continued until November 1924, when four separate companies purchased portions of the property at foreclosure
Foreclosure
Foreclosure is the legal process by which a mortgage lender , or other lien holder, obtains a termination of a mortgage borrower 's equitable right of redemption, either by court order or by operation of law...
sale:
- Alton and Eastern Railroad, Granite City to Grafton, including the lease of the Alton Terminal Railway; leased to the Illinois Terminal Company in 1930 and merged in 1937; now part of the Norfolk Southern RailwayNorfolk Southern RailwayThe Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I railroad in the United States, owned by the Norfolk Southern Corporation. With headquarters in Norfolk, Virginia, the company operates 21,500 route miles in 22 eastern states, the District of Columbia and the province of Ontario, Canada...
- Chicago, Springfield and St. Louis Railway, Lockhaven to Springfield; later abandoned
- Springfield, Havana and Peoria Railroad, Springfield to Pekin; leased to the Chicago and Illinois Midland RailwayChicago and Illinois Midland RailwayThe Illinois and Midland Railroad is a railroad in the U.S. state of Illinois, serving Peoria, Springfield and Taylorville. Until 1996, when Genesee & Wyoming Inc. bought it, the company was named the Chicago and Illinois Midland Railway...
in 1926 and merged in 1936; now part of the Illinois and Midland Railroad - Jacksonville and Havana Railroad, Jacksonville to Havana; later abandoned

