
Civilian casualties of the U.S. invasion of Afghanistan
Encyclopedia
The decade-long War in Afghanistan (2001–present)
has caused the deaths of thousands of Afghan civilians directly from insurgent and foreign military action, as well as the deaths of possibly tens of thousands of Afghan civilians indirectly as a consequence of displacement, starvation, disease, exposure, lack of medical treatment, crime and lawlessness resulting from the war. The war, launched by the United States as "Operation Enduring Freedom" in 2001, began with an initial air campaign that almost immediately prompted concerns over the number of Afghan civilians being killed as well as international protests
. With civilian deaths from airstrikes rising again in recent years, the number of Afghan civilians being killed by foreign military operations has led to mounting tension between the foreign countries and the government of Afghanistan. In May 2007, President Hamid Karzai
summoned foreign military commanders to warn them of the consequences of further Afghan civilian deaths.
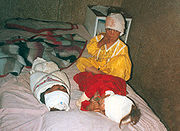
Most, if not all, of the sources state that their estimates are likely to be underestimates.
In an opinion article published in August 2002 in the neoconservative magazine The Weekly Standard
, Joshua Muravchik
of the American Enterprise Institute
, a self-described neoconservative, questioned Professor Herold's study entirely on the basis of one single incident that involved 25-93 deaths. He did not provide any estimate his own.
In a pair of January 2002 studies, Carl Conetta of the Project on Defense Alternatives estimates that, at least 4,200-4,500 civilians were killed by mid-January 2002 as a result of the U.S. war and airstrikes, both directly as casualties of the aerial bombing campaign, and indirectly in the humanitarian crisis that the war and airstrikes contributed to.
His first study, "Operation Enduring Freedom: Why a Higher Rate of Civilian Bombing Casualties?", released January 18, 2002, estimates that, at the low end, at least 1,000-1,300 civilians were directly killed in the aerial bombing campaign in just the 3 months between October 7, 2001 to January 1, 2002. The author found it impossible to provide an upper-end estimate to direct civilian casualties from the Operation Enduring Freedom bombing campaign that he noted as having an increased use of cluster bombs. In this lower-end estimate, only Western press sources were used for hard numbers, while heavy "reduction factors" were applied to Afghan government reports so that their estimates were reduced by as much as 75%.
In his companion study, "Strange Victory: A critical appraisal of Operation Enduring Freedom and the Afghanistan war", released January 30, 2002, Conetta estimates that at least 3,200 more Afghans died by mid-January 2002, of "starvation, exposure, associated illnesses, or injury sustained while in flight from war zones", as a result of the U.S. war and airstrikes.
In similar numbers, a Los Angeles Times
review of U.S., British, and Pakistani newspapers and international wire services found that between 1,067 and 1,201 direct civilian deaths were reported by those news organizations during the five months from October 7, 2001 to February 28, 2002. This review excluded all civilian deaths in Afghanistan that did not get reported by U.S., British, or Pakistani news, excluded 497 deaths that did get reported in U.S., British, and Pakistani news but that were not specifically identified as civilian or military, and excluded 754 civilian deaths that were reported by the Taliban but not independently confirmed.
According to Jonathan Steele
of The Guardian
, up to 20,000 Afghans may have died as a consequence of the first four months of U.S. airstrikes on Afghanistan.
An Associated Press tally based on reports from Afghan, NATO and coalition officials puts the overall death toll slightly lower, at about 4,000, most of them militants.
More than 1,900 people were killed in the first eight months of the year by the end of August.
With by far the most comprehensive research into Afghan civilian casualties, Professor Marc W. Herold of the University of New Hampshire
estimated in September 2007 that between 5,700 and 6,500 Afghan civilians had been killed so far in the war by American and NATO military forces. He stressed that this was an "absolute minimum" and probably "a vast underestimate" because the figures do not include:
On the other hand, according to NATO forces only about 1,000 civilians were killed during the whole year.
Going into further detail, UNAMA reported that out of 2,118 civilian deaths in 2008, 1,160 non-combatants were killed by anti-government forces, accounting for 55% of the 2008 total, while 828 were killed by international-led military forces, accounting for 39% of the 2008 total. The remaining 6% – 130 deaths – could not be attributed to any of the parties since some of them died as a result of crossfire or were killed by unexploded ordnance
, for example. Of the civilians killed by anti-government elements, 85% died as a result of suicide or improvised explosive devices. Of the civilians killed by pro-government forces, 64% were killed by U.S./NATO airstrikes.
(Note: UNAMA's report includes in its count of civilian/non-combatant deaths any "members of the military who are not being utilized in counter insurgency operations, including when they are off-duty.")
The Afghan Independent Human Rights Commission (AIHRC)
estimated the number of civilians killed as a result of the armed hostilities in 2008 at around 1,800, with about 1,000 killed by militant groups and about 800 killed by U.S.-led military forces.
The Afghanistan Rights Monitor(ARM), a Kabul-based rights watchdog, estimated that in 2008 about 3,917 civilians were killed, over 6,800 were wounded, and around 120,000 were forced out of their homes. ARM estimated that insurgents killed over 2,300 civilians, including 930 in suicide bombings, and that U.S.-led military forces killed over 1,620 civilians, with 1,100 civilians killed by U.S.-led NATO and coalition forces and 520 civilians killed by Afghan military forces. Out of these, 680 Afghan civilians killed in air strikes by the US-led forces, with U.S. combat aircraft conducting at least 15,000 close air support missions over the year. Another 2,800 civilians were injured and 80,000 displaced from their homes by the U.S.-led NATO and coalition military operations.
According to Afghanistan's ambassador to Australia, Amanullah Jayhoon, 1,000 Afghan civilians were killed by coalition forces in 2008.
Meanwhile, NATO's International Security Assistance Force has said that only just over 200 civilians were mistakenly killed by foreign troops last year.
According to NATO spokesman James Appathurai, 97 civilian deaths were caused by ISAF
in 2008, while 987 civilian deaths were caused by militant groups. The number of civilian deaths caused by US-led military forces operating outside of ISAF was not mentioned in that statement.
In October 2008, Professor Marc W. Herold of the University of New Hampshire
reported that the number of civilians killed in direct action by U.S. and other NATO forces from 2005 up that point in 2008 was at least between 2,699 and 3,273. These figures represent underestimates of the number of Afghan civilians killed because civilians are sometimes labelled militants by the military and because these figures only include civilians that died immediately at the scene and not civilians that died later of their injuries.
In 2008, 38 aid workers, almost all from NGO's, were killed, double the number from 2007, and 147 were abducted.
According to the Afghanistan Rights Monitor(ARM) more than 1,100 Afghan police and 530 Afghan soldiers lost their lives in 2008.
According to NATO forces, 5,000 militants were killed in 2008.
Of these, UNAMA attributed two-thirds, or 1,630, of the deaths to the action of anti-government forces, around a quarter, 596, of the deaths to action by American-led military forces, and was not able to clearly attribute another 186 civilian deaths to any one side. Airstrikes continued to be the main cause of civilian deaths resulting from US-led military action, with 359 Afghan civilians killed by US/NATO airstrikes in 2009.
In addition to a growing number of Afghan civilians being killed, Afghan populations caught in the eight-year war have also suffered from loss of livelihood, displacement, and the destruction of their homes, property, and personal assets.
In its mid-year report, the UNAMA underlined that "if the non-combatant status of one or more victim(s) remains under significant doubt, such deaths are not included in the overall number of civilian casualties. Thus, there is a significant possibility that UNAMA is under-reporting civilian casualties."
In September 2009, the U.N. reported that August had been the deadliest month of 2009 to date for Afghan civilians as a result of the August 20th election
. The U.N. also reported that about 1,500 people were killed from the start of the year through August. The report stated: "August (was) the deadliest month since the beginning of 2009. ... These figures reflect an increasing trend in insecurity over recent months and in elections-related violence." UN Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) attributed 68% of the deaths to anti-government elements and 23% of the deaths to international-led military forces – most of them in airstrikes. In 9% of the civilian deaths, UNAMA was unable to clearly attribute the cause to any one side of the parties in the conflict. The number of civilians killed represented an increase of 31% over the same period in 2008, when 1,145 civilians were killed.
According to the UN Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) and the Afghanistan Independent Human Rights Commission (AIHRC), 2,777 Afghan civilians were killed in the U.S.-led war in 2010, a jump of 15% over the civilian toll in 2009.
Of these, UNAMA/AIHRC attributed 2,080 civilian deaths as having been caused by anti-government elements, up 28% from 2009 and representing 74.9% of the 2,777 Afghan civilian deaths they recorded in the war in 2010. 1,141 or 55% of these deaths were caused by suicide attacks and improvised explosive devices (IEs).
UNAMA/AIHRC attributed 440 of the Afghan civilian deaths in 2010 as having been caused by U.S.-led military forces, a reduction of 26% from 2009 and representing 15.9% of the 2,777 Afghan civilian deaths they recorded for 2010. Airstrikes caused 171, or 39% of these deaths.
In 9% of the civilian deaths, UNAMA/AIHRC were unable to clearly attribute the cause to any one side.
In addition to the civilian deaths, a total of 4,343 civilians were documented by UNAMA/AIHRC to have been wounded in the war in 2010, a jump of 22% from 2009.
UNAMA/AIHRC attributed 1,167 of those deaths as having been caused by anti-government elements, up 28% from the same period in 2010 and representing 79.8% of the civilian deaths.
UNAMA/AIHRC attributed 207 Afghan civilian deaths as having been caused by U.S.-led military forces, down 9% from the same period in 2010 and representing 14.2% of the civilian deaths.
In 6% of the civilian deaths, UNAMA and AIHRC were unable to clearly attribute the cause to any one side.
The use of improvised explosive devices (IEDs) increased and became more widespread, suicide attack
s became more complex and sophisticated, targeted killing
s intensified, ground fighting increased, and civilian deaths from airstrikes, particularly by Apache attack helicopters, also increased.
has repeatedly pleaded with the foreign military forces in his country to stop killing so many Afghan civilians in their operations.
(Senior Afghan officials were furious that it took five days before President Bush telephoned Mr. Karzai to offer sympathy and that Donald Rumsfeld
, the US Defense Secretary, had expressed no remorse or apology.)
in eastern Afghanistan to protest the killing of 26 young men by Taliban militants. A Taliban spokesperson said the men who were taken off a bus were targeted because they were members or recruits of Afghan security forces, but Afghan officials said that the men were civilians on their way to Iran to find work.
In considering civilian casualties caused collectively by insurgent forces, it should be noted that the armed insurgency in Afghanistan against the government and foreign military forces is composed of many diverse individuals and groups that are motivated by a range of different goals and ideologies, that do not necessarily identify as "Taliban", and that do not act under a single line of authority.
Protests
around the world, starting with large-scale global demonstrations in the days leading up to the official launch of U.S. Operation Enduring Freedom's under George W. Bush
and Donald Rumsfeld
in October 2001, have taken place every year since.
War in Afghanistan (2001–present)
The War in Afghanistan began on October 7, 2001, as the armed forces of the United States of America, the United Kingdom, Australia, and the Afghan United Front launched Operation Enduring Freedom...
has caused the deaths of thousands of Afghan civilians directly from insurgent and foreign military action, as well as the deaths of possibly tens of thousands of Afghan civilians indirectly as a consequence of displacement, starvation, disease, exposure, lack of medical treatment, crime and lawlessness resulting from the war. The war, launched by the United States as "Operation Enduring Freedom" in 2001, began with an initial air campaign that almost immediately prompted concerns over the number of Afghan civilians being killed as well as international protests
Protests against the invasion of Afghanistan
The ongoing decade-long War in Afghanistan has prompted large protests around the world, with the first large-scale demonstrations beginning in the days leading up to the war's official launch on October 7, 2001....
. With civilian deaths from airstrikes rising again in recent years, the number of Afghan civilians being killed by foreign military operations has led to mounting tension between the foreign countries and the government of Afghanistan. In May 2007, President Hamid Karzai
Hamid Karzai
Hamid Karzai, GCMG is the 12th and current President of Afghanistan, taking office on 7 December 2004. He became a dominant political figure after the removal of the Taliban regime in late 2001...
summoned foreign military commanders to warn them of the consequences of further Afghan civilian deaths.

Estimates
There is no single official figure for the overall number of civilians killed by the war since 2001, but estimates for specific years or periods have been published by a number of independent organizations and are presented here.Most, if not all, of the sources state that their estimates are likely to be underestimates.
Aggregation of estimates
| Year | Civilians killed as a result of insurgent actions | Civilians killed as a result of U.S-led military actions | Civilians killed as a result of the war |
| 2001 | n/a |
|
2001-2003:
|
| 2002 | n/a | ||
| 2003 | n/a | ||
| 2004 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 2005 | n/a |
|
|
| 2006 |
|
|
|
| 2007 |
|
|
|
| 2008 |
|
|
|
| 2009 |
|
|
|
| 2010 |
|
|
|
| 2011 |
|
|
|
| Total |
|
|
|
| Year | Civilians killed as a result of insurgent actions
(Total of available estimates, lower - upper) |
Civilians killed as a result of U.S-led military actions* (Total of available estimates, lower - upper) |
Civilians killed as a result of the war* (Total of available estimates, lower - upper) |
- *Note: In UNAMA/AIHRC methodology, whenever it remains uncertain whether a victim is a civilian after they have assessed the facts available to them, UNAMA/AIHRC does not count that victim as a possible civilian casualty. The number of such victims is not provided.
Civilian casualties (2001-2003)
According to Marc W. Herold's extensive database, Dossier on Civilian Victims of United States' Aerial Bombing, between 3,100 and 3,600 civilians were directly killed by U.S. Operation Enduring Freedom bombing and Special Forces attacks between October 7, 2001 and June 3, 2003. This estimate counts only "impact deaths" – deaths that occurred in the immediate aftermath of an explosion or shooting – and does not count deaths that occurred later as a result of injuries sustained, or deaths that occurred as an indirect consequence of the U.S. airstrikes and invasion.In an opinion article published in August 2002 in the neoconservative magazine The Weekly Standard
The Weekly Standard
The Weekly Standard is an American neoconservative opinion magazine published 48 times per year. Its founding publisher, News Corporation, debuted the title September 18, 1995. Currently edited by founder William Kristol and Fred Barnes, the Standard has been described as a "redoubt of...
, Joshua Muravchik
Joshua Muravchik
Joshua Muravchik is a scholar formerly at the American Enterprise Institute for Public Policy Research and now a fellow at the School of Advanced International Studies of Johns Hopkins University....
of the American Enterprise Institute
American Enterprise Institute
The American Enterprise Institute for Public Policy Research is a conservative think tank founded in 1943. Its stated mission is "to defend the principles and improve the institutions of American freedom and democratic capitalism—limited government, private enterprise, individual liberty and...
, a self-described neoconservative, questioned Professor Herold's study entirely on the basis of one single incident that involved 25-93 deaths. He did not provide any estimate his own.
In a pair of January 2002 studies, Carl Conetta of the Project on Defense Alternatives estimates that, at least 4,200-4,500 civilians were killed by mid-January 2002 as a result of the U.S. war and airstrikes, both directly as casualties of the aerial bombing campaign, and indirectly in the humanitarian crisis that the war and airstrikes contributed to.
His first study, "Operation Enduring Freedom: Why a Higher Rate of Civilian Bombing Casualties?", released January 18, 2002, estimates that, at the low end, at least 1,000-1,300 civilians were directly killed in the aerial bombing campaign in just the 3 months between October 7, 2001 to January 1, 2002. The author found it impossible to provide an upper-end estimate to direct civilian casualties from the Operation Enduring Freedom bombing campaign that he noted as having an increased use of cluster bombs. In this lower-end estimate, only Western press sources were used for hard numbers, while heavy "reduction factors" were applied to Afghan government reports so that their estimates were reduced by as much as 75%.
In his companion study, "Strange Victory: A critical appraisal of Operation Enduring Freedom and the Afghanistan war", released January 30, 2002, Conetta estimates that at least 3,200 more Afghans died by mid-January 2002, of "starvation, exposure, associated illnesses, or injury sustained while in flight from war zones", as a result of the U.S. war and airstrikes.
In similar numbers, a Los Angeles Times
Los Angeles Times
The Los Angeles Times is a daily newspaper published in Los Angeles, California, since 1881. It was the second-largest metropolitan newspaper in circulation in the United States in 2008 and the fourth most widely distributed newspaper in the country....
review of U.S., British, and Pakistani newspapers and international wire services found that between 1,067 and 1,201 direct civilian deaths were reported by those news organizations during the five months from October 7, 2001 to February 28, 2002. This review excluded all civilian deaths in Afghanistan that did not get reported by U.S., British, or Pakistani news, excluded 497 deaths that did get reported in U.S., British, and Pakistani news but that were not specifically identified as civilian or military, and excluded 754 civilian deaths that were reported by the Taliban but not independently confirmed.
According to Jonathan Steele
Jonathan Steele
Jonathan Steele is a British journalist, author of several books on international affairs.Jonathan Steele was educated at King's College, Cambridge and Yale University . He has reported on Afghanistan, Russia, Iraq, and other countries. He was Washington Bureau Chief, Moscow Bureau Chief, and...
of The Guardian
The Guardian
The Guardian, formerly known as The Manchester Guardian , is a British national daily newspaper in the Berliner format...
, up to 20,000 Afghans may have died as a consequence of the first four months of U.S. airstrikes on Afghanistan.
Civilian and overall casualties (2005)
An estimated 1,700 people were killed in 2005 according to an Associated Press count, including civilians, insurgents and security forces members. Some 600 policemen were killed between Hamid Karzai's election as president of Afghanistan in early December 2004 and mid-May 2005.Civilian and overall casualties (2006)
A report by Human Rights Watch said that 4,400 Afghans had been killed in 2006, more than 1,000 of them civilians. Some 2,077 militants were killed in Coalition operations between September 1 and December 13.An Associated Press tally based on reports from Afghan, NATO and coalition officials puts the overall death toll slightly lower, at about 4,000, most of them militants.
More than 1,900 people were killed in the first eight months of the year by the end of August.
Civilian and overall casualties (2007)
More than 7,700 people were killed in 2007, including: 1,019 Afghan policemen; 4,478 militants; 1,980 civilians and 232 foreign soldiers.With by far the most comprehensive research into Afghan civilian casualties, Professor Marc W. Herold of the University of New Hampshire
University of New Hampshire
The University of New Hampshire is a public university in the University System of New Hampshire , United States. The main campus is in Durham, New Hampshire. An additional campus is located in Manchester. With over 15,000 students, UNH is the largest university in New Hampshire. The university is...
estimated in September 2007 that between 5,700 and 6,500 Afghan civilians had been killed so far in the war by American and NATO military forces. He stressed that this was an "absolute minimum" and probably "a vast underestimate" because the figures do not include:
- the dead among the tens of thousands of Afghans displaced during the initial military operation in 2001-2002, who ended up in refugee camps or elsewhere with little or no supplies for long periods;
- civilian victims of U.S./NATO bombing in mountainous areas, which have few or no communications links or which the U.S./NATO forces "cordon off as part of news management";
- and civilians that did not die immediately at the scene but died later of their injuries.
Civilian and overall casualties (2008)
The UN Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) reported that 2,118 civilians were killed as a result of armed conflict in Afghanistan in 2008, the highest civilian death toll since the end of the initial 2001 invasion. This represents an increase of about 40 percent over UNAMA's figure of 1,523 civilians killed in 2007.On the other hand, according to NATO forces only about 1,000 civilians were killed during the whole year.
Going into further detail, UNAMA reported that out of 2,118 civilian deaths in 2008, 1,160 non-combatants were killed by anti-government forces, accounting for 55% of the 2008 total, while 828 were killed by international-led military forces, accounting for 39% of the 2008 total. The remaining 6% – 130 deaths – could not be attributed to any of the parties since some of them died as a result of crossfire or were killed by unexploded ordnance
Unexploded ordnance
Unexploded ordnance are explosive weapons that did not explode when they were employed and still pose a risk of detonation, potentially many decades after they were used or discarded.While "UXO" is widely and informally used, munitions and explosives of...
, for example. Of the civilians killed by anti-government elements, 85% died as a result of suicide or improvised explosive devices. Of the civilians killed by pro-government forces, 64% were killed by U.S./NATO airstrikes.
(Note: UNAMA's report includes in its count of civilian/non-combatant deaths any "members of the military who are not being utilized in counter insurgency operations, including when they are off-duty.")
The Afghan Independent Human Rights Commission (AIHRC)
Afghan Independent Human Rights Commission
The Afghan Independent Human Rights Commission is an Afghan organisation dedicated to the preservation of human rights and the investigation of human rights abuses....
estimated the number of civilians killed as a result of the armed hostilities in 2008 at around 1,800, with about 1,000 killed by militant groups and about 800 killed by U.S.-led military forces.
The Afghanistan Rights Monitor(ARM), a Kabul-based rights watchdog, estimated that in 2008 about 3,917 civilians were killed, over 6,800 were wounded, and around 120,000 were forced out of their homes. ARM estimated that insurgents killed over 2,300 civilians, including 930 in suicide bombings, and that U.S.-led military forces killed over 1,620 civilians, with 1,100 civilians killed by U.S.-led NATO and coalition forces and 520 civilians killed by Afghan military forces. Out of these, 680 Afghan civilians killed in air strikes by the US-led forces, with U.S. combat aircraft conducting at least 15,000 close air support missions over the year. Another 2,800 civilians were injured and 80,000 displaced from their homes by the U.S.-led NATO and coalition military operations.
According to Afghanistan's ambassador to Australia, Amanullah Jayhoon, 1,000 Afghan civilians were killed by coalition forces in 2008.
Meanwhile, NATO's International Security Assistance Force has said that only just over 200 civilians were mistakenly killed by foreign troops last year.
According to NATO spokesman James Appathurai, 97 civilian deaths were caused by ISAF
International Security Assistance Force
The International Security Assistance Force is a NATO-led security mission in Afghanistan established by the United Nations Security Council on 20 December 2001 by Resolution 1386 as envisaged by the Bonn Agreement...
in 2008, while 987 civilian deaths were caused by militant groups. The number of civilian deaths caused by US-led military forces operating outside of ISAF was not mentioned in that statement.
In October 2008, Professor Marc W. Herold of the University of New Hampshire
University of New Hampshire
The University of New Hampshire is a public university in the University System of New Hampshire , United States. The main campus is in Durham, New Hampshire. An additional campus is located in Manchester. With over 15,000 students, UNH is the largest university in New Hampshire. The university is...
reported that the number of civilians killed in direct action by U.S. and other NATO forces from 2005 up that point in 2008 was at least between 2,699 and 3,273. These figures represent underestimates of the number of Afghan civilians killed because civilians are sometimes labelled militants by the military and because these figures only include civilians that died immediately at the scene and not civilians that died later of their injuries.
In 2008, 38 aid workers, almost all from NGO's, were killed, double the number from 2007, and 147 were abducted.
According to the Afghanistan Rights Monitor(ARM) more than 1,100 Afghan police and 530 Afghan soldiers lost their lives in 2008.
According to NATO forces, 5,000 militants were killed in 2008.
Civilian and overall casualties (2009)
2009 was again the most lethal year for Afghan civilians in the American-led war since the fall of the Taliban government in late 2001. According to the UN Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA), 2,412 civilians were killed by the war in 2009, a jump of 14% over the number that lost their lives in 2008. An additional 3,566 Afghan civilians were wounded as a result of the war in 2009.Of these, UNAMA attributed two-thirds, or 1,630, of the deaths to the action of anti-government forces, around a quarter, 596, of the deaths to action by American-led military forces, and was not able to clearly attribute another 186 civilian deaths to any one side. Airstrikes continued to be the main cause of civilian deaths resulting from US-led military action, with 359 Afghan civilians killed by US/NATO airstrikes in 2009.
In addition to a growing number of Afghan civilians being killed, Afghan populations caught in the eight-year war have also suffered from loss of livelihood, displacement, and the destruction of their homes, property, and personal assets.
In its mid-year report, the UNAMA underlined that "if the non-combatant status of one or more victim(s) remains under significant doubt, such deaths are not included in the overall number of civilian casualties. Thus, there is a significant possibility that UNAMA is under-reporting civilian casualties."
In September 2009, the U.N. reported that August had been the deadliest month of 2009 to date for Afghan civilians as a result of the August 20th election
Afghan presidential election, 2009
The 2009 presidential election in Afghanistan was characterized by lack of security, low voter turnout and widespread ballot stuffing, intimidation, and other electoral fraud....
. The U.N. also reported that about 1,500 people were killed from the start of the year through August. The report stated: "August (was) the deadliest month since the beginning of 2009. ... These figures reflect an increasing trend in insecurity over recent months and in elections-related violence." UN Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) attributed 68% of the deaths to anti-government elements and 23% of the deaths to international-led military forces – most of them in airstrikes. In 9% of the civilian deaths, UNAMA was unable to clearly attribute the cause to any one side of the parties in the conflict. The number of civilians killed represented an increase of 31% over the same period in 2008, when 1,145 civilians were killed.
Civilian and overall casualties (2010)
2010 was again the deadliest year for Afghan civilians in the U.S.-led war since the fall of the Taliban government in late 2001, as insecurity and volatility continued to spread to the northern, eastern, and western regions of Afghanistan.According to the UN Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) and the Afghanistan Independent Human Rights Commission (AIHRC), 2,777 Afghan civilians were killed in the U.S.-led war in 2010, a jump of 15% over the civilian toll in 2009.
Of these, UNAMA/AIHRC attributed 2,080 civilian deaths as having been caused by anti-government elements, up 28% from 2009 and representing 74.9% of the 2,777 Afghan civilian deaths they recorded in the war in 2010. 1,141 or 55% of these deaths were caused by suicide attacks and improvised explosive devices (IEs).
UNAMA/AIHRC attributed 440 of the Afghan civilian deaths in 2010 as having been caused by U.S.-led military forces, a reduction of 26% from 2009 and representing 15.9% of the 2,777 Afghan civilian deaths they recorded for 2010. Airstrikes caused 171, or 39% of these deaths.
In 9% of the civilian deaths, UNAMA/AIHRC were unable to clearly attribute the cause to any one side.
In addition to the civilian deaths, a total of 4,343 civilians were documented by UNAMA/AIHRC to have been wounded in the war in 2010, a jump of 22% from 2009.
Civilian and overall casualties (2011)
In the first half of of 2011, the U.S.-led war in Afghanistan again brought yet higher numbers of civilian deaths as violence intensified and security spiralled downward. According to UNAMA/AIHRC figures, 1,462 Afghan civilians were killed in the first six months of 2011, another 15% jump over the same period in 2010.UNAMA/AIHRC attributed 1,167 of those deaths as having been caused by anti-government elements, up 28% from the same period in 2010 and representing 79.8% of the civilian deaths.
UNAMA/AIHRC attributed 207 Afghan civilian deaths as having been caused by U.S.-led military forces, down 9% from the same period in 2010 and representing 14.2% of the civilian deaths.
In 6% of the civilian deaths, UNAMA and AIHRC were unable to clearly attribute the cause to any one side.
The use of improvised explosive devices (IEDs) increased and became more widespread, suicide attack
Suicide attack
A suicide attack is a type of attack in which the attacker expects or intends to die in the process.- Historical :...
s became more complex and sophisticated, targeted killing
Targeted killing
Targeted killing is the deliberate, specific targeting and killing, by a government or its agents, of a supposed terrorist or of a supposed "unlawful combatant" who is not in that government's custody...
s intensified, ground fighting increased, and civilian deaths from airstrikes, particularly by Apache attack helicopters, also increased.
Afghan President Hamid Karzai's repeated pleas to the foreign military forces
Over the past seven years, the Afghan President Hamid KarzaiHamid Karzai
Hamid Karzai, GCMG is the 12th and current President of Afghanistan, taking office on 7 December 2004. He became a dominant political figure after the removal of the Taliban regime in late 2001...
has repeatedly pleaded with the foreign military forces in his country to stop killing so many Afghan civilians in their operations.
- In July 2002, following an American bombing raid in which Afghan officials say 44 people were killed, including many celebrating a wedding and many children, the Afghan president protested to the U.S. military authorities, and urged them to be more careful in their targeting to prevent any more civilian deaths. U.S. President George W. BushGeorge W. BushGeorge Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
offered his condolences.
(Senior Afghan officials were furious that it took five days before President Bush telephoned Mr. Karzai to offer sympathy and that Donald Rumsfeld
Donald Rumsfeld
Donald Henry Rumsfeld is an American politician and businessman. Rumsfeld served as the 13th Secretary of Defense from 1975 to 1977 under President Gerald Ford, and as the 21st Secretary of Defense from 2001 to 2006 under President George W. Bush. He is both the youngest and the oldest person to...
, the US Defense Secretary, had expressed no remorse or apology.)
- In May 2005, Afghan President Hamid Karzai expressed "concern" about the occurrence of civilian deaths by the international military forces in his country, and asked them to exercise "extreme caution" while acting in civilian areas. He insisted that the Afghan government be able to veto U.S. military operations in Afghanistan, promised to correct "mistakes" made by US forces, especially intrusive searches of village homes by American troops, and called for the return of hundreds of Afghan nationals being held prisoner by the U.S. in Cuba at Guantanamo Bay.
- In September 2005, Afghan President Hamid Karzai questioned the continued use of airstrikes by the U.S.-led military forces in his country. He also asked that the United States stop raiding Afghan houses without authorization from the Afghan government. Both the airstrikes, which have caused many civilian casualties, and the house searches by foreign military troops have grown increasingly unpopular in Afghanistan. This was not the first time the Afghan president has complained about the American military presence. In May his request for some more authority over U.S. military operations in his own country was rejected by President Bush.
- In May 2006, Afghan President Hamid KarzaiHamid KarzaiHamid Karzai, GCMG is the 12th and current President of Afghanistan, taking office on 7 December 2004. He became a dominant political figure after the removal of the Taliban regime in late 2001...
summoned the commander of U.S. forces in Afghanistan, Lt. Gen. Karl EikenberryKarl EikenberryKarl Winfrid Eikenberry is a retired United States Army Lieutenant General and former U.S. ambassador to Afghanistan.-Education:Eikenberry graduated from Goldsboro High School in Goldsboro, North Carolina in 1969 and then attended West Point, where he was commissioned as a Second Lieutenant upon...
, to demand an explanation in the deaths of at least 16 Afghan civilians during airstrikes at Taliban militants in the south.
- In December 2006, a tearful President Hamid Karzai lamented that Afghan children were being maimed and killed by NATO and U.S. bombs and by the terrorism brought on by the war. In a heartfelt speech that brought audience members to tears, Karzai said the cruelty imposed on his people "is too much" and that Afghanistan cannot stop "the coalition from killing our children."
- In May 2007, after heavy aerial bombing by the American military had recently killed 40 to 60 Afghan civilians, including women and children, wounded about 50 more, and destroyed some 100 houses, President Hamid Karzai summoned top foreign generals and diplomats to his palace to reiterate years of complaints over blameless deaths. At a news conference afterward, he said that Afghan lives should be valued too, and the Afghan people could no longer tolerate such casualties:
- In June 2007, after the deaths of more than 90 civilians in 10 days, President Hamid Karzai accused ISAFInternational Security Assistance ForceThe International Security Assistance Force is a NATO-led security mission in Afghanistan established by the United Nations Security Council on 20 December 2001 by Resolution 1386 as envisaged by the Bonn Agreement...
and the US-led military coalition in his country of "extreme" and "disproportionate" use of force. In his protestations, the Afghan president said that the foreign military forces in his country had to start working in accordance with his government's wishes.
- On October 28, 2007, in an interview on 60 Minutes60 Minutes60 Minutes is an American television news magazine, which has run on CBS since 1968. The program was created by producer Don Hewitt who set it apart by using a unique style of reporter-centered investigation....
, Afghan President Hamid Karzai stated that he had explicitly asked U.S. President George W. BushGeorge W. BushGeorge Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
to roll back the use of airstrikes – which had killed more than 270 civilians in 17 air strikes to date in 2007 alone – in his country, saying that he had delivered the message privately to Bush using "clear words" in August.
- In August 2008, President Hamid Karzai ordered a review of foreign troops in Afghanistan after his administration said 96 civilians were killed in an air raid by the U.S.-led coalition in western Herat. Already more than 500 civilians had been killed during operations by foreign and Afghan forces in 2008 according to the Afghan government and some aid groups.
- In September 2008, Afghan President Hamid Karzai protested the continued killing of innocent Afghan civilians by the foreign troops in his country when he addressed the United Nations General AssemblyUnited Nations General AssemblyFor two articles dealing with membership in the General Assembly, see:* General Assembly members* General Assembly observersThe United Nations General Assembly is one of the five principal organs of the United Nations and the only one in which all member nations have equal representation...
's annual gathering of world leaders in New York, and pointed out that it threatens the credibility that the current military situation is a partnership:
- On November 5, 2008, Afghan President Hamid Karzai pleaded U.S. President-elect Barack ObamaBarack ObamaBarack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
to put an end to civilian casualties in Afghanistan as villagers said U.S. warplanes bombed a wedding party, killing 37 people, including 23 children and 10 women. Karzai again demanded an immediate end of civilian-killing air strikes by U.S. warplanes, saying:
- On December 18, 2008, Afghan President Hamid Karzai again spoke of asking the United States to cooperate with his government in their military operations in his country. In a speech, he said that in the previous month he had again asked that the U.S. military in his country cooperate with his government, sending the U.S. government a list of demands about troop conduct, but did not say if he had received any response back.
- In April 2009, after American-led military forces killed 5 civilians, including two children and a nine-month-old baby, in a U.S. night raid in Khost province, Afghan President Hamid Karzai ordered his interior and defence ministries, the intelligence service and local government to investigate and present their findings to him. Those killed were the wife, brother, son, and daughter of an Afghan army colonel, as well as the unborn nine-month-old baby of his cousin's wife. Another daughter and his cousin's wife were wounded but survived. In a statement Karzai said that he had "for several years repeatedly asked the international military forces (to) carry out their counter-terrorism operations in ways that do not cause civilian casualties." He reiterated this demand and insisted that foreign forces adhere to a directive signed months ago to fully coordinate their operations with their Afghan counterparts and base them on accurate information.
- In March 2011, Karzai rejected American President Obama's and Gen. David Petraeus' apologies for U.S. helicopter gunners killing 9 Afghan boys ages 7–13 who were collecting firewood. "The apology is not enough," Karzai said. "Civilian casualties produced by the military operations of coalition forces are the cause of tension in relations between Afghanistan and the United States of America. The people of Afghanistan are fed up from these brutal incidents and apologies and condemnation cannot cure their pain." In response to the deaths of the boys, Petraeus ordered all field commanders and helicopter crews to again study their rules of engagement. One source claims more than 200 civilians killed in military operations and insurgent attacks in "recent weeks".
- In May 2011, Karzai Karzai issued a "final warning" as more civilians were killed in NATO airstrikes. He said the Afghan people can no longer tolerate the attacks, and that the U.S.-led coalition risks being seen as an "occupying force".
Afghan public protests over civilian deaths
- On July 4, 2002, in the first anti-American protest since the overthrow of the Taliban, about 200 Afghans marched through the streets of Kabul to express their outrage over attacks by U.S. forces which killed scores of civilians, including many children and 25 members of one family. According to Afghan Foreign Minister Abdullah, 44 people were killed and 120 wounded in the U.S. attacks on about a half dozen villages in Uruzgan province, which villagers said included an attack on a pre-wedding party.
- On May 29, 2006, large-scale rioting, fueled by anti-U.S. anger, swept through Afghanistan's capital, KabulKabulKabul , spelt Caubul in some classic literatures, is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. It is also the capital of the Kabul Province, located in the eastern section of Afghanistan...
, after a U.S. military truck crashed into a crowd of Afghan pedestrians. Afghan President Hamid Karzai's office said five people were killed in the vehicle crash. The U.S. military, in a statement issued earlier, had said at least one person was killed in the crash and six wounded, two of them critically. Afghan officials called it the worst day of rioting in Kabul since the overthrow of the Taliban regime. At least 8 people were killed and 109 wounded in the widespread anti-U.S. protests through the capital. Video from one rioting site after the crash showed a U.S. military vehicle firing in the direction of a crowd of Afghans. Dozens of protesters outside the U.S. Embassy screamed "Death to Americans!" while embassy personnel retreated to bunkers. "We want America out of this country! We hate America! They have no responsibility!" said protester Ajmal Jan.
- On April 30, 2007, thousands of Afghans staged a protest accusing USA-led coalition and Afghan troops of killing civilians in the western province of Herat. The protesters stormed a government district headquarters in Shindand, south of Herat city, where Western troops have a large base. The anti-U.S. protest came a day after an angry demonstration in eastern Nangahar province over the killing of civilians by coalition and Afghan forces there.
- On May 2, 2007, about 500 Afghan university students protested in the eastern province of Nangarhar alleging six civilians had been killed by US-led coalition troops a few days before. On that same day, Afghan and UN teams announced that their investigations had found that around 50 civilians were killed in days of ground fighting and bombing in a remote valley in the western province of Herat.
- On September 26, 2007, following a raid by foreign troops that left two religious leaders dead, about 500 Afghan protesters shut down the main highway out of KandaharKandaharKandahar is the second largest city in Afghanistan, with a population of about 512,200 as of 2011. It is the capital of Kandahar Province, located in the south of the country at about 1,005 m above sea level...
city with some chanting "Death to Canada" and "Death to foreigners" and calling on foreign troops to leave their country. The protesters accused American and Canadian soldiers of killing the two religious leaders during night raids on houses in Senjaray, a community on the outskirts of Kandahar city. Anger was also directed at Afghan President Hamid Karzai for allowing the foreign military presence in their country.
- On August 23, 2008, about 250 Afghan villagers gathered in angry demonstration to protest the deaths of 76 civilians, most of them children, killed in U.S.-led airstrikes near the village of Azizabad, about 120 kilometres south of HeratHeratHerāt is the capital of Herat province in Afghanistan. It is the third largest city of Afghanistan, with a population of about 397,456 as of 2006. It is situated in the valley of the Hari River, which flows from the mountains of central Afghanistan to the Karakum Desert in Turkmenistan...
city in western Afghanistan.
- On September 1, 2008, hundreds of citizens in the Afghan capital Kabul rushed into the streets and burnt tires on the Kabul-Jalalabad highway protesting the killing of three members of a Kabuli family, including two children, by U.S.-led troops. Residents said the U.S.-led troops, carrying out a pre-dawn raid in Hud Kheil area in the eastern quarter of Kabul, threw hand grenades into a house, killing Noorullah and two of his sons, one of whom was eight months old. Their deaths were the latest in a string of incidents that have angered Afghans and caused a split between the Afghan government and foreign troops.
- On October 16, 2008, protests by crowds condemning British forces and the Afghan government took place in Lashkar Gah, capital city of Helmand provinceHelmand ProvinceHelmand is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. It is in the southwest of the country. Its capital is Lashkar Gah. The Helmand River flows through the mainly desert region, providing water for irrigation....
, after a NATO airstrike killed as many as 18 women and children.
- On December 26, 2008, a crowd of hundreds of Afghans protested in Maywand districtMaywand DistrictMaiwand District is situated in the western part of the Kandahar Province, Afghanistan. It borders Helmand Province to the west, Ghorak District to the north, Khakrez District to the northeast, Zhari District to the east, and Panjwai District to the south. The population is 51,900 . The district...
in Kandahar provinceKandahar ProvinceKandahar or Qandahar is one of the largest of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan. It is located in southern Afghanistan, between Helmand, Oruzgan and Zabul provinces. Its capital is the city of Kandahar, which is located on the Arghandab River. The province has a population of nearly...
following overnight raids by U.S. military forces, claiming that innocent people were killed in the attack. Local villagers, angered by the military raids, blocked the main highway for three hours and burned tires.
- On March 7, 2009, hundreds of Afghan demonstrators in eastern Afghanistan blocked the path of a U.S. military convoy to condemn an early morning raid in Khost provinceKhost ProvinceKhost is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan. It is in the east of the country. Khost province used to be part of Paktia province in the past...
that killed four people and wounded two. Tahir Khan Sabari, the deputy governor of the province, said the four people killed were civilians, but the American military claimed they were militants. Demonstrators in KhostKhostKhost or Khowst is a city in eastern Afghanistan. It is the capital of Khost province, which is a mountainous region near Afghanistan's border with Pakistan...
city threw rocks at the American military convoy, shouted "Death to America", and burned tires, sending up dark plumes of smoke.
- On May 7, 2009, thousands of Afghan villagers shouting "Death to America" and "Death to the Government" protested in FarahFarah, AfghanistanFarah is a city in western Afghanistan, situated at 650 m altitude, and located on the Farah River. It is the capital of Farah Province, and has a population of approximately 109,409....
city over American bomber air strikes on May 4 that killed 147 civilians. Clashes with police started when people from the three villages struck by US B1-bombers brought 15 newly-discovered bodies in a truck to the house of the provincial governor. Four protesters were wounded when police opened fire. Going by the account of survivors, the air raid was not a brief attack by several aircraft acting on mistaken intelligence, but a sustained bombardment in which three villages were pounded to pieces. An Afghan government investigation concluded on May 16, 2009 with the Afghan Defense Ministry announcing an official death toll of 140 villagers. A copy of the government's list of the names and ages of each of the 140 dead showed that 93 of those killed were children, and only 22 were adult males.
- On December 9, 2009, some 5,000 Afghan villagers marched in protest over the killing of civilians in a pre-dawn attack by U.S. troops in Armul village, Laghman province in eastern Afghanistan. President Hamid Karzai's office said the attack had killed 6 civilians, including one woman, while NATO denied that any civilians had been killed in its military attack. A Reuters journalist, on the other hand, saw the bodies of a woman and 12 males, including two teenagers, and the top Laghman provincial council leader said that 13 civilians had been killed. The protesters were chanting slogans against the foreign troops in their country, as well as against Afghan president Hamid Karzai and the provincial governor, when Afghan troops opened fire on them. Four protesters were hit by bullets, two dying instantly and two were taken to a hospital, where residents said they died of their wounds.
- On December 30, 2009, protesters in Jalalabad set alight a US flag and an effigy of President Obama after chanting “Death to Obama” and “Death to foreign forces”. In Kabul, protesters held up banners showing photographs of dead children alongside placards demanding “Foreign troops leave Afghanistan” and “Stop killing us”. This was in response to reports that US-led forces had shot 10 villagers in their home, including 8 children, during a raid in the Ghazi Khan village in Narang district of the eastern province of Kunar.
- On January 21, 2010, angry Afghan villagers took to the streets in GhazniGhazniFor the Province of Ghazni see Ghazni ProvinceGhazni is a city in central-east Afghanistan with a population of about 141,000 people...
province to protest the deaths of civilians they claimed were killed in a raid by NATO troops. NATO's International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) claimed it had killed four insurgents including a 15-year-old boy during their raid in the Qarabagh District of Ghazni province the previous night. But 50 villagers brought five coffins to the provincial capital Ghazni city, claiming that three of the dead were civilians, including two children below the age of seven. The head of the provincial hospital where the bodies were initially taken said that his doctors told him that two children were among the bodies brought to them.
- On January 28, 2010, angry demonstrations took place outside Camp PhoenixCamp PhoenixCamp Phoenix is a NATO military installation in Afghanistan, maintained by the United States Army. It is located in Kabul, about six miles from the Kabul International Airport . Camp Phoenix is administered by the 26th "YANKEE" Maneuver Enhancement Brigade , Massachusetts Army National Guard...
, a U.S. military base on the outskirts of Kabul, after NATO troops killed an Afghan religious leader who had been sitting in a parked car with his two young sons while waiting for a NATO ISAF convoy to pass by. According to witnesses, the fourth ISAF vehicle in the convoy opened fire on the parked car without provocation. At least 16 bullet holes were later counted on the car's exterior and Mullah Mohmmad Younas was killed by three bullets in his chest and one in his abdomen. ISAF confirmed the shooting of a civilian, offered sympathies, and said it was investigating.
Civilian casualties by insurgent forces
While most of the Afghan protests have been over the civilian casualties caused by international military forces, on October 24, 2008, over 1,000 Afghans also took to the streets of MihtarlamMihtarlam
Mihtarlam , also spelled Mehtar Lam, is a town in Afghanistan, the capital of Laghman Province and center of Mihtarlam District. It is the only large urban settlement in the province. The town is situated in the valley formed by the Alishing and Alingar rivers, 47 km northwest of the city of...
in eastern Afghanistan to protest the killing of 26 young men by Taliban militants. A Taliban spokesperson said the men who were taken off a bus were targeted because they were members or recruits of Afghan security forces, but Afghan officials said that the men were civilians on their way to Iran to find work.
In considering civilian casualties caused collectively by insurgent forces, it should be noted that the armed insurgency in Afghanistan against the government and foreign military forces is composed of many diverse individuals and groups that are motivated by a range of different goals and ideologies, that do not necessarily identify as "Taliban", and that do not act under a single line of authority.
International protests, demonstrations and rallies
The deaths of thousands of Afghan civilians caused directly and indirectly by the U.S. and NATO bombing campaigns have been a major underlying focus of protests against the war in Afghanistan since it began a decade ago.Protests
Protests against the invasion of Afghanistan
The ongoing decade-long War in Afghanistan has prompted large protests around the world, with the first large-scale demonstrations beginning in the days leading up to the war's official launch on October 7, 2001....
around the world, starting with large-scale global demonstrations in the days leading up to the official launch of U.S. Operation Enduring Freedom's under George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
and Donald Rumsfeld
Donald Rumsfeld
Donald Henry Rumsfeld is an American politician and businessman. Rumsfeld served as the 13th Secretary of Defense from 1975 to 1977 under President Gerald Ford, and as the 21st Secretary of Defense from 2001 to 2006 under President George W. Bush. He is both the youngest and the oldest person to...
in October 2001, have taken place every year since.
See also
- British forces casualties in AfghanistanBritish forces casualties in AfghanistanThe United Kingdom was one of the first countries which took part in Operation Enduring Freedom to topple the Taliban regime in autumn 2001.As of 27 November 2011 there has been a total of 390 fatalities of British Forces personnel including MoD civilians...
- Bagram torture and prisoner abuseBagram torture and prisoner abuseIn 2005, The New York Times obtained a 2,000-page United States Army report concerning the homicides of two unarmed civilian Afghan prisoners by U.S. armed forces in 2002 at the Bagram Theater Internment Facility in Bagram, Afghanistan. The prisoners, Habibullah and Dilawar, were chained to the...
- Canadian Forces casualties in AfghanistanCanadian Forces casualties in AfghanistanThe number of Canadian Forces' fatalities resulting from Canadian military activities in Afghanistan is the largest for any single Canadian military mission since the Korean War between 1950 and 1953...
- Canadian Afghan detainee abuse scandalCanadian Afghan detainee abuse scandalThe Canadian Afghan detainee issue concerns whether or not the Government of Canada and/or the Canadian Forces had knowledge about alleged abusive treatment of detainees in Afghanistan...
- Coalition casualties in AfghanistanCoalition casualties in AfghanistanAs of November 30, 2011, there have been 2,744 coalition deaths in Afghanistan as part of ongoing coalition operations since the invasion in 2001. In this total, the American figure is for deaths "In and Around Afghanistan" which, as defined by the U.S...
- Criticism of the War on TerrorismCriticism of the War on TerrorismCriticism of the War on Terror addresses the issues, morals, ethics, efficiency, economics, and other questions surrounding the War on Terror...
- Casualties of the Iraq War
- International public opinion on the war in AfghanistanInternational public opinion on the war in AfghanistanInternational public opinion is largely opposed to the war in Afghanistan. A 47-nation global survey of public opinion conducted in June 2007 by the Pew Global Attitudes Project found considerable opposition to the U.S. and NATO military operations in Afghanistan...
- Protests against the invasion of AfghanistanProtests against the invasion of AfghanistanThe ongoing decade-long War in Afghanistan has prompted large protests around the world, with the first large-scale demonstrations beginning in the days leading up to the war's official launch on October 7, 2001....
- Chenagai airstrikeChenagai airstrikeThe Chenagai airstrike took place on October 30, 2006, around 5:00 am. local time. Missiles were fired at a madrassa in Chenagai village in Bajaur region of Pakistan. An eyewitness has stated that the madrassa was filled with local students who had resumed studies after the Eid ul-Fitr holiday. 82...
- Azizabad airstrikeAzizabad airstrikeThe Azizabad airstrike took place on Friday 22 August 2008 in the village of Azizabad which is located in Shindand district, Herat Province, Afghanistan...
- Granai Incident
- Kunduz airstrikeKunduz airstrikeThe Kunduz airstrike took place on Friday 4 September 2009 at roughly 2:30 am local time, southwest of Kunduz City, Kunduz province in northern Afghanistan, near the hamlets of Omar Kheil by the border of the Chahar Dara and Ali Abad districts...
External links
- Rethink Afghanistan – Part 4: Civilian Casualties 12 min. section of the full documentary film Rethink Afghanistan available online
- Afghanistan Under the US "War on Terror" photo gallery from RAWA, an Afghan women's association
- After First Denying Involvement, US Forces Admit Killing Two Pregnant Afghan Women & Teenager – video report by Democracy Now!Democracy Now!Democracy Now! and its staff have received several journalism awards, including the Gracie Award from American Women in Radio & Television; the George Polk Award for its 1998 radio documentary Drilling and Killing: Chevron and Nigeria's Oil Dictatorship, on the Chevron Corporation and the deaths of...
- The Afghan Victim Memorial Project database and photos
- "War Against Terrorism" in Afghanistan
- Casualties in Afghanistan & Iraq
- War Report Afghan Archives – Civilian Casualties
- Casualty Monitor: Monitoring and analysis of data on civilian and British military casualties in Afghanistan and Iraq
- The Worsening Situation in Afghanistan
- The Reality Page

