
Dalton's law
Encyclopedia
In chemistry
and physics
, Dalton's law (also called Dalton's law of partial pressures) states that the total pressure
exerted by a gas
eous mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressure
s of each individual component in a gas mixture. This empirical
law was observed by John Dalton
in 1801 and is related to the ideal
gas laws
.
Mathematically, the pressure of a mixture of gases can be defined as the summation
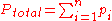 or
or 
where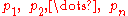 represent the partial pressure of each component.
represent the partial pressure of each component.
It is assumed that the gases do not react
with each other.
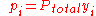
where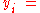 the mole fraction of the i-th component in the total mixture of n components .
the mole fraction of the i-th component in the total mixture of n components .
The relationship below provides a way to determine the volume based concentration
of any individual gaseous component.
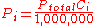
where: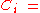 is the concentration of the ith component expressed in ppm.
is the concentration of the ith component expressed in ppm.
Dalton's law is not exactly followed by real gases. Those deviations are considerably large at high pressures. In such conditions, the volume occupied by the molecules can become significant compared to the free space between them. Moreover, the short average distances between molecules raises the intensity of intermolecular force
s between gas molecules enough to substantially change the pressure exerted by them. Neither of those effects are considered by the ideal gas model.
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
and physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, Dalton's law (also called Dalton's law of partial pressures) states that the total pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
exerted by a gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
eous mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressure
Partial pressure
In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
s of each individual component in a gas mixture. This empirical
Empirical
The word empirical denotes information gained by means of observation or experimentation. Empirical data are data produced by an experiment or observation....
law was observed by John Dalton
John Dalton
John Dalton FRS was an English chemist, meteorologist and physicist. He is best known for his pioneering work in the development of modern atomic theory, and his research into colour blindness .-Early life:John Dalton was born into a Quaker family at Eaglesfield, near Cockermouth, Cumberland,...
in 1801 and is related to the ideal
Ideal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of a set of randomly-moving, non-interacting point particles. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics.At normal conditions such as...
gas laws
Gas laws
The early gas laws were developed at the end of the 18th century, when scientists began to realize that relationships between the pressure, volume and temperature of a sample of gas could be obtained which would hold for all gases...
.
Mathematically, the pressure of a mixture of gases can be defined as the summation
 or
or 
where
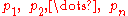 represent the partial pressure of each component.
represent the partial pressure of each component.It is assumed that the gases do not react
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
with each other.
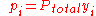
where
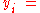 the mole fraction of the i-th component in the total mixture of n components .
the mole fraction of the i-th component in the total mixture of n components .The relationship below provides a way to determine the volume based concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of any individual gaseous component.
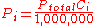
where:
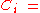 is the concentration of the ith component expressed in ppm.
is the concentration of the ith component expressed in ppm.Dalton's law is not exactly followed by real gases. Those deviations are considerably large at high pressures. In such conditions, the volume occupied by the molecules can become significant compared to the free space between them. Moreover, the short average distances between molecules raises the intensity of intermolecular force
Intermolecular force
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction or repulsion which act between neighboring particles: atoms, molecules or ions. They are weak compared to the intramolecular forces, the forces which keep a molecule together...
s between gas molecules enough to substantially change the pressure exerted by them. Neither of those effects are considered by the ideal gas model.
See also
- Henry's lawHenry's lawIn physics, Henry's law is one of the gas laws formulated by William Henry in 1803. It states that:An equivalent way of stating the law is that the solubility of a gas in a liquid at a particular temperature is proportional to the pressure of that gas above the liquid...
- Amagat's lawAmagat's lawAmagat's law or the Law of Partial Volumes of 1880 describes the behaviour and properties of mixtures of ideal gases...
- Boyle's lawBoyle's lawBoyle's law is one of many gas laws and a special case of the ideal gas law. Boyle's law describes the inversely proportional relationship between the absolute pressure and volume of a gas, if the temperature is kept constant within a closed system...
- Combined gas lawCombined gas lawThe combined gas law is a gas law which combines Charles's law, Boyle's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. These laws each relate one thermodynamic variable to another mathematically while holding everything else constant. Charles's law states that volume and temperature are directly proportional to each...
- Gay-Lussac's lawGay-Lussac's lawThe expression Gay-Lussac's law is used for each of the two relationships named after the French chemist Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac and which concern the properties of gases, though it is more usually applied to his law of combining volumes, the first listed here...
- Mole (unit)Mole (unit)The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
- Partial pressurePartial pressureIn a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
- Raoult's law

