
Finkelstein's test
Encyclopedia

Medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis refers both to the process of attempting to determine or identify a possible disease or disorder , and to the opinion reached by this process...
DeQuervain's tenosynovitis
DeQuervain's syndrome
De Quervain syndrome , is a tendinosis of the sheath or tunnel that surrounds two tendons that control movement of the thumb.-Eponym:It is named after the Swiss surgeon Fritz de Quervain who first identified it in 1895...
in people who have wrist
Wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as 1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand;...
pain
Pain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
. To perform the test, the examining physician grasps the thumb and the hand is ulnar deviated sharply, as shown in the image. If sharp pain occurs along the distal radius (top of forearm, close to wrist; see image), DeQuervain's tenosynovitis is likely.
Some other doctors ask their patients to flex their thumb and clench their fist over the thumb followed by ulnar deviation for Finkelstein's test.
Purpose: Finkelstein's test is one way to determine if there is tenosynovitis
Tenosynovitis
Tenosynovitis is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sheath that surrounds a tendon. Symptoms of tenosynovitis include pain, swelling and difficulty moving the particular joint where the inflammation occurs. When the condition causes the finger to "stick" in a flexed position, this is called...
in the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons of the wrist. These two tendons belong to the first dorsal compartment.
First dorsal compartment: abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis.
Second dorsal compartment: extensor carpi radialis longus and extensor carpi radialis brevis.
Third dorsal compartment: extensor pollicis longus.
Fourth dorsal compartment: extensor digitorum and extensor indicis.
Fifth dorsal compartment: extensor digiti minimi.
Sixth dorsal compartment: extensor carpi ulnaris.
Origin/Background on Finkelstein: Finkelstein's test was described by Harry Finkelstein (1865-1939), an American surgeon
Surgeon
In medicine, a surgeon is a specialist in surgery. Surgery is a broad category of invasive medical treatment that involves the cutting of a body, whether human or animal, for a specific reason such as the removal of diseased tissue or to repair a tear or breakage...
, in 1930. A similar test was previously described by Eichoff, in which the thumb is placed in the palm of the hand and held with the fingers, and the hand is then ulnar deviated (see second image), causing intense pain over the radial styloid which disappears if the thumb is released. This test produces more false positive results than the test described by Finkelstein.
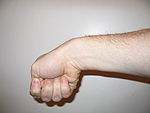
Evaluation procedure: The examiner then moves the wrist into ulnar deviation.
Positive test: If there is an increased pain in the radial styloid process and along the length of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons, then the test is positive for De Quervain’s syndrome.
Special Considerations/implications: Because this test may create pain in other tissues to come back a false positive or may come back negative though de Quervain’s or katherines syndrome is still suspected, the patient can radially deviate against resistance to possibly reproduce pain.

