
Fuchs's theorem
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, the Fuchs' theorem, named after Lazarus Fuchs
, states that a second order differential equation
of the form
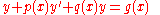
has a solution expressible by a generalised Frobenius series when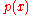 ,
, 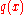 and
and 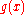 are analytical at
are analytical at  or
or  is a regular singular point. That is, any solution to this second order differential equation can be written as
is a regular singular point. That is, any solution to this second order differential equation can be written as
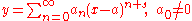
for some real s, or

for some real r, where y0 is a solution of the first kind.
Its radius of convergence is at least as large as the minimum of the radii of convergence of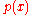 ,
, 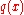 and
and 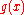 .
.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, the Fuchs' theorem, named after Lazarus Fuchs
Lazarus Fuchs
Lazarus Immanuel Fuchs was a German mathematician who contributed important research in the field of linear differential equations...
, states that a second order differential equation
Differential equation
A differential equation is a mathematical equation for an unknown function of one or several variables that relates the values of the function itself and its derivatives of various orders...
of the form
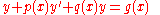
has a solution expressible by a generalised Frobenius series when
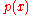 ,
, 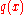 and
and 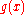 are analytical at
are analytical at  or
or  is a regular singular point. That is, any solution to this second order differential equation can be written as
is a regular singular point. That is, any solution to this second order differential equation can be written as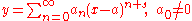
for some real s, or

for some real r, where y0 is a solution of the first kind.
Its radius of convergence is at least as large as the minimum of the radii of convergence of
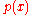 ,
, 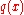 and
and 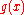 .
.

