
Grubbs' test for outliers
Encyclopedia
Grubbs' test also known as the maximum normed residual
test, is a statistical test
used to detect outlier
s in a univariate
data set assumed to come from a normally distributed population.
Grubbs' test detects one outlier at a time. This outlier is expunged from the dataset and the test is iterated until no outliers are detected. However, multiple iterations change the probabilities of detection, and the test should not be used for sample sizes of six or less since it frequently tags most of the points as outliers.
Grubbs' test is defined for the hypothesis:
The Grubbs' test statistic is defined as: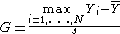
with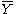 and s denoting the sample mean and standard deviation
and s denoting the sample mean and standard deviation
, respectively. The Grubbs test statistic is the largest absolute deviation from the sample mean in units of the sample standard deviation.
This is the two-sided version of the test. The Grubbs test can also be defined as a one-sided test. To test whether the minimum value is an outlier, the test statistic is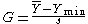
with Ymin denoting the minimum value. To test whether the maximum value is an outlier, the test statistic is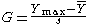
with Ymax denoting the maximum value.
For the two-sided test, the hypothesis of no outliers is rejected at significance level α if
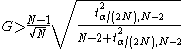
with tα/(2N),N−2 denoting the upper critical value
of the t-distribution with N − 2 degrees of freedom
and a significance level of α/(2N). For the one-sided tests, replace α/(2N) with α/N.
, or a histogram
should show any obviously outlying points. A normal probability plot
may also be useful.
Errors and residuals in statistics
In statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
test, is a statistical test
Statistical hypothesis testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of making decisions using data, whether from a controlled experiment or an observational study . In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, according to a pre-determined threshold...
used to detect outlier
Outlier
In statistics, an outlier is an observation that is numerically distant from the rest of the data. Grubbs defined an outlier as: An outlying observation, or outlier, is one that appears to deviate markedly from other members of the sample in which it occurs....
s in a univariate
Univariate
In mathematics, univariate refers to an expression, equation, function or polynomial of only one variable. Objects of any of these types but involving more than one variable may be called multivariate...
data set assumed to come from a normally distributed population.
Definition
Grubbs' test is based on the assumption of normality. That is, one should first verify that the data can be reasonably approximated by a normal distribution before applying the Grubbs' test.Grubbs' test detects one outlier at a time. This outlier is expunged from the dataset and the test is iterated until no outliers are detected. However, multiple iterations change the probabilities of detection, and the test should not be used for sample sizes of six or less since it frequently tags most of the points as outliers.
Grubbs' test is defined for the hypothesis:
- H0: There are no outliers in the data set
- Ha: There is at least one outlier in the data set
The Grubbs' test statistic is defined as:
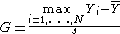
with
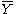 and s denoting the sample mean and standard deviation
and s denoting the sample mean and standard deviationStandard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
, respectively. The Grubbs test statistic is the largest absolute deviation from the sample mean in units of the sample standard deviation.
This is the two-sided version of the test. The Grubbs test can also be defined as a one-sided test. To test whether the minimum value is an outlier, the test statistic is
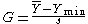
with Ymin denoting the minimum value. To test whether the maximum value is an outlier, the test statistic is
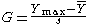
with Ymax denoting the maximum value.
For the two-sided test, the hypothesis of no outliers is rejected at significance level α if
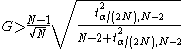
with tα/(2N),N−2 denoting the upper critical value
Critical value
-Differential topology:In differential topology, a critical value of a differentiable function between differentiable manifolds is the image ƒ in N of a critical point x in M.The basic result on critical values is Sard's lemma...
of the t-distribution with N − 2 degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom (statistics)
In statistics, the number of degrees of freedom is the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary.Estimates of statistical parameters can be based upon different amounts of information or data. The number of independent pieces of information that go into the...
and a significance level of α/(2N). For the one-sided tests, replace α/(2N) with α/N.
Related techniques
Several graphical techniques can, and should, be used to detect outliers. A simple run sequence plot, a box plotBox plot
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot is a convenient way of graphically depicting groups of numerical data through their five-number summaries: the smallest observation , lower quartile , median , upper quartile , and largest observation...
, or a histogram
Histogram
In statistics, a histogram is a graphical representation showing a visual impression of the distribution of data. It is an estimate of the probability distribution of a continuous variable and was first introduced by Karl Pearson...
should show any obviously outlying points. A normal probability plot
Normal probability plot
The normal probability plot is a graphical technique for normality testing: assessing whether or not a data set is approximately normally distributed....
may also be useful.

