
Görtler vortices
Encyclopedia
In fluid dynamics
, Görtler vortices are secondary flows that appears in a boundary layer flow along a concave wall. If the boundary layer is thin compared to the radius of curvature
of the wall, the pressure remains constant across the boundary layer. On the other hand, if the boundary layer thickness is comparable to the radius of curvature, the centrifugal action creates a pressure variation across the boundary layer. This leads to the centrifugal instability (Görtler instability) of the boundary layer and consequent formation of Görtler vortices.
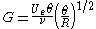
where
Görtler instability occurs when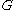 exceeds, about 0.3.
exceeds, about 0.3.
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
, Görtler vortices are secondary flows that appears in a boundary layer flow along a concave wall. If the boundary layer is thin compared to the radius of curvature
Radius of curvature (mathematics)
In geometry, the radius of curvature, R, of a curve at a point is a measure of the radius of the circular arc which best approximates the curve at that point. If this value taken to be positive when the curve turns anticlockwise and negative when the curve turns clockwise...
of the wall, the pressure remains constant across the boundary layer. On the other hand, if the boundary layer thickness is comparable to the radius of curvature, the centrifugal action creates a pressure variation across the boundary layer. This leads to the centrifugal instability (Görtler instability) of the boundary layer and consequent formation of Görtler vortices.
Görtler number
The onset of Görtler vortices can be predicted using the dimensionless number called Görtler number. It is the ratio of centrifugal effects to the viscous effects in the boundary layer and is defined as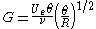
where
-
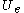 = external velocity
= external velocity -
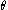 = momentum thickness
= momentum thickness -
 = kinematic viscosity
= kinematic viscosity -
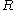 = radius of curvature of the wall
= radius of curvature of the wall
Görtler instability occurs when
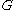 exceeds, about 0.3.
exceeds, about 0.3.

