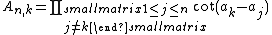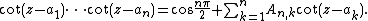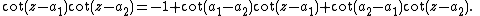Hermite's cotangent identity
Encyclopedia
In mathematics, Hermite's cotangent identity is a trigonometric identity discovered by Charles Hermite
. Suppose a1, ..., an are complex number
s, no two of which differ by an integer multiple of π. Let
(in particular, A1,1, being an empty product
, is 1). Then
The simplest non-trivial example is the case n = 2:
Charles Hermite
Charles Hermite was a French mathematician who did research on number theory, quadratic forms, invariant theory, orthogonal polynomials, elliptic functions, and algebra....
. Suppose a1, ..., an are complex number
Complex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
s, no two of which differ by an integer multiple of π. Let
(in particular, A1,1, being an empty product
Empty product
In mathematics, an empty product, or nullary product, is the result of multiplying no factors. It is equal to the multiplicative identity 1, given that it exists for the multiplication operation in question, just as the empty sum—the result of adding no numbers—is zero, or the additive...
, is 1). Then
The simplest non-trivial example is the case n = 2: