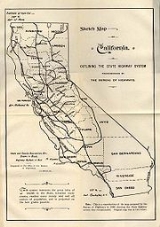
History of California's state highway system
Encyclopedia
The state highway
system in the U.S. state
of California
dates back to 1896, when the state took over maintenance of the Lake Tahoe Wagon Road. Construction of a large connected system began in 1912, after the state's voters approved an $18 million bond issue for over 3000 miles (4900 km) of highways. The last large addition was made by the California State Assembly
in 1959, after which only minor changes have been made.
 The first state road was authorized on March 26, 1895, when a law created the post of "Lake Tahoe Wagon Road Commissioner" to maintain the Lake Tahoe Wagon Road (the 1852 Johnson's Cut-off of the California Trail
The first state road was authorized on March 26, 1895, when a law created the post of "Lake Tahoe Wagon Road Commissioner" to maintain the Lake Tahoe Wagon Road (the 1852 Johnson's Cut-off of the California Trail
), now US 50 from Smith Flat - 3 miles (5 km) east of Placerville - to the Nevada
state line. The 58 mile (93 km) road had been operated as a toll road
until 1886, when El Dorado County bought it; the county deed
ed the road to the state on February 28, 1896. Funding was only enough for minimal improvements, including a stone bridge
over the South Fork American River in 1901.
 Also in 1895, on March 27, the legislature created the three-person Bureau of Highways to coordinate efforts by the counties to build good roads. The bureau traveled to every county of the state in 1895 and 1896 and prepared a map of a recommended system of state roads, which they submitted to the governor
Also in 1895, on March 27, the legislature created the three-person Bureau of Highways to coordinate efforts by the counties to build good roads. The bureau traveled to every county of the state in 1895 and 1896 and prepared a map of a recommended system of state roads, which they submitted to the governor
on November 25, 1896. The legislature replaced the Bureau of Highways with the Department of Highways on April 1, 1897, three days after it passed a law creating a second state highway from Sacramento to Folsom - another part of what became US 50 - to be maintained by three "Folsom Highway Commissioners". This was the last highway maintained by a separate authority, as the next state road, the Mono Lake Basin State Road (now part of SR 120), was designated by the legislature in 1899 to be built and maintained by the Department of Highways.
Several more state highways were legislated in the next decade, and the legislature passed a law creating the Department of Engineering on March 11, 1907. This new department, in addition to non-highway duties, was to maintain all state highways, including the Lake Tahoe Wagon Road. On March 22, 1909 the "State Highways Act" was passed, taking effect on December 31, 1910 after a successful vote by the people of the state in November. This law authorized the Department of Engineering to issue $18 million in bond
s for a "continuous and connected state highway system" that would connect all county seat
s. To this end, the department created the three-member California Highway Commission
on August 8, 1911 to take full charge of the construction and maintenance of this system. As with the 1896 plan by the Bureau of Highways, the Highway Commission traveled the state to determine the best routes, which ended up stretching about 3100 miles (5000 km). Construction began in mid-1912, with groundbreaking
on Contract One - now part of SR 82 in San Mateo County - on August 7. Noteworthy portions of the system built by the commission included the Ridge Route
in southern California
and the Yolo Causeway
west from Sacramento.
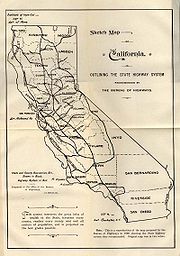
 Because the first bond issue did not provide enough funding, the "State Highways Act of 1915" was approved by the legislature on May 20, 1915 and the voters in November 1916, taking effect on December 31. This gave the Department of Engineering an additional $12 million to complete the original system and $3 million for a further approximately 680 miles (1100 km) specified by the law. At this time, each route was assigned a number from 1 to 34; this system of labeling routes, although never marked with signs, remained until the 1964 renumbering. In 1917, the legislature gave the California Highway Commission statutory recognition, and turned over the approximately 750 miles (1200 km) of roads adopted by legislative act, until then maintained by the State Engineer, to the commission. Where not serving as extensions of existing routes, these - and routes subsequently added legislatively in 1917 and 1919 - were given numbers from 35 to 45. A third bond issue was approved by the voters at a special election on July 1, 1919, and provided $20 million more for the existing routes and the same amount for new extensions totaling about 1800 miles (2900 km), adding Routes 46 to 64 to the system. The three bond issues together totaled 5560 miles (8948 km), of which just over 40% (60% if the 1919 bond issue is left out) was completed or under construction in mid-1920.
Because the first bond issue did not provide enough funding, the "State Highways Act of 1915" was approved by the legislature on May 20, 1915 and the voters in November 1916, taking effect on December 31. This gave the Department of Engineering an additional $12 million to complete the original system and $3 million for a further approximately 680 miles (1100 km) specified by the law. At this time, each route was assigned a number from 1 to 34; this system of labeling routes, although never marked with signs, remained until the 1964 renumbering. In 1917, the legislature gave the California Highway Commission statutory recognition, and turned over the approximately 750 miles (1200 km) of roads adopted by legislative act, until then maintained by the State Engineer, to the commission. Where not serving as extensions of existing routes, these - and routes subsequently added legislatively in 1917 and 1919 - were given numbers from 35 to 45. A third bond issue was approved by the voters at a special election on July 1, 1919, and provided $20 million more for the existing routes and the same amount for new extensions totaling about 1800 miles (2900 km), adding Routes 46 to 64 to the system. The three bond issues together totaled 5560 miles (8948 km), of which just over 40% (60% if the 1919 bond issue is left out) was completed or under construction in mid-1920.
 The Department of Engineering became part of the new Department of Public Works in 1921, and the California Highway Commission was entirely separated as its own department in 1923. In order to pay for the roads, a 2-cent per gallon gasoline tax was approved in 1923. The legislature continued to add highways to the system, including the Mother Lode Highway (now part of SR 49) in 1921 and the Arrowhead Trail (now I-15 north of Barstow) in 1925. In January 1928, the California State Automobile Association
The Department of Engineering became part of the new Department of Public Works in 1921, and the California Highway Commission was entirely separated as its own department in 1923. In order to pay for the roads, a 2-cent per gallon gasoline tax was approved in 1923. The legislature continued to add highways to the system, including the Mother Lode Highway (now part of SR 49) in 1921 and the Arrowhead Trail (now I-15 north of Barstow) in 1925. In January 1928, the California State Automobile Association
and Automobile Club of Southern California
, which had already been placing guide and warning signs along state highways, marked the U.S. Highways along several of the most major state highways. The California Toll Bridge Authority was created in 1929 to acquire and operate all toll bridges on state highways, including the San Francisco – Oakland Bay Bridge and Carquinez Bridge
.
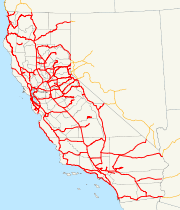 After 1927 and 1929, in which no highways were added to the system, the legislature authorized the construction of 23 new routes in 1931, which were numbered from 72 to 80 when not forming extensions of existing routes. Two years later, another 213 sections of highway were added, almost doubling the total length of state highways to about 14000 miles (23000 km); the last-assigned route number jumped from 80 to 202. Many of these new routes, as well as a number of existing routes, were incorporated into the initial system of state sign routes in 1934, also posted by the auto clubs.
After 1927 and 1929, in which no highways were added to the system, the legislature authorized the construction of 23 new routes in 1931, which were numbered from 72 to 80 when not forming extensions of existing routes. Two years later, another 213 sections of highway were added, almost doubling the total length of state highways to about 14000 miles (23000 km); the last-assigned route number jumped from 80 to 202. Many of these new routes, as well as a number of existing routes, were incorporated into the initial system of state sign routes in 1934, also posted by the auto clubs.
The Division of Highways took over signage on state highways from the auto clubs in 1947, though at least the Auto Club of Southern California continued to place signs on city streets until 1956.
State highway
State highway, state road or state route can refer to one of three related concepts, two of them related to a state or provincial government in a country that is divided into states or provinces :#A...
system in the U.S. state
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
of California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
dates back to 1896, when the state took over maintenance of the Lake Tahoe Wagon Road. Construction of a large connected system began in 1912, after the state's voters approved an $18 million bond issue for over 3000 miles (4900 km) of highways. The last large addition was made by the California State Assembly
California State Assembly
The California State Assembly is the lower house of the California State Legislature. There are 80 members in the Assembly, representing an approximately equal number of constituents, with each district having a population of at least 420,000...
in 1959, after which only minor changes have been made.
1895 to 1919

California Trail
The California Trail was an emigrant trail of about across the western half of the North American continent from Missouri River towns to what is now the state of California...
), now US 50 from Smith Flat - 3 miles (5 km) east of Placerville - to the Nevada
Nevada
Nevada is a state in the western, mountain west, and southwestern regions of the United States. With an area of and a population of about 2.7 million, it is the 7th-largest and 35th-most populous state. Over two-thirds of Nevada's people live in the Las Vegas metropolitan area, which contains its...
state line. The 58 mile (93 km) road had been operated as a toll road
Toll road
A toll road is a privately or publicly built road for which a driver pays a toll for use. Structures for which tolls are charged include toll bridges and toll tunnels. Non-toll roads are financed using other sources of revenue, most typically fuel tax or general tax funds...
until 1886, when El Dorado County bought it; the county deed
Deed
A deed is any legal instrument in writing which passes, or affirms or confirms something which passes, an interest, right, or property and that is signed, attested, delivered, and in some jurisdictions sealed...
ed the road to the state on February 28, 1896. Funding was only enough for minimal improvements, including a stone bridge
Stone Bridge
Stone Bridge may refer to:Bridges by that name:* Stone Bridge , the bridge across the Seyhan River in Adana, Turkey.* Stone Bridge , the bridge across Griboedov Canal in Saint Petersburg, Russia....
over the South Fork American River in 1901.

Governor of California
The Governor of California is the chief executive of the California state government, whose responsibilities include making annual State of the State addresses to the California State Legislature, submitting the budget, and ensuring that state laws are enforced...
on November 25, 1896. The legislature replaced the Bureau of Highways with the Department of Highways on April 1, 1897, three days after it passed a law creating a second state highway from Sacramento to Folsom - another part of what became US 50 - to be maintained by three "Folsom Highway Commissioners". This was the last highway maintained by a separate authority, as the next state road, the Mono Lake Basin State Road (now part of SR 120), was designated by the legislature in 1899 to be built and maintained by the Department of Highways.
Several more state highways were legislated in the next decade, and the legislature passed a law creating the Department of Engineering on March 11, 1907. This new department, in addition to non-highway duties, was to maintain all state highways, including the Lake Tahoe Wagon Road. On March 22, 1909 the "State Highways Act" was passed, taking effect on December 31, 1910 after a successful vote by the people of the state in November. This law authorized the Department of Engineering to issue $18 million in bond
Bond (finance)
In finance, a bond is a debt security, in which the authorized issuer owes the holders a debt and, depending on the terms of the bond, is obliged to pay interest to use and/or to repay the principal at a later date, termed maturity...
s for a "continuous and connected state highway system" that would connect all county seat
County seat
A county seat is an administrative center, or seat of government, for a county or civil parish. The term is primarily used in the United States....
s. To this end, the department created the three-member California Highway Commission
California Highway Commission
The California Highway Commission was established in 1895 and continued until 1978 as the primary state highway bureaucracy in California.Their first noticeable efforts centered on the Lake Tahoe Wagon Road over the Sierra Nevada mountains...
on August 8, 1911 to take full charge of the construction and maintenance of this system. As with the 1896 plan by the Bureau of Highways, the Highway Commission traveled the state to determine the best routes, which ended up stretching about 3100 miles (5000 km). Construction began in mid-1912, with groundbreaking
Groundbreaking
Groundbreaking, also known as cutting, sod-cutting, turning the first sod or a sod-turning ceremony, is a traditional ceremony in many cultures that celebrates the first day of construction for a building or other project. Such ceremonies are often attended by dignitaries such as politicians and...
on Contract One - now part of SR 82 in San Mateo County - on August 7. Noteworthy portions of the system built by the commission included the Ridge Route
Ridge Route
The Ridge Route, officially the Castaic-Tejon Route, was a two-lane highway running between Los Angeles and Kern counties, California. Opened in 1915 and paved with concrete between 1917 and 1921, the road was the first paved highway directly linking the Los Angeles Basin with the San Joaquin...
in southern California
Southern California
Southern California is a megaregion, or megapolitan area, in the southern area of the U.S. state of California. Large urban areas include Greater Los Angeles and Greater San Diego. The urban area stretches along the coast from Ventura through the Southland and Inland Empire to San Diego...
and the Yolo Causeway
Yolo Causeway
The Yolo Causeway is a 3.2-mile long elevated highway viaduct on Interstate 80 that crosses the Yolo Bypass floodplain and connects the cities of Sacramento, California and Davis, California ....
west from Sacramento.

1920 to 1958

California State Automobile Association
AAA Northern California, Nevada and Utah , formerly known as the California State Automobile Association , is one of the largest motor clubs in the American Automobile Association National Federation...
and Automobile Club of Southern California
Automobile Club of Southern California
The Automobile Club of Southern California is the Southern California affiliate of the American Automobile Association federation of motor clubs...
, which had already been placing guide and warning signs along state highways, marked the U.S. Highways along several of the most major state highways. The California Toll Bridge Authority was created in 1929 to acquire and operate all toll bridges on state highways, including the San Francisco – Oakland Bay Bridge and Carquinez Bridge
Carquinez Bridge
The Carquinez Bridge refers to parallel bridges spanning the Carquinez Strait, forming part of Interstate 80 between Crockett and Vallejo, California. The name originally referred to a single cantilever bridge built in 1927, helping to form a direct route between San Francisco and Sacramento. A...
.

The Division of Highways took over signage on state highways from the auto clubs in 1947, though at least the Auto Club of Southern California continued to place signs on city streets until 1956.
List of route numbers, 1917-1931
| Approximate present number(s) | From | To | History | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | US 101, US 199 | Sausalito | Oregon Oregon Oregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern... |
|
| 2 | US 101, I-5 | San Francisco | San Diego | |
| 3 | I-80, SR 65, SR 99, I-5 | Sacramento | Oregon Oregon Oregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern... |
|
| 4 | SR 99, I-5 | Sacramento | Los Angeles | |
| 5 | I-5, I-205, I-580, SR 238, I-680, SR 17 | Stockton | Santa Cruz, with a branch to Oakland | |
| 6 | I-80 | Sacramento | Davis | |
| 7 | I-680, I-80, SR 113, I-5 | Benicia | Red Bluff | |
| 8 | SR 37, SR 121, SR 12 | Novato | Fairfield | |
| 9 | SR 118, I-210, SR 66 | San Fernando | San Bernardino | |
| 10 | SR 198 | San Lucas | Sequoia National Park Sequoia National Park Sequoia National Park is a national park in the southern Sierra Nevada east of Visalia, California, in the United States. It was established on September 25, 1890. The park spans . Encompassing a vertical relief of nearly , the park contains among its natural resources the highest point in the... |
|
| 11 | US 50 | Sacramento | Nevada Nevada Nevada is a state in the western, mountain west, and southwestern regions of the United States. With an area of and a population of about 2.7 million, it is the 7th-largest and 35th-most populous state. Over two-thirds of Nevada's people live in the Las Vegas metropolitan area, which contains its... |
|
| 12 | I-8 | San Diego | El Centro | |
| 13 | SR 219, SR 108 | Salida | East of Sonora Pass Sonora Pass Sonora Pass is the second-highest highway pass in the Sierra Nevada, lower by 321 ft. than Tioga Pass to the south. State Route 108 traverses the pass.-Description:... |
|
| 14 | SR 123, I-80 | Oakland | Martinez | |
| 15 | SR 20 | Ukiah | Emigrant Gap | |
| 16 | SR 175 | Hopland | Lakeport | |
| 17 | I-80, SR 49 | Roseville | Nevada City | |
| 18 | SR 140 | Merced | Yosemite National Park Yosemite National Park Yosemite National Park is a United States National Park spanning eastern portions of Tuolumne, Mariposa and Madera counties in east central California, United States. The park covers an area of and reaches across the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada mountain chain... |
|
| 19 | SR 71, SR 60 | West of Claremont | Riverside | |
| 20 | SR 299 | Arcata | Redding | 1910 bond issue: Weaverville to Redding (Trinity County seat lateral) 1916 bond issue: Arcata to Salyer and Helena to Weaverville}} |
| 21 | SR 162, SR 70 | Richvale | Quincy | |
| 22 | SR 156 | North of Hollister | San Juan Bautista | |
| 23 | SR 14, US 395, SR 89 | Saugus | South Lake Tahoe | |
| 24 | SR 12, SR 49, SR 4 | Lodi | Southeast of Markleeville | |
| 25 | SR 49 | Nevada City | Downieville | |
| 26 | I-10, SR 86 | San Bernardino | El Centro | |
| 27 | I-8 | El Centro | Arizona Arizona Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix... |
|
| 28 | SR 299 | Redding | Nevada Nevada Nevada is a state in the western, mountain west, and southwestern regions of the United States. With an area of and a population of about 2.7 million, it is the 7th-largest and 35th-most populous state. Over two-thirds of Nevada's people live in the Las Vegas metropolitan area, which contains its... |
|
| 29 | SR 36, US 395 | Red Bluff | Nevada Nevada Nevada is a state in the western, mountain west, and southwestern regions of the United States. With an area of and a population of about 2.7 million, it is the 7th-largest and 35th-most populous state. Over two-thirds of Nevada's people live in the Las Vegas metropolitan area, which contains its... |
|
| 30 | SR 70 | Oroville | Quincy | |
| 31 | I-215, I-15 | San Bernardino | Nevada Nevada Nevada is a state in the western, mountain west, and southwestern regions of the United States. With an area of and a population of about 2.7 million, it is the 7th-largest and 35th-most populous state. Over two-thirds of Nevada's people live in the Las Vegas metropolitan area, which contains its... |
|
| 32 | SR 152 | Chowchilla | Gilroy | |
| 33 | SR 46 | Bakersfield | Paso Robles | |
| 34 | SR 104, SR 88 | Galt | Southeast of Luther Pass Luther Pass Luther Pass is a mountain pass in California in the Sierra Nevada, between the Carson River basin and Lake Tahoe. It is traversed by State Route 89 and lies on the boundary between Alpine County and El Dorado County... |
|
| 35 | SR 36, SR 3 | Mad River Mad River, California Mad River is a census-designated place in Trinity County, California. Mad River is located in the in southern part of the county. Mad River sits at an elevation of . The ZIP Code is 95552 and Mad River is inside area code 530... |
Peanut Peanut, California Peanut is a tiny unincorporated community in Trinity County, California. It is located on Highway 3, south of Hayfork and north of Highway 36 at an elevation of 2499 feet.... |
|
| 36 | N/A | Northwest of Downieville | Downieville | |
| 37 | I-80 | Auburn | Truckee | |
| 38 | SR 89, I-80 | South Lake Tahoe | Nevada Nevada Nevada is a state in the western, mountain west, and southwestern regions of the United States. With an area of and a population of about 2.7 million, it is the 7th-largest and 35th-most populous state. Over two-thirds of Nevada's people live in the Las Vegas metropolitan area, which contains its... |
|
| 39 | SR 28 | Tahoe City | Nevada Nevada Nevada is a state in the western, mountain west, and southwestern regions of the United States. With an area of and a population of about 2.7 million, it is the 7th-largest and 35th-most populous state. Over two-thirds of Nevada's people live in the Las Vegas metropolitan area, which contains its... |
|
| 40 | SR 120 | West of Chinese Camp | Lee Vining | |
| 41 | SR 180 | General Grant Grove | Kings Canyon | |
| 42 | SR 9, SR 236 | Saratoga Gap | Big Basin Redwoods State Park Big Basin Redwoods State Park Big Basin Redwoods State Park is a state park in the U.S. state of California, located in Santa Cruz County, about northwest of Santa Cruz. The park contains almost all of the Waddell Creek watershed, which was formed by the seismic uplift of its rim, and the erosion of its center by the many... |
|
| 43 | SR 18 | Waterman Canyon | Big Bear Lake Big Bear Lake Big Bear Lake is a reservoir in the San Bernardino Mountains, in San Bernardino County, California, United States. At a surface elevation of , it has an east-west length of approximately 7 miles and is approximately 2.5 miles at its widest measurement, though the lake's width mostly averages a... |
|
| 44 | SR 236 | Boulder Creek | Big Basin Redwoods State Park Big Basin Redwoods State Park Big Basin Redwoods State Park is a state park in the U.S. state of California, located in Santa Cruz County, about northwest of Santa Cruz. The park contains almost all of the Waddell Creek watershed, which was formed by the seismic uplift of its rim, and the erosion of its center by the many... |
|
| 45 | SR 162 | Biggs | Willows | |
| 46 | SR 96, SR 169 | North of Yreka | Klamath | |
| 47 | SR 32 | Orland | Chico | |
| 48 | SR 128 | Cloverdale | Albion | |
| 49 | SR 29, SR 53 | Calistoga | North of Lower Lake | |
| 50 | SR 16 | Northeast of Lower Lake | Rumsey Rumsey, California Rumsey is an unincorporated community in Yolo County, California. It is located northwest of Esparto, in the Capay Valley, in the northwestern part of the county. Rumsey's ZIP Code is 95679 and its area code 530. It lies at an elevation of 420 feet .... |
|
| 51 | SR 12 | Santa Rosa | Sonoma | |
| 52 | SR 131 | Tiburon | Mill Valley | |
| 53 | SR 12 | Fairfield | Lodi | |
| 54 | SR 16 | East of Sloughhouse Sloughhouse, California Sloughhouse is an unincorporated community in Sacramento County, California, United States. Sloughhouse is located on California State Route 16 east-southeast of downtown Sacramento. Sloughhouse has a post office with ZIP code 95683, which was established in 1916. Jared Sheldon, who built a... |
Plymouth | |
| 55 | SR 35 | San Francisco | North of Santa Cruz | |
| 56 | SR 1 | Cambria | Carmel | |
| 57 | SR 166, SR 119, SR 178 | Santa Maria | Freeman Junction Freeman Junction, California Freeman Junction, a ghost town in Kern County, California, USA, was first homesteaded in the 1920s by Clare C. Miley, who was born in 1900. By the 1930s a restaurant, gas station and mining activities dominated the site.... |
|
| 58 | SR 58, I-40 | Mojave | Arizona Arizona Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix... |
|
| 59 | SR 138 | Gorman | Lancaster | |
| 60 | SR 1 | El Rio | San Juan Capistrano | |
| 61 | SR 2 | La Canada Flintridge | Red Box Gap | |
| 62 | SR 39 | Azusa | San Gabriel Canyon | |
| 63 | SR 168 | Big Pine | Oasis Oasis, Mono County, California Oasis is an unincorporated community in Mono County, California. It is located in Fish Lake Valley east-southeast of Mount Bancroft. Oasis is at the junction of California State Route 266 and California State Route 168. The 2000 Census reports that Oasis had a population of 22.A post office... |
|
| 64 | I-10 | Mecca | Blythe | |
| 65 | SR 49 | Auburn | Sonora | |
| 66 | SR 120 | Lathrop | Manteca | |
| 67 | SR 129 | San Juan Bautista | Chittenden | |
| 68 | US 101 | San Francisco | San Jose | |
| 69 | I-580 | San Rafael | Point San Quentin | |
| 70 | SR 222 | Ukiah | Mendocino State Hospital | |
| 71 | US 101 | Crescent City | Oregon Oregon Oregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern... |
See Also
- El Camino Real (California)El Camino Real (California)El Camino Real and sometimes associated with Calle Real usually refers to the 600-mile California Mission Trail, connecting the former Alta California's 21 missions , 4 presidios, and several pueblos, stretching from Mission San Diego de Alcalá in San Diego...
- El Camino ViejoEl Camino ViejoEl Camino Viejo à Los Angeles , also known as the Old Los Angeles Trail, established in 1820's, was the oldest north-south trail in the interior of Alta California...
- California TrailCalifornia TrailThe California Trail was an emigrant trail of about across the western half of the North American continent from Missouri River towns to what is now the state of California...
- Southern Immigrant Trail
- Stockton - Los Angeles RoadStockton - Los Angeles RoadStockton-Los Angeles Road, also known as the Millerton Road, Stockton-Mariposa Road, Stockton-Fort Miller Road or the Stockton-Visalia Road was established about 1853 following the discovery of gold on the Kern River in Old Tulare County...
- Butterfield Overland MailButterfield Overland MailThe Butterfield Overland Mail Trail was a stagecoach route in the United States, operating from 1857 to 1861. It was a conduit for the U.S. mail from two eastern termini, Memphis, Tennessee and St. Louis, Missouri, meeting Fort Smith, Arkansas, and continuing through Indian Territory, New Mexico,...

