
Hotelling's lemma
Encyclopedia
Hotelling's lemma is a result in microeconomics that relates the supply of a good to the profit of the good's producer. It was first shown by Harold Hotelling
, and is widely used in the theory of the firm
. The lemma is very simple, and can be stated:
Let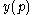 be a firm's net supply function in terms of a certain good's price (
be a firm's net supply function in terms of a certain good's price (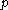 ). Then:
). Then:
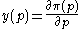
for the profit function of the firm in terms of the good's price, assuming that
the profit function of the firm in terms of the good's price, assuming that 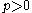 and that derivative exists.
and that derivative exists.
The proof of the theorem stems from the fact that for a profit-maximizing firm, the maximum of the firm's profit at some output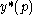 is given by the minimum? of
is given by the minimum? of 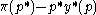 at some price,
at some price, 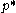 , namely where
, namely where  holds. Thus,
holds. Thus, 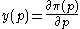 ; QED.
; QED.
The proof is also a corollary of the envelope theorem
.
π(p * ) should be "maximized" not minimized
See, Tan calculus or Varian Micro Economic Analysis
Harold Hotelling
Harold Hotelling was a mathematical statistician and an influential economic theorist.He was Associate Professor of Mathematics at Stanford University from 1927 until 1931, a member of the faculty of Columbia University from 1931 until 1946, and a Professor of Mathematical Statistics at the...
, and is widely used in the theory of the firm
Theory of the firm
The theory of the firm consists of a number of economic theories that describe the nature of the firm, company, or corporation, including its existence, behavior, structure, and relationship to the market.-Overview:...
. The lemma is very simple, and can be stated:
Let
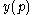 be a firm's net supply function in terms of a certain good's price (
be a firm's net supply function in terms of a certain good's price (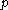 ). Then:
). Then: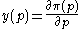
for
 the profit function of the firm in terms of the good's price, assuming that
the profit function of the firm in terms of the good's price, assuming that 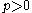 and that derivative exists.
and that derivative exists.The proof of the theorem stems from the fact that for a profit-maximizing firm, the maximum of the firm's profit at some output
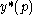 is given by the minimum? of
is given by the minimum? of 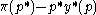 at some price,
at some price, 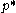 , namely where
, namely where  holds. Thus,
holds. Thus, 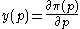 ; QED.
; QED.The proof is also a corollary of the envelope theorem
Envelope theorem
The envelope theorem is a theorem about optimization problems in microeconomics. It may be used to prove Hotelling's lemma, Shephard's lemma, and Roy's identity...
.
See also
- Hotelling's lawHotelling's lawHotelling's law is an observation in economics that in many markets it is rational for producers to make their products as similar as possible. This is also referred to as the principle of minimum differentiation as well as Hotelling's "linear city model"...
- Hotelling's ruleHotelling's ruleHotelling's rule states that the most socially and economically profitable extraction path of a non-renewable resource is one along which the price of the resource, determined by the marginal net revenue from the sale of the resource, increases at the rate of interest...
- Supply and demandSupply and demandSupply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded by consumers will equal the quantity supplied by producers , resulting in an...
- Shephard's lemmaShephard's lemmaShephard's lemma is a major result in microeconomics having applications in the theory of the firm and in consumer choice. The lemma states that if indifference curves of the expenditure or cost function are convex, then the cost minimizing point of a given good with price p_i is unique...
π(p * ) should be "maximized" not minimized
See, Tan calculus or Varian Micro Economic Analysis

