
Köhler theory
Encyclopedia
Water vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
condenses and forms liquid cloud drops, and is based on equilibrium thermodynamics. It combines the Kelvin effect, which describes the change in saturation vapor pressure due to a curved surface, and Raoult's Law, which relates the saturation vapor pressure to the solute. It is an important process in the field of cloud physics
Cloud physics
Cloud physics is the study of the physical processes that lead to the formation, growth and precipitation of clouds. Cloud formations are composed of microscopic droplets of liquid water , tiny crystals of ice , or both...
.
Köhler equation:
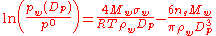
where
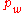 is the droplet water vapor pressure,
is the droplet water vapor pressure, 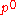 is the corresponding saturation vapor pressure over a flat surface,
is the corresponding saturation vapor pressure over a flat surface, 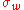 is the droplet surface tension,
is the droplet surface tension, 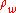 is the density of pure water,
is the density of pure water, 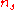 is the moles of solute,
is the moles of solute, 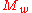 is the molecular weight of water, and
is the molecular weight of water, and 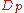 is the cloud drop diameter.
is the cloud drop diameter.Köhler curve
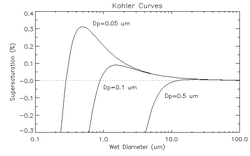
The Köhler curve is the visual representation of the Köhler equation. It shows the supersaturation at which the cloud drop is in equilibrium with the environment over a range of droplet diameters. The exact shape of the curve is dependent upon the amount and composition of the solute. The Köhler curves where the solute is sodium chlorideSodium chloride
Sodium chloride, also known as salt, common salt, table salt or halite, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaCl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of the ocean and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms...
are different than when the solute is sodium nitrate
Sodium nitrate
Sodium nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula NaNO3. This salt, also known as Chile saltpeter or Peru saltpeter to distinguish it from ordinary saltpeter, potassium nitrate, is a white solid which is very soluble in water...
or ammonium sulfate
Ammonium sulfate
Ammonium sulfate , 2SO4, is an inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses. The most common use is as a soil fertilizer. It contains 21% nitrogen as ammonium cations, and 24% sulfur as sulfate anions...
.
The figure above shows three Köhler curves of sodium chloride. Consider a point on the graph where the wet diameter is 0.1 micrometers and the supersaturation is 0.35%. Since the relative humidity
Relative humidity
Relative humidity is a term used to describe the amount of water vapor in a mixture of air and water vapor. It is defined as the partial pressure of water vapor in the air-water mixture, given as a percentage of the saturated vapor pressure under those conditions...
is above 100%, the droplet will grow until it is in thermodynamic equilibrium. As the droplet grows, it never encounters equilibrium, and thus grows without bound. However, if the supersaturation is only 0.3%, the drop will only grow until about 0.5 micrometers. The supersaturation at which the drop will grow without bound is called the critical supersaturation. The diameter at which the curve peaks is called the critical diameter.

