
La Ferrería
Encyclopedia
| Chalchihuites Culture – Archaeological Site | ||
| Name: | La Ferrería Archaeological site | |
| Type: | Mesoamerican archaeology | |
| Location: | City of Durango Durango, Durango -Climate:The city of Durango has a semi-arid climate, classified as Bsk in the Koppen system. The climate is temperate in the western portion , with the average annual temperature being 15 °C and consisting of an average annual rainfall of 1,600 millimeters. In the eastern region, the average... , Durango Durango Durango officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Durango is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is located in Northwest Mexico. With a population of 1,632,934, it has Mexico's second-lowest population density, after Baja... |
|
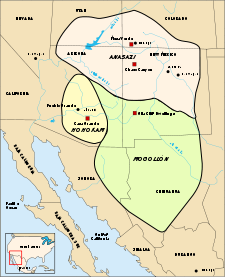
| Region: | Oasisamerica Oasisamerica Oasisamerica was a broad cultural area in pre-Columbian southwestern North America. It extended from modern-day Utah down to southern Chihuahua, and from the coast on the Gulf of California eastward to the Río Bravo river valley... - Mesoamerica Mesoamerica Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and... |
|
| Coordinates: | 23°57′39"N 104°38′55"W | |
| Culture: | Chichimec - Chalchihuites | |
| Language: | ||
| Chronology: | 875- 1450 CE | |
| Period: | Mesoamerican Classical - Postclassical | |
| INAH Web Page: | La Ferrería Archaeological site | |
La Ferrería is an archaeological site located 7 kilometers south of the City of Durango
Durango, Durango
-Climate:The city of Durango has a semi-arid climate, classified as Bsk in the Koppen system. The climate is temperate in the western portion , with the average annual temperature being 15 °C and consisting of an average annual rainfall of 1,600 millimeters. In the eastern region, the average...
, in the state of Durango
Durango
Durango officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Durango is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is located in Northwest Mexico. With a population of 1,632,934, it has Mexico's second-lowest population density, after Baja...
, México, at the “Cerro de La Ferrería”, on the side of the Tunal River.
In the surrounding region mainly are Mesquite and Aloe, the fauna comprises hares, rabbits, foxes, coyotes, squirrel and lizards.
The first inhabitants of this region were Nahua, nomads from the North of the continent, two thousand years ago. During the postclassical period the city was occupied by Zacatecas people and their contemporaries tepehuanos, from the southeast of the Guadiana Valley up to “Nombre de Dios”.
La Ferrería was first inhabited by a group that basically subsisted from farming corn, beans and squash, and were hunter-gatherers to complete their diet; because of its proximity to the Tunal river, it is assumed that hunting and fishing were common activities. It has been detected that the site was occupied several times between 875 and 1450 CE.
The site includes archaeological finds such as: circular ritual spaces, bird bones and stone rings, that provide indications of ties with cultures of the American southwest and especially with Paquimé, which could hypothetically mean or suggest a fusion between late northern Mesoamerican cultures and the American southwest.
Background
Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a mountain range in western Mexico.-Setting:The range runs north to south, from just south of the Sonora–Arizona border southeast through eastern Sonora, western Chihuahua, Sinaloa, Durango, Zacatecas, Nayarit, Jalisco, Aguascalientes to Guanajuato, where it joins...
offered to the Toltec
Toltec
The Toltec culture is an archaeological Mesoamerican culture that dominated a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo in the early post-classic period of Mesoamerican chronology...
and Nahuatlaca tribes, both whom took advantage of the large accidental stone conformations to survive in the wilderness of the territory. The new formations formed as the only security for the tribes that moved among Northern Mexico and the Valley of Anahuac, eventually becoming a home-state for these tribes who then began to form small communities, united by language and region.
The Huichol, Cora
Cora people
The Cora are an indigenous ethnic group of Western Central Mexico that live in the Sierra de Nayarit and in La Mesa de Nayar in the Mexican states of Jalisco and Nayarit. They call themselves náayarite , whence the name of the present day Mexican state of Nayarit...
, and Tarahumara
Tarahumara
The Rarámuri or Tarahumara are a Native American people of northwestern Mexico who are renowned for their long-distance running ability...
Tepehuanos incorporated perfectly distinct nations, each with evident sedentary purposes, and a strong family structure, all whilst setting aside the bellicose attitude of the Chichimec tribe of the center of the then-current Republic. The exceptions were the Acaxee
Acaxee
Acaxee was a tribe or group of tribes in the Sierra Madre Occidental in eastern Sinaloa and NW Durango. The spoke a Tarachatitian language in the Southern Uto-Aztecan language family. Their culture was based on horticulture and the exploitation of wild animal and plant life...
, Humas, and Xiximes who were constantly at war but always on the look-out for final settlements in the region of the Quebradas.
On the east bank of the state a longitudinal zone can be found, that extends from the current state of Zacatecas
Zacatecas
Zacatecas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Zacatecas is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas....
to the la Laguna
Comarca Lagunera
The Comarca Lagunera is the 9th largest metropolitan area in Mexico, and is located between two states, Coahuila and Durango.-Geography:The Comarca Lagunera is formed by 15 municipios; 5 in Coahuila The Comarca Lagunera is the 9th largest metropolitan area in Mexico, and is located between two...
area between the entities of Durango and Coahuila
Coahuila
Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Coahuila de Zaragoza is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico...
. The "Indios Laguneros" (Laguna Indians) traveled interchangeably between this area, they were characterized by their rebellious attitude, instability, religious customs and for being hunters and gatherers. These Natives of which so little was recorded were the first inhabitants of the region long before they were exterminated by the Spanish
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
colonists. Today, only a few remain of the Tepehuanos, Huicholes, Coras and Tarahumara tribes.
There is an opinion which assumes that Mesoamerican cultures would have migrated northward. Hence Oasisamerica
Oasisamerica
Oasisamerica was a broad cultural area in pre-Columbian southwestern North America. It extended from modern-day Utah down to southern Chihuahua, and from the coast on the Gulf of California eastward to the Río Bravo river valley...
would be a branch of neighboring southerners. In that regard, the development of Oasisamerican cultures, such as those from northern Mesoamerica, would have been related to groups originally inhabiting western Mexico. Archaeological evidence suggests an affiliation with uto-nahua groups would have taken agriculture to the Oasisamerican region. Although agricultural techniques were imported from the south, Oasisamerican villages built a civilization with particular characteristics, that maintained relations with Mesoamerica farmers.
Must remember that Durango is at the south border of the Mogollon – Anasazi cultures influence area
Site Investigation
Spanish exploration began in 1531 with the Nuño de Guzmán expedition. In the following decades, especially under the command of Francisco de IbarraFrancisco de Ibarra
Francisco de Ibarra was a Spanish Basque explorer, founder of the city of Durango, and governor of the Spanish province of Nueva Vizcaya, in present-day Mexico.-Biography:...
, several settlements were founded in the territory and further north of the city of Zacatecas
Zacatecas
Zacatecas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Zacatecas is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and its capital city is Zacatecas....
, when silver deposits were discovered. Ibarra named the new area Nueva Vizcaya in honor of his native land Biscay
Biscay
Biscay is a province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country, heir of the ancient Lord of Biscay. Its capital city is Bilbao...
(one of the Basque historical territories). Nueva Vizcaya included the current states of Chihuahua and Durango, as well as certain areas of eastern Sonora
Sonora
Sonora officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 72 municipalities; the capital city is Hermosillo....
and Sinaloa
Sinaloa
Sinaloa officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sinaloa is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 18 municipalities and its capital city is Culiacán Rosales....
and southeast of Coahuila
Coahuila
Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Coahuila de Zaragoza is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico...
. The region fell under the legal jurisdiction of the “Royal Guadalajara Audiencia”.
The first scientific news on this site was in 1948, by American anthropologist Alden Mason; four years later Charles Kelley, with a group of students from University of Chicago, started initial research work, from which he removed multiple archaeological pieces and prepared three essays.
The final disposition of archaeological material is unknown; however these were used by Kelley to establish occupation periods and site characterization. A proposed occupation between 800 to 1450 CE, was established, and its possible affiliation with the Chalchihuites culture, Guadiana branch.
After Kelley research, the site was abandoned by the authorities for 40 years, with the consequent destruction and looting by professional dealers of archaeological pieces.
Since 1993 there has been a few sporadic investigations.
The Site
The site has traces of at least two human groups occupation in the past, a nomad group that inhabited the site originally and a second group, sedentary, that built the larger structures on the hill.The site occupation is related to Chalchihuites culture,that had its most important site in Altavista
Altavista (Zacatecas)
Alta Vista, o Chalchihuites, is a mesoamerican archaeological site near the municipality of Chalchihuites in the Mexican state of Zacatecas, in the northwest of Mexico...
in the Zacatecas state, formed part of a branch called Guadiana, that reached up to El Zape, in the north of the state.
The cultural group that inhabited La Ferrería basically subsisted farming corn, beans and squash, and were hunter-gatherers.
Structures
There are important archaeological complexes, among them: circular ritual spaces, eastern pyramidal structure, ballgame court, columns and sunken patios.Casa de la estructuras escalonadas
The “stepped structures house” Is a small set with a sunken patio, characteristic detailed of prehispanic construction in the region; There are platforms on three sides of the patio, built with stone and clay, probably as a foundation of other ancient structures. Grinding activities were made in this area.Casa de los dirigentes
It is thought that the “Governor’s House” structure had residential uses, has a sunken patio carved in large rocks. There are remains of buildings perimeter as well as original drains.Just as other structures, platforms surround it, probably foundations of houses made with tree trunk columns and grass roofs. These buildings are adjacent to the columns hall and the small house.
Sala de las columnas
The “columns hall” are remnants of a small platform made of stone with large cylindrical columns, probably a meeting place, possibly ritual character.Casa colonial
The “colonial house” is next to the columns hall, are the foundations of a small, rustic house possibly colonial; It is a single room house, with evidence of metal foundry.Casa con piso de piedra
The “house with stone floors” is located at the top, it is necessary to climb the hill over an original pathway. There are two fixed mortars, probably from a nomadic group occupation, possibly reused by the later farmers groups.At the House, at the middle of the slope is a small sunken patio, one side was carved into the rock forming two walls and the floor. In one corner is a fixed mortar.
Casa de los sacerdotes
The “Priests House” has remains of houses layout, a cistern and several drainage channels of a pyramidal basement, probably a temple support, this structure is austere; had stairs and ramps, as well as a small sunken patio in the top.Ballgame court
It is one of the most damaged structures at the site; it comprises two stone parallel walls, of a construction that seems to be a ritual ballgame court. There are stone two stools inside, a platform, probably of large dimensions.Petroglyphs
There are two large engraved rocks:One of them depicts a small image that represents a priest with the arms high and wears a ceremonial ornament with antlers. The rock was partially polished and is the focal point of a small area dedicated to the cult, maybe considered the place of protective deities.
The second is located at the foot of the hill, it is very deteriorated, a hunting scene can be identified, a man with a bow, associated with two mammals.
Others Objects
Several objects were found on the site: pieces of ceramic, complete lithic pieces such as arrowheads, axes and mortars.Site Museum
The Museum was inaugurated in 2000. Has two exhibition halls of archaeological materials from La Ferrería, the chalchihuites culture, from the ritual everyday life, relations with other peoples and the archaeological work in the area.There is ceramic with abstract decorations, Catalan-style red band and some ceramic boxes. Large pots which served fro burials and Obsidian knives.
See also
- City of DurangoDurango, Durango-Climate:The city of Durango has a semi-arid climate, classified as Bsk in the Koppen system. The climate is temperate in the western portion , with the average annual temperature being 15 °C and consisting of an average annual rainfall of 1,600 millimeters. In the eastern region, the average...
- Durango StateDurangoDurango officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Durango is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is located in Northwest Mexico. With a population of 1,632,934, it has Mexico's second-lowest population density, after Baja...
- Altavista (Zacatecas)Altavista (Zacatecas)Alta Vista, o Chalchihuites, is a mesoamerican archaeological site near the municipality of Chalchihuites in the Mexican state of Zacatecas, in the northwest of Mexico...
- OasisamericaOasisamericaOasisamerica was a broad cultural area in pre-Columbian southwestern North America. It extended from modern-day Utah down to southern Chihuahua, and from the coast on the Gulf of California eastward to the Río Bravo river valley...

