
Maavägi
Encyclopedia
The Estonian Ground Force is the name of the unified ground forces
among the Estonian Defence Forces
where it has an offensive military formation role. It is currently also the largest military branch with the average size during the peacetime with around 6,000 soldiers, conscripts and officers.
The Maavägi development priorities are the capability to participate in missions outside the national territory and the capability to perform operations to protect the territory of Estonia, also in co-operation with the Allies. The Maavägi component of the operational structure consists of an infantry brigade and a homeland security structure. Deployable infantry battalion tactical group and some deployable CS, CSS units will developed in the Army structure in accordance with NATO Force Proposals requirements. Infantry brigade will act as a training and support frame for deployable units. Homeland security structure units will have the capability to carry out territorial military tasks and support civil structures.
The Maavägi is structured according to the principle of a reserve force which means that the main part of the defence forces of the state are units in a trained reserve. For a state with few human and economic resources, a reserve force based on the will of defence of the citizens is the only viable form of national defence.
In peacetime the reservists conduct normal lives and the state takes care of their training and the procurement of equipment and weapons. In wartime the reservists are mobilized into military units. The reserve units are formed on the territorial principle, i.e. conscripts from one area are called up at one time to one unit and after service they are sent to the reserve as one unit. The Estonian Army is always in constant defence readiness in co-operation with the other services.
was formed on 21 December 1918.
On 21 November 1928 eight 'Single Infantry Battalions' were created. The peacetime purpose of these battalions was to train conscripts. In wartime the battalion would reorganize itself into a regiment with a similar order of battle as the two initial reaction force regiments covering the eastern and southern borders. Each battalion's peacetime strength was a total 237 soldiers, in a regimental staff, a Signal Platoon, an Engineering Platoon, a Ski-Bicycle Platoon, a Building Platoon, and three infantry companies.
The war time order of battle would have transformed the battalion into a regiment size unit carrying the same unit number and would have included 3 infantry battalions, Signal Company, Engineering Company, Ski-Bicycle Company, Cavalry Company, Building Company, Commandant Commando and a CB Commando
. In total of 3153 men.
The 2nd Single Infantry Battalion was located at Tartu
; the 3rd Single Infantry Battalion was located at Valga; the 4th at Jõhvi
; the 5th at Rakvere
; the 6th Single Infantry Battalion was located at Pärnu
; the 8th Single Infantry Battalion at Valga; the 9th at Pärnu
; and the 10th Single Infantry Battalion was located at Tallinn
.
A reorganisation took place on February 1, 1940 and four divisions were created. The 4th Division staff was based in Viljandi
. The division was made up by the Pärnu-Viljandi Military District and Valga Military District. The division's last commander was Colonel
Jaan Maide. The four divisions were active until the Soviet occupation of Estonia.
(Fire and maneuver team), the
Salk
(Fireteam), the Jagu
(Section), the Rühm
(Platoon), the Kompanii
(Company), the Pataljon
(Battalion), and the Brigaad
(Brigade). The Diviis
or in (Division) is not in active use.
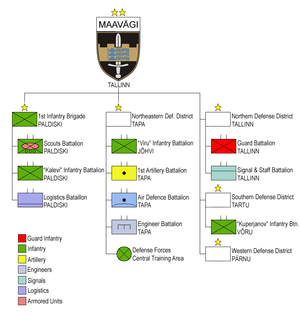 1st Infantry Brigade
1st Infantry Brigade
(likely to be motorized with APC-s) (Paldiski
)
North-Eastern Defence Command (Tapa
)
Northern Defence Command (Tallinn
)
Southern Defence Command (Võru
)
Western Defence Comamand (Pärnu
)
vehicles, also former Soviet, the modernization of the army branch is in the national defence policy agenda. In recent years Estonia has purchased more modern transport vehicles for the armed forces of the republic.
A partial list of planned new weapon purchases for the Defence Forces include:
Armoured fighting vehicles
Armoured vehicles
Anti-tank systems
Anti-air systems
Aviation
Army
An army An army An army (from Latin arma "arms, weapons" via Old French armée, "armed" (feminine), in the broadest sense, is the land-based military of a nation or state. It may also include other branches of the military such as the air force via means of aviation corps...
among the Estonian Defence Forces
Military of Estonia
The Estonian Defence Forces is the name of the unified armed forces of the Republic of Estonia. The Estonian military is a defence force consisting of Maavägi , Merevägi , Õhuvägi and a paramilitary organization Kaitseliit...
where it has an offensive military formation role. It is currently also the largest military branch with the average size during the peacetime with around 6,000 soldiers, conscripts and officers.
The Maavägi development priorities are the capability to participate in missions outside the national territory and the capability to perform operations to protect the territory of Estonia, also in co-operation with the Allies. The Maavägi component of the operational structure consists of an infantry brigade and a homeland security structure. Deployable infantry battalion tactical group and some deployable CS, CSS units will developed in the Army structure in accordance with NATO Force Proposals requirements. Infantry brigade will act as a training and support frame for deployable units. Homeland security structure units will have the capability to carry out territorial military tasks and support civil structures.
The Maavägi is structured according to the principle of a reserve force which means that the main part of the defence forces of the state are units in a trained reserve. For a state with few human and economic resources, a reserve force based on the will of defence of the citizens is the only viable form of national defence.
In peacetime the reservists conduct normal lives and the state takes care of their training and the procurement of equipment and weapons. In wartime the reservists are mobilized into military units. The reserve units are formed on the territorial principle, i.e. conscripts from one area are called up at one time to one unit and after service they are sent to the reserve as one unit. The Estonian Army is always in constant defence readiness in co-operation with the other services.
Interwar history
The 1st and 2nd Divisions were created during the Estonian War of Independence, the 2nd Division in December 1918-January 1919. The Scouts Single Infantry BattalionScouts Single Infantry Battalion
The Scoutspataljon is a professional infantry battalion of the Estonian Defence Forces.-History:The Scouts Single Infantry Battalion was founded on 21 December 1918 and was disbanded in 1940...
was formed on 21 December 1918.
On 21 November 1928 eight 'Single Infantry Battalions' were created. The peacetime purpose of these battalions was to train conscripts. In wartime the battalion would reorganize itself into a regiment with a similar order of battle as the two initial reaction force regiments covering the eastern and southern borders. Each battalion's peacetime strength was a total 237 soldiers, in a regimental staff, a Signal Platoon, an Engineering Platoon, a Ski-Bicycle Platoon, a Building Platoon, and three infantry companies.
The war time order of battle would have transformed the battalion into a regiment size unit carrying the same unit number and would have included 3 infantry battalions, Signal Company, Engineering Company, Ski-Bicycle Company, Cavalry Company, Building Company, Commandant Commando and a CB Commando
NCB
NCB is a three-letter abbreviation for:* Balanced Noise Criterion, a function for measuring noise levels* Narcotics Control Bureau - the Indian drug enforcement agency.* National Cargo Bureau* Nanyang Commercial Bank...
. In total of 3153 men.
The 2nd Single Infantry Battalion was located at Tartu
Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city of Estonia. In contrast to Estonia's political and financial capital Tallinn, Tartu is often considered the intellectual and cultural hub, especially since it is home to Estonia's oldest and most renowned university. Situated 186 km southeast of Tallinn, the...
; the 3rd Single Infantry Battalion was located at Valga; the 4th at Jõhvi
Jõhvi
Jõhvi is a town in north-eastern Estonia, and the capital of Ida-Viru County. The town is also an administrative centre of Jõhvi Parish. It is situated 50 km from the Russian border....
; the 5th at Rakvere
Rakvere
Rakvere is a town in northern Estonia and the county seat of Lääne-Viru County, 20 km south of the Gulf of Finland.-History:The earliest signs of human settlement dating back to the 3rd-5th centuries AD have been found on the present theatre hill. Probably to protect that settlement, a wooden...
; the 6th Single Infantry Battalion was located at Pärnu
Pärnu
Pärnu is a city in southwestern Estonia on the coast of Pärnu Bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea. It is a popular summer vacation resort with many hotels, restaurants, and large beaches. The Pärnu River flows through the city and drains into the Gulf of Riga...
; the 8th Single Infantry Battalion at Valga; the 9th at Pärnu
Pärnu
Pärnu is a city in southwestern Estonia on the coast of Pärnu Bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea. It is a popular summer vacation resort with many hotels, restaurants, and large beaches. The Pärnu River flows through the city and drains into the Gulf of Riga...
; and the 10th Single Infantry Battalion was located at Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
.
A reorganisation took place on February 1, 1940 and four divisions were created. The 4th Division staff was based in Viljandi
Viljandi
Viljandi is a town and municipality in southern Estonia with a population of 19,150 . It is the capital of Viljandi County. The town was first mentioned in 1283, upon being granted its town charter by Wilhelm von Endorpe....
. The division was made up by the Pärnu-Viljandi Military District and Valga Military District. The division's last commander was Colonel
Colonel
Colonel , abbreviated Col or COL, is a military rank of a senior commissioned officer. It or a corresponding rank exists in most armies and in many air forces; the naval equivalent rank is generally "Captain". It is also used in some police forces and other paramilitary rank structures...
Jaan Maide. The four divisions were active until the Soviet occupation of Estonia.
Organization
The Estonian Ground Force actively uses seven sizes of military unit: the LahingpaarLahingpaar
Lahingpaar, is a very small Estonian military unit led by a soldier that is subordinate to an infantry fireteam. Lahingpaar is bigger than an individual soldier but smaller than a salk . It is also the smallest military formation among the Estonian Ground Force infantry units.-Leadership:It...
(Fire and maneuver team), the
Salk
Salk
Salk, is a small military unit led by a senior soldier that is subordinate to an infantry squad. Salk is bigger than a lahingpaar but smaller than a jagu...
(Fireteam), the Jagu
Jagu
Jagu, is a small military unit led by a non-commissioned officer that is subordinate to an infantry platoon. Jagu is bigger than a salk but smaller than a rühm...
(Section), the Rühm
Rühm
Rühm, is a small military unit in the armed forces of Estonia led by a non-commissioned officer that is subordinate to an infantry company. Rühm is bigger than a jagu but smaller than a kompanii...
(Platoon), the Kompanii
Kompanii
Kompanii, is a medium military unit led by a junior officer that is subordinate to an infantry battalion. Kompanii is bigger than a rühm but smaller than a pataljon...
(Company), the Pataljon
Pataljon
Pataljon, is an average military unit led by a senior officer that is subordinate to an infantry brigade. Pataljon is bigger than a kompanii but smaller than a brigaad...
(Battalion), and the Brigaad
Brigaad
A brigaad, is a military unit commanded by a senior officer that is subordinate to an infantry division. A Brigade is bigger than a pataljon but smaller than a diviis...
(Brigade). The Diviis
Diviis
Diviis, is a large military unit led by a superior officer that is subordinate to an infantry brigade. Diviis is bigger than a brigaad but smaller than a korpus . There are currently no divisions among the Estonian Ground Force infantry units.-Leadership:It usually consists of 20000 to 35000...
or in (Division) is not in active use.
Peacetime structure

1st Infantry Brigade (Estonia)
The 1st Infantry Brigade is an infantry brigade of the military of Estonia. The brigade is stationed in Harju County, North Estonia and is a made up by the Ground Force reservists.-Peacetime Organization :* 1st Infantry Brigade...
(likely to be motorized with APC-s) (Paldiski
Paldiski
Paldiski is a town and Baltic Sea port situated on the Pakri peninsula of north-western Estonia. Originally a Swedish settlement known as Rågervik, it became a Russian naval base in the 18th century. The Russians renamed it Балтийский Порт Paldiski is a town and Baltic Sea port situated on the...
)
- Scouts BattalionScouts Single Infantry BattalionThe Scoutspataljon is a professional infantry battalion of the Estonian Defence Forces.-History:The Scouts Single Infantry Battalion was founded on 21 December 1918 and was disbanded in 1940...
(Paldiski) - Kalevi Infantry Battalion (Paldiski)
- Combat Service Support BattalionLogistics Battalion (Estonia)The Logistics Battalion is the name of the Estonian Defence Forces logistics force which has a supportive military formation role among the Estonian Ground Forces.-Role:...
(Paldiski)
North-Eastern Defence Command (Tapa
Tapa, Estonia
Tapa is a town in Lääne-Viru County, Estonia. Located at the junction of the country's Tallinn-Narva and Tallinn-Tartu-Valga railway lines, it is an important centre of transit for freight as well as rail passengers...
)
-
 Engineer BattalionPioneervägiThe Pioneeripataljon is the name of the Estonian Defence Forces combat engineering force which has a supportive military formation role among the Estonian Ground Forces.-Role:...
Engineer BattalionPioneervägiThe Pioneeripataljon is the name of the Estonian Defence Forces combat engineering force which has a supportive military formation role among the Estonian Ground Forces.-Role:...
(Tapa) - Artillery Battalion (Tapa)
- Air Defence Battalion (Tapa)
-
 Central Training AreaKeskpolügoonKeskpolügoon or the Central training area is the main military training field of the six areas used by the Estonian Defence Forces. Defense Forces central training area covers and is located in the eastern part of the Kuusalu municipality in Harju County...
Central Training AreaKeskpolügoonKeskpolügoon or the Central training area is the main military training field of the six areas used by the Estonian Defence Forces. Defense Forces central training area covers and is located in the eastern part of the Kuusalu municipality in Harju County... - Viru Infantry Battalion (JõhviJõhviJõhvi is a town in north-eastern Estonia, and the capital of Ida-Viru County. The town is also an administrative centre of Jõhvi Parish. It is situated 50 km from the Russian border....
)
Northern Defence Command (Tallinn
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
)
- Headquarters and Signal Battalion (Tallin)
- Guard Battalion (Tallin)
Southern Defence Command (Võru
Võru
Võru is a town and a municipality in south-eastern Estonia. It is the capital of Võru County and the centre of Võru Parish.-History:Võru was founded on 21 August 1784, according to the wish of the Empress Catherine II of Russia, by the order of Riga Governor general count George Browne, on the...
)
- Kuperjanov Infantry BattalionKuperjanov BattalionThe Kuperjanov Battalion is an Estonian Army infantry battalion of the Estonian Defence Forces...
(VõruVõruVõru is a town and a municipality in south-eastern Estonia. It is the capital of Võru County and the centre of Võru Parish.-History:Võru was founded on 21 August 1784, according to the wish of the Empress Catherine II of Russia, by the order of Riga Governor general count George Browne, on the...
)
Western Defence Comamand (Pärnu
Pärnu
Pärnu is a city in southwestern Estonia on the coast of Pärnu Bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea. It is a popular summer vacation resort with many hotels, restaurants, and large beaches. The Pärnu River flows through the city and drains into the Gulf of Riga...
)
- no regular military units
Wartime structure
Since the Maavägi is based on the principles of the reserve army, during the wartime it can man and arm during the conflict the following wartime structure:- 4 infantry brigadesBrigaadA brigaad, is a military unit commanded by a senior officer that is subordinate to an infantry division. A Brigade is bigger than a pataljon but smaller than a diviis...
- 3 air-defence battalions
- 2 engineer battalions
- 3 artillery battalions
- 2 combat support service battalions
- 2 scouts companies
- 2 anti-tank companies
- 2 signal companies
Equipment
Since the restoration of the Estonian Defence Forces on September 3, 1991 the Maavägi has developed with a great deal. Today the Ground Force operates with modern weapons and weapon-systems on foreign missions and future battlefields. Even though the current logistic support is still based on variety of different and mainly older WesternWestern world
The Western world, also known as the West and the Occident , is a term referring to the countries of Western Europe , the countries of the Americas, as well all countries of Northern and Central Europe, Australia and New Zealand...
vehicles, also former Soviet, the modernization of the army branch is in the national defence policy agenda. In recent years Estonia has purchased more modern transport vehicles for the armed forces of the republic.
Modernization
According to the long-term defence development plan the Ground Force is currently undergoing a modernization program. By the year 2018 the Ground Force is likely to be equipped with the modern tanks and infantry fighting vehicles along with the additional armoured personnel carriers. The artillery capabilities were greatly increased in 2008 with the purchase of 122mm field howitzers from Finland. The army is also planning to add some tactical air surveillance and transport capabilities in terms of helicopters.A partial list of planned new weapon purchases for the Defence Forces include:
Armoured fighting vehicles
- Main battle tankMain battle tankA main battle tank , also known as a battle tank or universal tank, is a tank that fills the heavy direct fire role of many modern armies. They were originally conceived to replace the light, medium, heavy and super-heavy tanks. Development was spurred onwards in the Cold War with the development...
s: ~50 units
Armoured vehicles
- Armoured personnel carrierArmoured personnel carrierAn armoured personnel carrier is an armoured fighting vehicle designed to transport infantry to the battlefield.APCs are usually armed with only a machine gun although variants carry recoilless rifles, anti-tank guided missiles , or mortars...
s: 57 units (Sisu XA-180) - Armoured personnel carrierArmoured personnel carrierAn armoured personnel carrier is an armoured fighting vehicle designed to transport infantry to the battlefield.APCs are usually armed with only a machine gun although variants carry recoilless rifles, anti-tank guided missiles , or mortars...
s: 81 units (Sisu XA-188)
Anti-tank systems
- C-90C90-CR (M3)The Instalaza C90 is a 90 mm disposable, shoulder-fired and one-man operated grenade launcher which can be fitted with a VN38-C night vision device for full night combat capability...
grenade launchers - Milan-2MILANMILAN " is French and German for "kite bird") is a European anti-tank guided missile. Design of the MILAN started in 1962. It was ready for trials in 1971, and was accepted for service in 1972. It is a wire guided SACLOS missile, which means the sight of the launch unit has to be aimed at the...
anti-tank guided missiles
Anti-air systems
- NASAMSNASAMSNASAMS is a distributed and networked medium to long range air-defence system. NASAMS was the first surface-based application for the AIM-120 AMRAAM and the first surface-to-air missile system in the western world with active radar guidance...
medium to long range anti-air systems. (most likely)
Aviation
- EC-135Eurocopter EC135The Eurocopter EC135 is a twin-engine civil helicopter produced by Eurocopter, widely used amongst police and ambulance services and for executive transport. It is capable of flight under instrument flight rules .-Development:...
transport helicopters (most likely)
Main bases of Estonian Ground Forces
- Jägala army base, expected 2014
- Tapa army baseTapa Army Base-History:Tapa military base is one of the few former Soviet military facilities which were taken over by the Estonian Defence Forces in early 90s. The first facility of the base was built in the autumn of 1939, an airfield, by the Red Army. After the end of World War II and the Soviet recapture of...

