
Nurgaliev's law
Encyclopedia
In population dynamics
, Nurgaliev's law is an equation that describes the rate of change of the size of a population at a given time, in terms of the current population size. It is a deterministic ordinary differential equation
in which the rate of change is expressed as a quadratic function
of the population size.
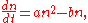
where 'n' is the size of a population, t is time measured in years, a is a half of the average probability of a birth of a male (the same for females) of a potential arbitrary parents pair within a year, b is an average probability of a death of a person within a year.
The first term is twice proportional to the half of population (number of males and number of females). The second term is responsible for death rate and has a clear and precise sense— death rates are constant in time but vary with position on the age scale (babies are at risk at birth, the middle aged are at risk of trauma
, old men become ill). It is known to demographers
, for example, that the probability of death within the first year of a life is precisely equal to similar probability for the 55th year of a life. Thus, in the given model, the average person dies under the same law as an unstable atomic nucleus
decays.
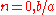 . The state with
. The state with  is stable whereas the state with
is stable whereas the state with 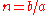 is unstable, meaning that the equation describes a population which crashes (tends to zero) when the death rate is greater than the birth rate and explodes (tends to infinity) when it is the birth rate that is greater.
is unstable, meaning that the equation describes a population which crashes (tends to zero) when the death rate is greater than the birth rate and explodes (tends to infinity) when it is the birth rate that is greater.
Population dynamics
Population dynamics is the branch of life sciences that studies short-term and long-term changes in the size and age composition of populations, and the biological and environmental processes influencing those changes...
, Nurgaliev's law is an equation that describes the rate of change of the size of a population at a given time, in terms of the current population size. It is a deterministic ordinary differential equation
Ordinary differential equation
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is a relation that contains functions of only one independent variable, and one or more of their derivatives with respect to that variable....
in which the rate of change is expressed as a quadratic function
Quadratic function
A quadratic function, in mathematics, is a polynomial function of the formf=ax^2+bx+c,\quad a \ne 0.The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola whose axis of symmetry is parallel to the y-axis....
of the population size.
Specification
Nurgaliev's law is expressed as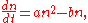
where 'n' is the size of a population, t is time measured in years, a is a half of the average probability of a birth of a male (the same for females) of a potential arbitrary parents pair within a year, b is an average probability of a death of a person within a year.
The first term is twice proportional to the half of population (number of males and number of females). The second term is responsible for death rate and has a clear and precise sense— death rates are constant in time but vary with position on the age scale (babies are at risk at birth, the middle aged are at risk of trauma
Physical trauma
Trauma refers to "a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident." It can also be described as "a physical wound or injury, such as a fracture or blow." Major trauma can result in secondary complications such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure and death...
, old men become ill). It is known to demographers
Demography
Demography is the statistical study of human population. It can be a very general science that can be applied to any kind of dynamic human population, that is, one that changes over time or space...
, for example, that the probability of death within the first year of a life is precisely equal to similar probability for the 55th year of a life. Thus, in the given model, the average person dies under the same law as an unstable atomic nucleus
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
decays.
Stability
The population has steady states at . The state with
. The state with  is stable whereas the state with
is stable whereas the state with 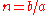 is unstable, meaning that the equation describes a population which crashes (tends to zero) when the death rate is greater than the birth rate and explodes (tends to infinity) when it is the birth rate that is greater.
is unstable, meaning that the equation describes a population which crashes (tends to zero) when the death rate is greater than the birth rate and explodes (tends to infinity) when it is the birth rate that is greater.Sources
- "'Law' of Two Hundred Billions in Context of Civil Society". In materials of Inter-regional scientific-practical conference The Civil Society: Ideas, Reality, Prospects, Kazan-Zelenodolsk; on April 27, 2006, , p. 204-207. ISBN 5-8399-0153-9.
- Nurgaliev I.S., "Kinematics of Demography", Report on 9th Global Strategic Forum. http://gsf.inesnet.ru/?p=161

