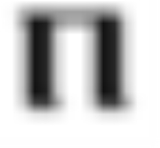
Peorð
Encyclopedia
is the rune denoting the sound p in the Elder Futhark
runic alphabet
, in the Anglo-Saxon rune poem
named peorð. It does not appear in the Younger Futhark
. In the poem, it is glossed with the enigmatic:
The name is not comprehensible from Old English
, i.e. the actual meaning of the word is not known. According to a 9th century manuscript of Alcuin (Codex Vindobonensis 795), written in Britain, the letters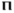 p (based on a Greek Π
p (based on a Greek Π
) and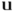 q (an inverted Π) are called "pairþra" and "qairþra", respectively, in Gothic. One of these names clearly is derived from the other. However, the names are not comprehensible in Gothic either, and it is not clear which is derived from which, except that we know that the Elder Futhark had a p, but no q rune. In any case, it seems evident that peorð is related to pairþra. Interestingly, the Anglo-Saxon futhorc adopted exactly the same approach for the addition of a labiovelar rune, cweorð, in both shape and name based on peorð, but unfortunately, we do not know if the Gothic runes already had a similar variant rune of p, or if the labiovelar letter was a 4th century creation of Ulfilas
q (an inverted Π) are called "pairþra" and "qairþra", respectively, in Gothic. One of these names clearly is derived from the other. However, the names are not comprehensible in Gothic either, and it is not clear which is derived from which, except that we know that the Elder Futhark had a p, but no q rune. In any case, it seems evident that peorð is related to pairþra. Interestingly, the Anglo-Saxon futhorc adopted exactly the same approach for the addition of a labiovelar rune, cweorð, in both shape and name based on peorð, but unfortunately, we do not know if the Gothic runes already had a similar variant rune of p, or if the labiovelar letter was a 4th century creation of Ulfilas
.
The Common Germanic name could be referring to a pear
-tree (or generally a fruit-tree). A common interpretation is that peorð refers to a sort of woodwind instrument. From peorð, a Proto-Germanic name *perðu, *perþō or *perþaz is sometimes reconstructed, with unknown meaning. The expected Proto-Germanic term for "pear tree" would be *pera-trewô (*pera being, however, a post-Proto-Germanic loan, either West Germanic, or Common Germanic, if Gothic pairþra meant "pear tree", from Vulgar Latin
pirum (plural pira), itself of unknown origin. Since the Elder Futhark
itself is post-Proto-Germanic, attested from the 2nd century, an early loanword as a letter name is perfectly possible). The Ogham
letter name Ceirt
, glossed as "apple tree", may in turn be a loan from Germanic into Primitive Irish.
The earliest attestation of the rune is in the Kylver Stone
futhark row (ca. AD 400). The earliest example in a linguistic context (as opposed to an abecedarium
) is already in futhorc, in the Kent II, III and IV coin inscriptions (the personal names pada and æpa/epa), dated to ca. AD 700. On St. Cuthbert's coffin
(AD 698), a p rune takes the place of Greek Ρ. The Westeremden yew-stick
(ca. AD 750) has op hæmu "at home" and up duna "on the hill".
Looijenga (1997) speculates that the p rune arose as a variant of the b
rune, parallel to the secondary nature of Ogham
peith. The uncertainty surrounding the rune is a consequence of the rarity of the *p phoneme in Proto-Germanic, itself due to the rarity of its parent-phoneme *b in Proto-Indo-European
.
The rune is discontinued in Younger Futhark
, which expresses /p/ with the b rune, for example on the Viking Age
Skarpåker Stone
,
for Old Norse
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark is the oldest form of the runic alphabet, used by Germanic tribes for Northwest Germanic and Migration period Germanic dialects of the 2nd to 8th centuries for inscriptions on artifacts such as jewellery, amulets, tools, weapons and runestones...
runic alphabet
Runic alphabet
The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
, in the Anglo-Saxon rune poem
Rune poem
The Rune Poems are three poems that list the letters of runic alphabets while providing an explanatory poetic stanza for each letter. Three different poems have been preserved: the Anglo-Saxon Rune Poem, the Norwegian Rune Poem, and the Icelandic Rune Poem.The Icelandic and Norwegian poems list 16...
named peorð. It does not appear in the Younger Futhark
Younger Futhark
The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet, a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, consisting of only 16 characters, in use from ca. 800 CE...
. In the poem, it is glossed with the enigmatic:
- peorð byþ symble plega and hlehter / wlancum [on middum], ðar wigan sittaþ / on beorsele bliþe ætsomne
- "Peorð is a source of recreation and amusement to the great, where warriors sit blithely together in the banqueting-hall."
The name is not comprehensible from Old English
Old English language
Old English or Anglo-Saxon is an early form of the English language that was spoken and written by the Anglo-Saxons and their descendants in parts of what are now England and southeastern Scotland between at least the mid-5th century and the mid-12th century...
, i.e. the actual meaning of the word is not known. According to a 9th century manuscript of Alcuin (Codex Vindobonensis 795), written in Britain, the letters
Pi (letter)
Pi is the sixteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 80. Letters that arose from pi include Cyrillic Pe , Coptic pi , and Gothic pairthra .The upper-case letter Π is used as a symbol for:...
) and
Ulfilas
Ulfilas, or Gothic Wulfila , bishop, missionary, and Bible translator, was a Goth or half-Goth and half-Greek from Cappadocia who had spent time inside the Roman Empire at the peak of the Arian controversy. Ulfilas was ordained a bishop by Eusebius of Nicomedia and returned to his people to work...
.
The Common Germanic name could be referring to a pear
Pear
The pear is any of several tree species of genus Pyrus and also the name of the pomaceous fruit of these trees. Several species of pear are valued by humans for their edible fruit, but the fruit of other species is small, hard, and astringent....
-tree (or generally a fruit-tree). A common interpretation is that peorð refers to a sort of woodwind instrument. From peorð, a Proto-Germanic name *perðu, *perþō or *perþaz is sometimes reconstructed, with unknown meaning. The expected Proto-Germanic term for "pear tree" would be *pera-trewô (*pera being, however, a post-Proto-Germanic loan, either West Germanic, or Common Germanic, if Gothic pairþra meant "pear tree", from Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin is any of the nonstandard forms of Latin from which the Romance languages developed. Because of its nonstandard nature, it had no official orthography. All written works used Classical Latin, with very few exceptions...
pirum (plural pira), itself of unknown origin. Since the Elder Futhark
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark is the oldest form of the runic alphabet, used by Germanic tribes for Northwest Germanic and Migration period Germanic dialects of the 2nd to 8th centuries for inscriptions on artifacts such as jewellery, amulets, tools, weapons and runestones...
itself is post-Proto-Germanic, attested from the 2nd century, an early loanword as a letter name is perfectly possible). The Ogham
Ogham
Ogham is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the Old Irish language, and occasionally the Brythonic language. Ogham is sometimes called the "Celtic Tree Alphabet", based on a High Medieval Bríatharogam tradition ascribing names of trees to the individual letters.There are roughly...
letter name Ceirt
Ceirt
Ceirt is a letter of the Ogham alphabet, transcribed as Q. It expresses the Primitive Irish labiovelar phoneme. The 14th century Auraicept na n-Éces glosses the name as aball, meaning "apple tree"...
, glossed as "apple tree", may in turn be a loan from Germanic into Primitive Irish.
The earliest attestation of the rune is in the Kylver Stone
Kylver Stone
The Kylver stone, listed in the Rundata catalog as runic inscription G 88, is a Swedish runestone which dates from about 400 CE notable for its listing of each of the runes in the elder futhark.-Description:...
futhark row (ca. AD 400). The earliest example in a linguistic context (as opposed to an abecedarium
Abecedarium
An abecedarium is an inscription consisting of the letters of an alphabet, almost always listed in order. Typically, abecedaria are practice exercises....
) is already in futhorc, in the Kent II, III and IV coin inscriptions (the personal names pada and æpa/epa), dated to ca. AD 700. On St. Cuthbert's coffin
St. Cuthbert's coffin
St. Cuthbert's coffin is an oak coffin in Durham Cathedral which between AD 698 and 1827 contained the remains of Saint Cuthbert, who died in 687. The coffin also contained the Stonyhurst Gospel and the best surviving examples of Anglo-Saxon embroidery or opus Anglicanum, a stole and maniple...
(AD 698), a p rune takes the place of Greek Ρ. The Westeremden yew-stick
Westeremden yew-stick
The Westeremden yew-stick is a yew-wood stick found in Westeremden B in the Groningen province of the Netherlands in 1917 that bears an Old Frisian Futhorc inscription.* , a Spiegelrune of , similar to a variant of stan, transliterated as B below...
(ca. AD 750) has op hæmu "at home" and up duna "on the hill".
Looijenga (1997) speculates that the p rune arose as a variant of the b
Berkanan
*Berkanan is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the b rune , meaning "birch". In the Younger Futhark it is called Bjarken in the Icelandic rune poem and Bjarkan in the Norwegian rune poem. In the Anglo-Saxon rune poem it is called beorc...
rune, parallel to the secondary nature of Ogham
Ogham
Ogham is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the Old Irish language, and occasionally the Brythonic language. Ogham is sometimes called the "Celtic Tree Alphabet", based on a High Medieval Bríatharogam tradition ascribing names of trees to the individual letters.There are roughly...
peith. The uncertainty surrounding the rune is a consequence of the rarity of the *p phoneme in Proto-Germanic, itself due to the rarity of its parent-phoneme *b in Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European language
The Proto-Indo-European language is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans...
.
The rune is discontinued in Younger Futhark
Younger Futhark
The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet, a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, consisting of only 16 characters, in use from ca. 800 CE...
, which expresses /p/ with the b rune, for example on the Viking Age
Viking Age
Viking Age is the term for the period in European history, especially Northern European and Scandinavian history, spanning the late 8th to 11th centuries. Scandinavian Vikings explored Europe by its oceans and rivers through trade and warfare. The Vikings also reached Iceland, Greenland,...
Skarpåker Stone
Skarpåker Stone
The Skarpåker Stone, designated by Rundata as Sö 154, is a Viking Age memorial runestone that was originally located in Skarpåker, Nyköping, Sörmland, Sweden, and which dates to the early 11th century.-Description:...
,
- iarþ sal rifna uk ubhimin
for Old Norse
Old Norse
Old Norse is a North Germanic language that was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and inhabitants of their overseas settlements during the Viking Age, until about 1300....
- JörðJörðIn Norse mythology, Jörð and also called Jarð as in Old East Norse, is a female jötunn. She is the mother of Thor and Meili, and the personification of the Earth. Fjörgyn and Hlôdyn are considered to be other names for Jörð...
skal rifna ok upphiminn. - "Earth shall be rent, and the heavens above."

