
Rhône Glacier
Encyclopedia
The Rhone Glacier, or sometimes Rhône Glacier (German: Rhonegletscher) is a glacier
in the Swiss Alps
and the source of the Rhone River
and one of the primary contributors to Lake Geneva
in the far eastern end of the Swiss canton of Valais
. Because the Glacier is located close to the Furka Pass
road it is easily accessible.
. It lies on the south side of the range at the source of the Rhone. The Undri Triftlimi (3,081 m) connects it to the Trift Glacier
. The glacier is located on the northernmost part of the canton of Valais, between the Grimsel Pass
and the Furka Pass
and is part of the Oberwald municipality. The Dammastock
(3,630 m) is the highest summit above the glacier.
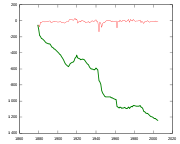 The Rhone Glacier is easily accessible so its evolution is observed since the 19th century. The glacier lost ~1300 m during the last 120 years leaving back a track of naked stone.
The Rhone Glacier is easily accessible so its evolution is observed since the 19th century. The glacier lost ~1300 m during the last 120 years leaving back a track of naked stone.
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
in the Swiss Alps
Swiss Alps
The Swiss Alps are the portion of the Alps mountain range that lies within Switzerland. Because of their central position within the entire Alpine range, they are also known as the Central Alps....
and the source of the Rhone River
Rhône River
The Rhone is one of the major rivers of Europe, rising in Switzerland and running from there through southeastern France. At Arles, near its mouth on the Mediterranean Sea, the river divides into two branches, known as the Great Rhone and the Little Rhone...
and one of the primary contributors to Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva or Lake Léman is a lake in Switzerland and France. It is one of the largest lakes in Western Europe. 59.53 % of it comes under the jurisdiction of Switzerland , and 40.47 % under France...
in the far eastern end of the Swiss canton of Valais
Valais
The Valais is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland in the southwestern part of the country, around the valley of the Rhône from its headwaters to Lake Geneva, separating the Pennine Alps from the Bernese Alps. The canton is one of the drier parts of Switzerland in its central Rhône valley...
. Because the Glacier is located close to the Furka Pass
Furka Pass
Furka Pass is a high mountain pass in the Swiss Alps connecting Gletsch, Valais with Realp, Uri. The Furka-Oberalp-Bahn line through the Furka Tunnel bypasses the pass...
road it is easily accessible.
Geography
The Rhone Glacier is the largest glacier in the Urner AlpsUrner Alps
The Urner Alps are a mountain range in central Switzerland in the western part of the Alps. They extend into the cantons of Obwalden, Valais, Lucerne, Bern, Uri and Nidwalden and are bordered by the Bernese Alps to the west, the Lepontine Alps to the south and the Glarus Alps to the east.The Urner...
. It lies on the south side of the range at the source of the Rhone. The Undri Triftlimi (3,081 m) connects it to the Trift Glacier
Trift Glacier
The Trift Glacier is a long glacier situated in the Urner Alps in the canton of Berne in Switzerland. In 1973 it had an area of .-See also:*Trift Bridge*Triftsee*List of glaciers in Switzerland*Swiss Alps-External links:*...
. The glacier is located on the northernmost part of the canton of Valais, between the Grimsel Pass
Grimsel Pass
Grimsel Pass is a Swiss high mountain pass.-Position:It connects the valley of the Rhone River in the canton of Valais and the Haslital in the canton of Bern....
and the Furka Pass
Furka Pass
Furka Pass is a high mountain pass in the Swiss Alps connecting Gletsch, Valais with Realp, Uri. The Furka-Oberalp-Bahn line through the Furka Tunnel bypasses the pass...
and is part of the Oberwald municipality. The Dammastock
Dammastock
The Dammastock is the highest mountain in the Urner Alps in Switzerland. Its summit ridge forms the border between the cantons of Uri and the Valais. It is the highest summit in the canton of Uri...
(3,630 m) is the highest summit above the glacier.
Evolution

External links
- Simulation of the shrinking of the glacier
- Swiss Glacier Monitoring Network: Rhone Glacier - with length variation measurements since 1879

