
Roll's critique
Encyclopedia
Roll's critique is a famous analysis of the validity of empirical tests of the Capital Asset Pricing Model
(CAPM). It concerns methods to formally test the statement of the CAPM, the equation
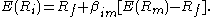
This equation relates the asset expected return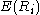 to the asset covariance
to the asset covariance 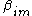 with the market portfolio return
with the market portfolio return 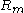 . The market return is defined as the wealth-weighted sum of all investment returns in the economy.
. The market return is defined as the wealth-weighted sum of all investment returns in the economy.
Roll's critique makes two statements regarding the market portfolio:
1. Mean-Variance Tautology: Any mean-variance efficient portfolio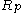 satisfies the CAPM equation exactly:
satisfies the CAPM equation exactly:
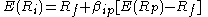 .
.
Mean-variance efficiency of the market portfolio is equivalent to the CAPM equation holding. This statement is a mathematical fact, requiring no model assumptions.
Given a proxy for the market portfolio, testing the CAPM equation is equivalent to testing mean-variance efficiency of the portfolio. The CAPM is tautological if the market is assumed to be mean-variance efficient. Proof of Mean Variance Tautology.
2. The Market Portfolio is Unobservable: The market portfolio in practice would necessarily include every single possible available asset, including real estate, precious metals, stamp collections, jewelry, and anything with any worth.
The returns on all possible investments opportunities are unobservable.
From statement 1, validity of the CAPM is equivalent to the market being mean-variance efficient with respect to all investment opportunities. Without observing all investment opportunities, it is not possible to test whether this portfolio, or indeed any portfolio, is mean-variance efficient. Consequently, it is not possible to test the CAPM.
and all asset-pricing models of the form
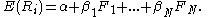
where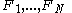 are unspecified factors. If the factors are returns on a mean-variance portfolio, the equation holds exactly.
are unspecified factors. If the factors are returns on a mean-variance portfolio, the equation holds exactly.
It is always possible to identify in-sample mean-variance efficient portfolios within a dataset of returns. Consequently, it is also always possible to construct in-sample asset pricing models that exactly satisfy the above pricing equation. This is an example of data dredging
.
Capital asset pricing model
In finance, the capital asset pricing model is used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, if that asset is to be added to an already well-diversified portfolio, given that asset's non-diversifiable risk...
(CAPM). It concerns methods to formally test the statement of the CAPM, the equation
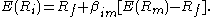
This equation relates the asset expected return
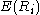 to the asset covariance
to the asset covariance 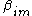 with the market portfolio return
with the market portfolio return 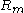 . The market return is defined as the wealth-weighted sum of all investment returns in the economy.
. The market return is defined as the wealth-weighted sum of all investment returns in the economy.Roll's critique makes two statements regarding the market portfolio:
1. Mean-Variance Tautology: Any mean-variance efficient portfolio
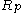 satisfies the CAPM equation exactly:
satisfies the CAPM equation exactly: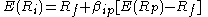 .
.Mean-variance efficiency of the market portfolio is equivalent to the CAPM equation holding. This statement is a mathematical fact, requiring no model assumptions.
Given a proxy for the market portfolio, testing the CAPM equation is equivalent to testing mean-variance efficiency of the portfolio. The CAPM is tautological if the market is assumed to be mean-variance efficient. Proof of Mean Variance Tautology.
2. The Market Portfolio is Unobservable: The market portfolio in practice would necessarily include every single possible available asset, including real estate, precious metals, stamp collections, jewelry, and anything with any worth.
The returns on all possible investments opportunities are unobservable.
From statement 1, validity of the CAPM is equivalent to the market being mean-variance efficient with respect to all investment opportunities. Without observing all investment opportunities, it is not possible to test whether this portfolio, or indeed any portfolio, is mean-variance efficient. Consequently, it is not possible to test the CAPM.
Relationship to the APT
The mean-variance tautology argument applies to the Arbitrage Pricing TheoryArbitrage pricing theory
In finance, arbitrage pricing theory is a general theory of asset pricing that holds that the expected return of a financial asset can be modeled as a linear function of various macro-economic factors or theoretical market indices, where sensitivity to changes in each factor is represented by a...
and all asset-pricing models of the form
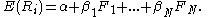
where
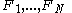 are unspecified factors. If the factors are returns on a mean-variance portfolio, the equation holds exactly.
are unspecified factors. If the factors are returns on a mean-variance portfolio, the equation holds exactly.It is always possible to identify in-sample mean-variance efficient portfolios within a dataset of returns. Consequently, it is also always possible to construct in-sample asset pricing models that exactly satisfy the above pricing equation. This is an example of data dredging
Data dredging
Data dredging is the inappropriate use of data mining to uncover misleading relationships in data. Data-snooping bias is a form of statistical bias that arises from this misuse of statistics...
.

