
Schrödinger method
Encyclopedia
In combinatorial
mathematics
and probability theory
, the Schrödinger method, named after the Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger
, is used to solve some problems of distribution and occupancy.
Suppose
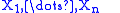
are independent
random variable
s that are uniformly distributed
on the interval [0, 1]. Let
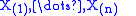
be the corresponding order statistic
s, i.e., the result of sorting these n random variables into increasing order. We seek the probability of some event A defined in terms of these order statistics. For example, we might seek the probability that in a certain seven-day period there were at most two days in on which only one phone call was received, given that the number of phone calls during that time was 20. This assumes uniform distribution of arrival times.
The Schrödinger method begins by assigning a Poisson distribution
with expected value
λt to the number of observations in the interval [0, t], the number of observations in non-overlapping subintervals being independent (see Poisson process
). The number N of observations is Poisson-distributed with expected value λ. Then we rely on the fact that the conditional probability
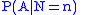
does not depend on λ (in the language of statisticians
, N is a sufficient statistic
for this parametrized family of probability distributions for the order statistics). We proceed as follows:
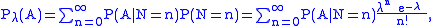
so that
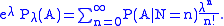
Now the lack of dependence of P(A | N = n) upon λ entails that the last sum displayed above is a power series in λ and P(A | N = n) is the value of its nth derivative at λ = 0, i.e.,
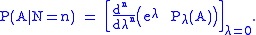
For this method to be of any use in finding P(A | N =n), must be possible to find Pλ(A) more directly than P(A | N = n). What makes that possible is the independence of the numbers of arrivals in non-overlapping subintervals.
Combinatorics
Combinatorics is a branch of mathematics concerning the study of finite or countable discrete structures. Aspects of combinatorics include counting the structures of a given kind and size , deciding when certain criteria can be met, and constructing and analyzing objects meeting the criteria ,...
mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
and probability theory
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, the Schrödinger method, named after the Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger was an Austrian physicist and theoretical biologist who was one of the fathers of quantum mechanics, and is famed for a number of important contributions to physics, especially the Schrödinger equation, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933...
, is used to solve some problems of distribution and occupancy.
Suppose
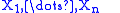
are independent
Statistical independence
In probability theory, to say that two events are independent intuitively means that the occurrence of one event makes it neither more nor less probable that the other occurs...
random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s that are uniformly distributed
Uniform distribution (continuous)
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distribution or rectangular distribution is a family of probability distributions such that for each member of the family, all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. The support is defined by...
on the interval [0, 1]. Let
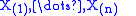
be the corresponding order statistic
Order statistic
In statistics, the kth order statistic of a statistical sample is equal to its kth-smallest value. Together with rank statistics, order statistics are among the most fundamental tools in non-parametric statistics and inference....
s, i.e., the result of sorting these n random variables into increasing order. We seek the probability of some event A defined in terms of these order statistics. For example, we might seek the probability that in a certain seven-day period there were at most two days in on which only one phone call was received, given that the number of phone calls during that time was 20. This assumes uniform distribution of arrival times.
The Schrödinger method begins by assigning a Poisson distribution
Poisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
with expected value
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
λt to the number of observations in the interval [0, t], the number of observations in non-overlapping subintervals being independent (see Poisson process
Poisson process
A Poisson process, named after the French mathematician Siméon-Denis Poisson , is a stochastic process in which events occur continuously and independently of one another...
). The number N of observations is Poisson-distributed with expected value λ. Then we rely on the fact that the conditional probability
Conditional probability
In probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
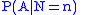
does not depend on λ (in the language of statisticians
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, N is a sufficient statistic
Sufficiency (statistics)
In statistics, a sufficient statistic is a statistic which has the property of sufficiency with respect to a statistical model and its associated unknown parameter, meaning that "no other statistic which can be calculated from the same sample provides any additional information as to the value of...
for this parametrized family of probability distributions for the order statistics). We proceed as follows:
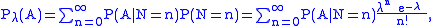
so that
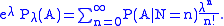
Now the lack of dependence of P(A | N = n) upon λ entails that the last sum displayed above is a power series in λ and P(A | N = n) is the value of its nth derivative at λ = 0, i.e.,
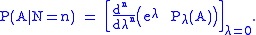
For this method to be of any use in finding P(A | N =n), must be possible to find Pλ(A) more directly than P(A | N = n). What makes that possible is the independence of the numbers of arrivals in non-overlapping subintervals.

