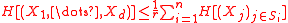Shearer's inequality
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
, Shearer's inequality states that if X1, ..., Xd are random variable
s and S1, ..., Sn are subsets of {1, 2, ..., d} such that every integer between 1 and d lies in exactly r of these subsets, then
where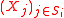 is the Cartesian product
is the Cartesian product
of random variables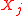 with indices j in
with indices j in 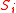 (so the dimension of this vector is equal to the size of
(so the dimension of this vector is equal to the size of 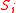 ).
).
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, Shearer's inequality states that if X1, ..., Xd are random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s and S1, ..., Sn are subsets of {1, 2, ..., d} such that every integer between 1 and d lies in exactly r of these subsets, then
where
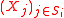 is the Cartesian product
is the Cartesian productCartesian product
In mathematics, a Cartesian product is a construction to build a new set out of a number of given sets. Each member of the Cartesian product corresponds to the selection of one element each in every one of those sets...
of random variables
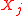 with indices j in
with indices j in 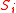 (so the dimension of this vector is equal to the size of
(so the dimension of this vector is equal to the size of 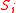 ).
).