Spörer Minimum
Encyclopedia
The Spörer Minimum was a 90-year span of low solar activity, from about 1460 until 1550, which was identified and named by John A. Eddy in a landmark 1976 paper published in Science
titled "The Maunder Minimum"
. It occurred before sunspot
s had been directly observed and was discovered instead by analysis of the proportion of carbon-14
in tree rings, which is strongly correlated with solar activity. It is named for the German astronomer Gustav Spörer
.
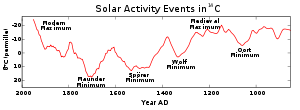
Like the subsequent Maunder Minimum
, the Spörer Minimum coincided with a time when Earth's climate
was colder than average. This correlation has generated hypotheses that low solar activity produces cooler than average global temperatures. Though a specific mechanism by which solar activity results in climate change
has not been established, one theory is modification of the Arctic Oscillation/North Atlantic Oscillation due to a change in solar output.
Wilfried Schröder published a table of observed aurora borealis during the Spörer Minimum which showed that the solar cycle was active (see: Wilfried Schröder, Annals Geophys. 1994)
For details on solar activity see: solar variation
.
Science (journal)
Science is the academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and is one of the world's top scientific journals....
titled "The Maunder Minimum"
Maunder Minimum
The Maunder Minimum is the name used for the period roughly spanning 1645 to 1715 when sunspots became exceedingly rare, as noted by solar observers of the time....
. It occurred before sunspot
Sunspot
Sunspots are temporary phenomena on the photosphere of the Sun that appear visibly as dark spots compared to surrounding regions. They are caused by intense magnetic activity, which inhibits convection by an effect comparable to the eddy current brake, forming areas of reduced surface temperature....
s had been directly observed and was discovered instead by analysis of the proportion of carbon-14
Carbon-14
Carbon-14, 14C, or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with a nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Its presence in organic materials is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and colleagues , to date archaeological, geological, and hydrogeological...
in tree rings, which is strongly correlated with solar activity. It is named for the German astronomer Gustav Spörer
Gustav Spörer
Friederich Wilhelm Gustav Spörer was a German astronomer.He is noted for his studies of sunspots and sunspot cycles. In this regard he is often mentioned together with Edward Maunder. Spörer was the first to note a prolonged period of low sunspot activity from 1645 to 1715...
.

| Event | Start | End |
|---|---|---|
| Oort minimum | 1010 | 1050 |
| Oort minimum (see Medieval Warm Period Medieval Warm Period The Medieval Warm Period , Medieval Climate Optimum, or Medieval Climatic Anomaly was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region, that may also have been related to other climate events around the world during that time, including in China, New Zealand, and other countries lasting from... ) |
1040 | 1080 |
| Medieval maximum (see Medieval Warm Period Medieval Warm Period The Medieval Warm Period , Medieval Climate Optimum, or Medieval Climatic Anomaly was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region, that may also have been related to other climate events around the world during that time, including in China, New Zealand, and other countries lasting from... ) |
1100 | 1250 |
| Wolf minimum | 1280 | 1350 |
| Spörer Minimum | 1460 | 1550 |
| Maunder Minimum Maunder Minimum The Maunder Minimum is the name used for the period roughly spanning 1645 to 1715 when sunspots became exceedingly rare, as noted by solar observers of the time.... |
1645 | 1715 |
| Dalton Minimum Dalton Minimum The Dalton Minimum was a period of low solar activity, named after the English meteorologist John Dalton, lasting from about 1790 to 1830. Like the Maunder Minimum and Spörer Minimum, the Dalton Minimum coincided with a period of lower-than-average global temperatures... |
1790 | 1820 |
| Modern Maximum Modern Maximum The Modern Maximum refers to the ongoing period of relatively high solar activity that began circa 1900. This period is a natural example of solar variation, and one of many that are known from proxy records of past solar variability. The Modern Maximum reached a double peak once in the 1950s and... |
1950 | ongoing |
| Little Ice Age Little Ice Age The Little Ice Age was a period of cooling that occurred after the Medieval Warm Period . While not a true ice age, the term was introduced into the scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939... |
1350 | 1850 |
Like the subsequent Maunder Minimum
Maunder Minimum
The Maunder Minimum is the name used for the period roughly spanning 1645 to 1715 when sunspots became exceedingly rare, as noted by solar observers of the time....
, the Spörer Minimum coincided with a time when Earth's climate
Climate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
was colder than average. This correlation has generated hypotheses that low solar activity produces cooler than average global temperatures. Though a specific mechanism by which solar activity results in climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
has not been established, one theory is modification of the Arctic Oscillation/North Atlantic Oscillation due to a change in solar output.
Wilfried Schröder published a table of observed aurora borealis during the Spörer Minimum which showed that the solar cycle was active (see: Wilfried Schröder, Annals Geophys. 1994)
For details on solar activity see: solar variation
Solar variation
Solar variation is the change in the amount of radiation emitted by the Sun and in its spectral distribution over years to millennia. These variations have periodic components, the main one being the approximately 11-year solar cycle . The changes also have aperiodic fluctuations...
.

