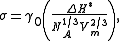Stefan's formula
Encyclopedia
In thermodynamics
, Stefan’s formula says that the specific surface energy
at a given interface is determined by the respective enthalpy
difference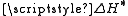 .
.
where σ is the specific surface energy
, NA is Avogadro's number
,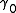 is a steric dimensionless coefficient, and Vm is the molar volume
is a steric dimensionless coefficient, and Vm is the molar volume
.
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
, Stefan’s formula says that the specific surface energy
Specific surface energy
specific surface energy, also known as surface free energy, is the amount of increase of free energy when the area of surface increases by every unit area. It can be calculated using Stefan's formula. Specific surface energy is the same as surface tension for isotropic materials, but different...
at a given interface is determined by the respective enthalpy
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
difference
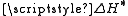 .
.where σ is the specific surface energy
Specific surface energy
specific surface energy, also known as surface free energy, is the amount of increase of free energy when the area of surface increases by every unit area. It can be calculated using Stefan's formula. Specific surface energy is the same as surface tension for isotropic materials, but different...
, NA is Avogadro's number
Avogadro's number
In chemistry and physics, the Avogadro constant is defined as the ratio of the number of constituent particles N in a sample to the amount of substance n through the relationship NA = N/n. Thus, it is the proportionality factor that relates the molar mass of an entity, i.e...
,
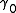 is a steric dimensionless coefficient, and Vm is the molar volume
is a steric dimensionless coefficient, and Vm is the molar volumeMolar volume
The molar volume, symbol Vm, is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar mass divided by the mass density...
.