
Stückelberg action
Encyclopedia
In field theory, the Stueckelberg action (named after Ernst Stueckelberg
) describes a massive spin-1 field as a R (the real number
s are the Lie algebra
of U(1)) Yang-Mills theory coupled to a real scalar field
φ which takes on values in a real 1D affine representation
of R with m as the coupling strength.
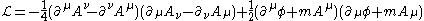
The usual Higgs mechanism
of spontaneous symmetry breaking
applies here. The only difference being we have an affine representation instead of a linear representation.
By gauge-fixing φ=0, we get the Proca action
.
This explains why, unlike the case for non-abelian vector fields, quantum electrodynamics
with a massive photon is renormalizable even though it's not manifestly gauge invariant (after the Stückelberg scalar has been eliminated in the Proca action).
without destroying the renormalizability of the theory and further provides a mechanism for
mass generation that is distinct from the Higgs
mechanism in the context of Abelian
gauge theories.
The model involves a non-trivial
mixing of the Stueckelberg and the Standard Model sectors by including an additional term in the effective Lagrangian of the Standard Model given by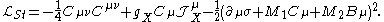
The first term above is the Stueckelberg field strength,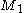 and
and 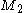 are topological mass parameters and
are topological mass parameters and  is the axion.
is the axion.
After symmetry breaking in the electroweak sector the photon remains massless. The model predicts a new type of gauge boson dubbed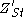 which inherits a very distinct narrow decay width in this model. The St sector of the StSM decouples from the SM in limit
which inherits a very distinct narrow decay width in this model. The St sector of the StSM decouples from the SM in limit 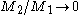 .
.
Stueckelberg type couplings arise quite naturally in theories involving compactifications of higher dimensional string theory
, in particular, these couplings appear in the dimensional reduction of the ten dimensional N = 1 supergravity
coupled to supersymmetric Yang-Mills gauge fields in the presence of internal gauge fluxes. In the context of intersecting D-brane
model building, products of U(N) gauge groups are broken to their SU(N) subgroups via the Stueckelberg couplings and thus the Abelian gauge fields become massive. Further, in a much simpler fashion one may consider a model with only one extra dimension (a type of Kaluza–Klein model) and compactify down to a four dimensional theory. The resulting Lagrangian will contain massive vector gauge bosons that acquire masses through the Stueckelberg mechanism.
Ernst Stueckelberg
Ernst Carl Gerlach Stueckelberg was a Swiss mathematician and physicist.- Career :In 1927 Stueckelberg got his Ph. D. at the University of Basel under August Hagenbach...
) describes a massive spin-1 field as a R (the real number
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
s are the Lie algebra
Lie algebra
In mathematics, a Lie algebra is an algebraic structure whose main use is in studying geometric objects such as Lie groups and differentiable manifolds. Lie algebras were introduced to study the concept of infinitesimal transformations. The term "Lie algebra" was introduced by Hermann Weyl in the...
of U(1)) Yang-Mills theory coupled to a real scalar field
Scalar field
In mathematics and physics, a scalar field associates a scalar value to every point in a space. The scalar may either be a mathematical number, or a physical quantity. Scalar fields are required to be coordinate-independent, meaning that any two observers using the same units will agree on the...
φ which takes on values in a real 1D affine representation
Affine representation
An affine representation of a topological group G on an affine space A is a continuous group homomorphism from G to the automorphism group of A, the affine group Aff...
of R with m as the coupling strength.
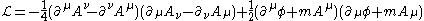
The usual Higgs mechanism
Higgs mechanism
In particle physics, the Higgs mechanism is the process in which gauge bosons in a gauge theory can acquire non-vanishing masses through absorption of Nambu-Goldstone bosons arising in spontaneous symmetry breaking....
of spontaneous symmetry breaking
Spontaneous symmetry breaking
Spontaneous symmetry breaking is the process by which a system described in a theoretically symmetrical way ends up in an apparently asymmetric state....
applies here. The only difference being we have an affine representation instead of a linear representation.
By gauge-fixing φ=0, we get the Proca action
Proca action
In physics, in the area of field theory, the Proca action describes a massive spin-1 field of mass m in Minkowski spacetime. The field involved is a real vector field A...
.
This explains why, unlike the case for non-abelian vector fields, quantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved...
with a massive photon is renormalizable even though it's not manifestly gauge invariant (after the Stückelberg scalar has been eliminated in the Proca action).
The Stueckelberg Extension of the Standard Model
The Stueckelberg Lagrangian of the StSM (Stueckelberg extension of the Standard Model) consists of a gauge invariant kinetic term for a massive U(1) gauge field. Such a term can be implemented into the Lagrangian of the Standard ModelStandard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, the current formulation was finalized in the mid 1970s upon...
without destroying the renormalizability of the theory and further provides a mechanism for
mass generation that is distinct from the Higgs
Higgs
The term Higgs appears in:* Alan Higgs, English businessman and philanthropist* Sir Derek Higgs, an English business leader and merchant banker* Eric Sidney Higgs, English archaeologist*Griffin Higgs...
mechanism in the context of Abelian
Abelian
In mathematics, Abelian refers to any of number of different mathematical concepts named after Niels Henrik Abel:- Group theory :*Abelian group, a group in which the binary operation is commutative...
gauge theories.
The model involves a non-trivial
mixing of the Stueckelberg and the Standard Model sectors by including an additional term in the effective Lagrangian of the Standard Model given by
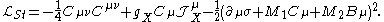
The first term above is the Stueckelberg field strength,
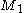 and
and 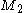 are topological mass parameters and
are topological mass parameters and  is the axion.
is the axion.After symmetry breaking in the electroweak sector the photon remains massless. The model predicts a new type of gauge boson dubbed
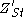 which inherits a very distinct narrow decay width in this model. The St sector of the StSM decouples from the SM in limit
which inherits a very distinct narrow decay width in this model. The St sector of the StSM decouples from the SM in limit 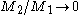 .
.Stueckelberg type couplings arise quite naturally in theories involving compactifications of higher dimensional string theory
String theory
String theory is an active research framework in particle physics that attempts to reconcile quantum mechanics and general relativity. It is a contender for a theory of everything , a manner of describing the known fundamental forces and matter in a mathematically complete system...
, in particular, these couplings appear in the dimensional reduction of the ten dimensional N = 1 supergravity
Supergravity
In theoretical physics, supergravity is a field theory that combines the principles of supersymmetry and general relativity. Together, these imply that, in supergravity, the supersymmetry is a local symmetry...
coupled to supersymmetric Yang-Mills gauge fields in the presence of internal gauge fluxes. In the context of intersecting D-brane
D-brane
In string theory, D-branes are a class of extended objects upon which open strings can end with Dirichlet boundary conditions, after which they are named. D-branes were discovered by Dai, Leigh and Polchinski, and independently by Hořava in 1989...
model building, products of U(N) gauge groups are broken to their SU(N) subgroups via the Stueckelberg couplings and thus the Abelian gauge fields become massive. Further, in a much simpler fashion one may consider a model with only one extra dimension (a type of Kaluza–Klein model) and compactify down to a four dimensional theory. The resulting Lagrangian will contain massive vector gauge bosons that acquire masses through the Stueckelberg mechanism.

