
Treaty of Brétigny
Encyclopedia

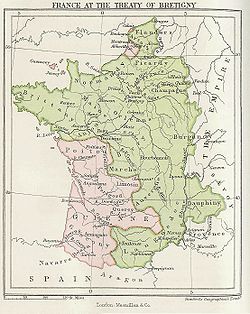
The Treaty of Brétigny was a treaty
Treaty
A treaty is an express agreement under international law entered into by actors in international law, namely sovereign states and international organizations. A treaty may also be known as an agreement, protocol, covenant, convention or exchange of letters, among other terms...
signed on May 9, 1360, between King Edward III
Edward III of England
Edward III was King of England from 1327 until his death and is noted for his military success. Restoring royal authority after the disastrous reign of his father, Edward II, Edward III went on to transform the Kingdom of England into one of the most formidable military powers in Europe...
of England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
and King John II
John II of France
John II , called John the Good , was the King of France from 1350 until his death. He was the second sovereign of the House of Valois and is perhaps best remembered as the king who was vanquished at the Battle of Poitiers and taken as a captive to England.The son of Philip VI and Joan the Lame,...
(the Good) of France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. In retrospect it is seen as having marked the end of the first phase of the Hundred Years' War
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War was a series of separate wars waged from 1337 to 1453 by the House of Valois and the House of Plantagenet, also known as the House of Anjou, for the French throne, which had become vacant upon the extinction of the senior Capetian line of French kings...
(1337–1453)—as well as the height of English hegemony
Hegemony
Hegemony is an indirect form of imperial dominance in which the hegemon rules sub-ordinate states by the implied means of power rather than direct military force. In Ancient Greece , hegemony denoted the politico–military dominance of a city-state over other city-states...
on the Continent
Continental Europe
Continental Europe, also referred to as mainland Europe or simply the Continent, is the continent of Europe, explicitly excluding European islands....
.
It was signed at Brétigny
Brétigny, Eure-et-Loir
Brétigny is a French village near Chartres, Eure-et-Loir department, notable for the 1360 Treaty of Brétigny ending the first phase of the Hundred Years' War....
, a village near Chartres
Chartres
Chartres is a commune and capital of the Eure-et-Loir department in northern France. It is located southwest of Paris.-Geography:Chartres is built on the left bank of the Eure River, on a hill crowned by its famous cathedral, the spires of which are a landmark in the surrounding country...
, and later ratified as the Treaty of Calais on 24 October 1360.
Background
The treaty was signed several years after John was taken as a prisoner of warPrisoner of war
A prisoner of war or enemy prisoner of war is a person, whether civilian or combatant, who is held in custody by an enemy power during or immediately after an armed conflict...
at the Battle of Poitiers
Battle of Poitiers (1356)
The Battle of Poitiers was fought between the Kingdoms of England and France on 19 September 1356 near Poitiers, resulting in the second of the three great English victories of the Hundred Years' War: Crécy, Poitiers, and Agincourt....
(19 September 1356). The ensuing conflicts in Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
between Étienne Marcel
Étienne Marcel
Etienne Marcel was provost of the merchants of Paris under King John II, called John the Good .Etienne Marcel was born into the wealthy Parisian bourgeoisie, being the son of the clothier Simon Marcel and his wife Isabelle Barbou...
and the Dauphin (later King Charles V
Charles V of France
Charles V , called the Wise, was King of France from 1364 to his death in 1380 and a member of the House of Valois...
) and the outbreak of the Jacquerie
Jacquerie
The Jacquerie was a popular revolt in late medieval Europe by peasants that took place in northern France in the summer of 1358, during the Hundred Years' War. The revolt, which was violently suppressed after a few weeks of violence, centered in the Oise valley north of Paris...
peasant revolt weakened French bargaining power.
The exactions of the English, who wished to yield as few as possible of the advantages claimed by them in the abortive Treaty of London
Treaty of London, 1359
The Treaty of London was proposed by England, accepted by France, and signed in 1359. After Edward of Woodstook soundly defeated the French at Poitiers , where they captured Jean II of France, the French were forced to accept the terms of the English...
the year before, made negotiations difficult, and the discussion of terms begun early in April lasted more than a month.
Terms
By virtue of this treaty Edward III obtained, besides GuyenneGuyenne
Guyenne or Guienne , , ; Occitan Guiana ) is a vaguely defined historic region of south-western France. The Province of Guyenne, sometimes called the Province of Guyenne and Gascony, was a large province of pre-revolutionary France....
and Gascony
Gascony
Gascony is an area of southwest France that was part of the "Province of Guyenne and Gascony" prior to the French Revolution. The region is vaguely defined and the distinction between Guyenne and Gascony is unclear; sometimes they are considered to overlap, and sometimes Gascony is considered a...
, Poitou
Poitou
Poitou was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers.The region of Poitou was called Thifalia in the sixth century....
, Saintonge
Saintonge
Saintonge is a small region on the Atlantic coast of France within the département Charente-Maritime, west and south of Charente in the administrative region of Poitou-Charentes....
and Aunis
Aunis
Aunis is a historical province of France, situated in the north-west of the department of Charente-Maritime. Its historic capital is La Rochelle, which took over from Castrum Allionis the historic capital which gives its name to the province....
, Agenais
Agenais
Agenais, or Agenois, was a province of France located in southwest France south of Périgord.In ancient Gaul the region was the country of the Nitiobroges with Aginnum for their capital, which in the fourth century was the Civitas Agennensium, which was a part of Aquitania Secunda and which formed...
, Périgord
Périgord
The Périgord is a former province of France, which corresponds roughly to the current Dordogne département, now forming the northern part of the Aquitaine région. It is divided into four regions, the Périgord Noir , the Périgord Blanc , the Périgord Vert and the Périgord Pourpre...
, Limousin
Limousin (province)
Limousin is one of the traditional provinces of France around the city of Limoges. Limousin lies in the foothills of the western edge of the Massif Central, with cold weather in the winter...
, Quercy
Quercy
Quercy is a former province of France located in the country's southwest, bounded on the north by Limousin, on the west by Périgord and Agenais, on the south by Gascony and Languedoc, and on the east by Rouergue and Auvergne....
, Bigorre
Bigorre
Bigorre is region in southwest France, historically an independent county and later a French province, located in the upper watershed of the Adour, on the northern slopes of the Pyrenees, part of the larger region known as Gascony...
, the countship of Gauré
Gauré
Gauré is a commune in the Haute-Garonne department in southwestern France.-Population:-References:*...
, Angoumois
Angoumois
Angoumois was a county and province of France, nearly corresponding today to the Charente département. Its capital was Angoulême....
, Rouergue
Rouergue
Rouergue is a former province of France, bounded on the north by Auvergne, on the south and southwest by Languedoc, on the east by Gévaudan and on the west by Quercy...
, Montreuil-sur-Mer
Montreuil-sur-Mer
Montreuil or Montreuil-sur-Mer is a sub-prefecture in the Pas-de-Calais department in northern France. It is located on the Canche river, not far from Étaples...
, Ponthieu
Ponthieu
Ponthieu was one of six feudal counties that eventually merged together to become part of the Province of Picardy, in northern France. Its chief town is Abbeville.- History :...
, Calais
Calais
Calais is a town in Northern France in the department of Pas-de-Calais, of which it is a sub-prefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's capital is its third-largest city of Arras....
, Sangatte
Sangatte
Sangatte is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department on the northern coast of France on the English Channel.Like many place names in French Flanders, the name is of Flemish origin and means "gap in the sand".-Engineering:...
, Ham and the countship of Guînes
Guînes
Guînes is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in northern France.-Geography:Guînes is located on the border of the two territories of the Boulonnais and Calaisis, at the edge of the now-drained marshes, which extend from here to the coast. The Guînes canal connects with...
. The king of England was to hold these free and clear, without doing homage
Homage (medieval)
Homage in the Middle Ages was the ceremony in which a feudal tenant or vassal pledged reverence and submission to his feudal lord, receiving in exchange the symbolic title to his new position . It was a symbolic acknowledgment to the lord that the vassal was, literally, his man . The oath known as...
for them. Furthermore the treaty established that title to all the islands that the King of England now holds
Channel Islands
The Channel Islands are an archipelago of British Crown Dependencies in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two separate bailiwicks: the Bailiwick of Guernsey and the Bailiwick of Jersey...
would no longer be under the Suzerainty
Suzerainty
Suzerainty occurs where a region or people is a tributary to a more powerful entity which controls its foreign affairs while allowing the tributary vassal state some limited domestic autonomy. The dominant entity in the suzerainty relationship, or the more powerful entity itself, is called a...
of the King of France.
On his side, the King of England gave up the duchy of Touraine
Touraine
The Touraine is one of the traditional provinces of France. Its capital was Tours. During the political reorganization of French territory in 1790, the Touraine was divided between the departments of Indre-et-Loire, :Loir-et-Cher and Indre.-Geography:...
, the countships of Anjou
Anjou
Anjou is a former county , duchy and province centred on the city of Angers in the lower Loire Valley of western France. It corresponds largely to the present-day département of Maine-et-Loire...
and Maine, and the suzerainty of Brittany
Brittany
Brittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain...
and of Flanders
Flanders
Flanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
. He also renounced all claims to the French throne. The terms of Brétigny were meant to disentangle the feudal responsibilities that had caused so much conflict, and as far as the English were concerned, would concentrate English territories in an expanded version of Aquitaine
Aquitaine
Aquitaine , archaic Guyenne/Guienne , is one of the 27 regions of France, in the south-western part of metropolitan France, along the Atlantic Ocean and the Pyrenees mountain range on the border with Spain. It comprises the 5 departments of Dordogne, :Lot et Garonne, :Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Landes...
.
John II had to pay three million gold crowns for his ransom, and would be released after he paid one million. The occasion was the first minting of the franc
Franc
The franc is the name of several currency units, most notably the Swiss franc, still a major world currency today due to the prominence of Swiss financial institutions and the former currency of France, the French franc until the Euro was adopted in 1999...
, equivalent to one livre tournois
Livre tournois
The livre tournois |pound]]) was:#one of numerous currencies used in France in the Middle Ages; and#a unit of account used in France in the Middle Ages and the early modern period.-Circulating currency:...
(20 sous
Solidus (coin)
The solidus was originally a gold coin issued by the Romans, and a weight measure for gold more generally, corresponding to 4.5 grams.-Roman and Byzantine coinage:...
). As a guarantee for the payment of his ransom, John gave as hostages two of his sons, several princes and nobles, four inhabitants of Paris, and two citizens from each of the nineteen principal towns of France. This treaty was ratified and sworn to by the two kings and by their eldest sons on 24 October 1360 at Calais
Calais
Calais is a town in Northern France in the department of Pas-de-Calais, of which it is a sub-prefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's capital is its third-largest city of Arras....
. At the same time the special conditions relating to each important article of the treaty and the renunciatory clauses in which the kings abandoned their rights over the territory they had yielded to one another were signed. Edward III retired finally to England, for the last time.
John II gives himself up
When his own son Louis I, Duc d'AnjouLouis I of Naples
Louis I of Anjou , or Louis I of Naples, was the second son of King John II of France and Bonne of Luxembourg...
(one of the hostages) escaped from England in 1362, John II gave himself up. He died in captivity in 1364 and Charles V
Charles V of France
Charles V , called the Wise, was King of France from 1364 to his death in 1380 and a member of the House of Valois...
succeeded him as king of France. In 1369, on the pretext that Edward III had failed to observe the terms of the treaty of Brétigny, the king of France declared war once again.
By the time of the death of Edward III in 1377, English forces had been pushed back into their territories in the southwest around Bordeaux
Bordeaux
Bordeaux is a port city on the Garonne River in the Gironde department in southwestern France.The Bordeaux-Arcachon-Libourne metropolitan area, has a population of 1,010,000 and constitutes the sixth-largest urban area in France. It is the capital of the Aquitaine region, as well as the prefecture...
.
Legacy
The treaty did not lead to lasting peace, but procured nine years' respite from the Hundred Years' War.In the following years, French forces were involved in battles against the Anglo-Navarrais (Bertrand du Guesclin
Bertrand du Guesclin
Bertrand du Guesclin , known as the Eagle of Brittany or the Black Dog of Brocéliande, was a Breton knight and French military commander during the Hundred Years' War. He was Constable of France from 1370 to his death...
's victory at Cocherel
Battle of Cocherel
The Battle of Cocherel it fought on May 16, 1364 between the king of France and the forces of Charles II of Navarre, over the succession to the dukedom of Burgundy....
on 16 May 1364) and the Breton
Brittany
Brittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain...
s.

